Application of RFID (ZigBee) system in third-party logistics
[ad_1]
This paper uses the flat warehouses of third-party logistics companies in Tianjin Binhai New Area as the application environment to establish a set of intelligent warehousing solutions based on the concept of the Internet of Things and with scalable value. In the RFID system of smart storage, each or several RFID electronic tags need to have their corresponding readers for information induction, and each group of RFID readers also need to exchange data with the server. However, in warehousing operations, a smooth road surface is required to ensure smooth operation of the lifting vehicle. In addition, the warehouse space is large and the flat space span is wide, so it is not convenient for wired layout. Wireless network must be used to realize wireless data interaction. Therefore, the increasingly mature ZigBee technology is used to wirelessly network the RFID card reader to realize dynamic data exchange.
1 Demonstration of ZigBee Ad Hoc Network Scheme
In view of the operation characteristics of third-party logistics warehousing and actual transmission distance requirements, after horizontally comparing several wireless transmission methods, a wireless ad hoc network solution based on ZigBee technology is selected. ZigBee Ad Hoc Network is a wireless communication technology based on IEEE802.1 5.4, a high-reliability wireless data transmission network platform composed of up to 65,535 wireless data transmission modules. Within the entire network, each ZigBee digital transmission module can communicate with each other, and the distance between nodes can be infinitely expanded from the standard 75 m. It is easy to use, reliable in work, and low in price.
Compared with other networking methods, ZigBee technology first adopts the ad hoc network communication method. Each ZigBee node can work independently. Once a node has a problem, data can be transmitted through other nodes, and new RFID can be transferred anytime and anywhere. If the reader joins the network, it will not affect the use of all networks; if Wifi technology is used, an AP failure will cause all RFID readers in the coverage area to be unable to achieve data exchange. Secondly, the ZigBee protocol stack is simple and the implementation is relatively easy. Running ZigBee requires a system The resource is about 28 Kb, and the Bluetooth protocol stack is relatively complex, requiring about 250 Kb of system resources; in addition, ZigBee is more flexible than Bluetooth and is more conducive to controlling system costs.
In warehousing operations, according to the operation process, a large number of data transmission nodes are required, the cost of a huge number of communication equipment and the communication cost during network operation directly affect the system cost; and the ZigB ee technology will not generate more in addition to the first batch of investment costs. Daily usage costs. Although the transmission rate of ZigBee is not fast (the 2.4 GHz frequency band is only 250 Kb/s), considering the characteristics of storage operations, the electronic label on the cargo pallet only writes the ID number of the cargo, and the byte length is usually within 32 B. Therefore, It will not have too much influence on the transmission rate and meet the normal working conditions. In addition, ZigBee has low power consumption. Under the same power supply environment, the continuous working time of Bluetooth and WIFI is much shorter than that of ZigBee.
RFID-related protocols only stipulate the communication interface, while ZigBee has a relatively complete communication networking protocol. ZigBee can choose the 2.4 GHz ISM frequency band (global universal frequency band) on the working frequency band, while RFID can work in 915 MHz or other frequency bands, both Do not interfere with each other on the communication frequency. Considering that the warehouse is an indoor environment and the nodes are close to each other, the ZigBee module can penetrate a certain thickness of obstacles during the working process, so the signal attenuation is negligible. Through the self-organizing network protocol, devices in the network can directly or indirectly communicate wirelessly. The reliability and frequency utilization of the network are very high, and ZigBee has a relatively complete security authentication mode.
In summary, it is most suitable to choose ZigBee technology as the data transmission network of the RFID system in the third-party logistics intelligent warehousing.
2 Network principle and structure
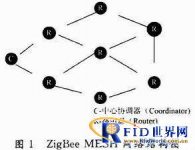
A ZigBee network needs to be composed of two parts: a central coordinator (Coordinator) and a router (Router). Each ZigBee network needs and only needs a central coordinator to create the network. When a node joins, it assigns addresses to the child nodes; while the router is responsible for sending and receiving data and forwarding data, and finding the most suitable routing path, when there are nodes When joining, you can assign addresses to nodes, so a ZigBee network may require multiple routers. When a network is composed of a central coordinator and N routers, this network is the real MESH network, and all data sent by each node is automatically routed to the target node.

The RFID system based on ZigBee ad hoc network technology adopts the MESH network structure and consists of a main control node and several sub-nodes (the number of sub-nodes depends on the number of RFID readers in the warehouse), as shown in Figure 1. The main control node is composed of a server through a serial port and a central coordinator; the child nodes are composed of a card reader through a serial port and a router. The serial port selects RS 232 two-way communication mode.
After all ZigBee devices are started, the master node will start to form a ZigBee network, add all sub-nodes to the network and assign network addresses to each sub-node, and store the information in the database. After the card reader collects the tag data, it first sends the data to the router connected to it. The router then sends the tag data together with the reader information to the master node for storage through the multi-hop ZigBee network. The master node needs to transfer the reader The parameter configuration command is sent to the reader through the communication with the router, and then the location node device enters the power saving mode; when the master node issues a command to the child node, the location node device can be awakened at any time by looking for the network of the child node Then, according to the network address, the command is transmitted to the router through the multi-hop network, and then transmitted to the corresponding card reader through the router. Finally, the router sends a confirmation notification of receipt of the command to the master control node.
3 Networking hardware layout
Take a third-party logistics flat warehouse as an example. Card readers are installed at various cargo positions and warehouse entrances and exits. Goods enter and leave the warehouse along with pallets. Electronic tags are attached to the pallets, and the tags store the ID numbers of the goods. The ZigBee equipment used for networking is based on TI’s CC2530F256 chip, running ZigBee2007/PRO protocol, and the integrated circuit ZigBee module, which has all the characteristics of the ZigBee protocol. The advantage of using the module is that the user does not need to understand the complex ZigBee protocol. All ZigBee protocol processing is automatically completed inside the ZigBee module, and the node programs are written into the module in an embedded manner, and the user only needs to transmit data through the serial port.
Among them, the ZigBee module, the card reader and the server follow the RS 232 asynchronous serial two-way communication format; all RFID card readers and their indicator signals are connected to the single-chip microcomputer through the hub device, and the single-chip microcomputer is uniformly controlled. The card reader It is also connected with the single-chip computer through the RS 232 serial port. The ZigBee module, RFID card reader, and single-chip power supply are all between 5 and 12 V, using standard TTL levels.
The server and the main control ZigBee module are installed in the warehouse’s general dispatching room, used for receiving and dispatching instructions and normal scheduling of warehousing operations; all card readers and ZigBee devices are installed in the actual warehouse location and warehouse entrance and exit to become a single network node, all nodes are composed RFID system based on ZigBee wireless transmission. The cargo position status indicator controlled by the single-chip microcomputer is installed above the cargo position to remind the staff of normal warehousing operations; the visual interface transformed after the database is processed is displayed on the host of the dispatching room on the one hand, and displayed on the warehouse on the other hand. The big screen is for staff to browse, as shown in Figure 2.

The specific work flow of data transfer in and out of the warehouse (location) is shown in Figure 3.

When other work processes and emergencies occur in the warehousing operation, such as inventory check, cargo storage area transfer, goods out of place or label damage, etc., the RFID reader wakes up the ZigBee router in time through real-time sensed signals, and then transmits the information in time The central coordinator is handed over to the back-end database for storage management. Almost all processes liberate the staff from the traditional operation methods. The accurate information collection mode improves the reliability of the system’s data management and effectively prevents human error.
4 Conclusion
After actual running tests, the ZigBee modules are separated by about 3 m in an indoor environment, and the signal is good. Under normal storage conditions, the server receives data packets within 20-40 ms, which meets normal working conditions.
An ordinary third-party warehouse with about 500 cargo spaces requires about 500 ZigBee modules. The unit price of ZigBee modules on the market is basically RMB 40-60. Therefore, to install a ZigBee ad hoc network system in the warehouse, the cost is between 20,000 and 30,000 yuan. For large and medium-sized warehousing companies, the cost performance is higher. However, for some small warehousing companies that value profits, it is still difficult to immediately improve their business. Therefore, if the cost cannot be effectively controlled, the plan will not be scalable. According to different enterprise scales and different warehouse characteristics, the number of ZigBee modules can be appropriately reduced in the actual implementation of the plan. For example, several adjacent RFID card readers can share a ZigBee module through a hub device, which effectively reduces costs. But the ensuing problem is that the amount of data that each ZigBee module transmits at a time is very limited. If the sequential data transmission mode and transmission interval problems cannot be solved well, it will greatly affect the response speed and work efficiency of the system. However, it is believed that these problems will be solved in the near future with the continuous development of ZigBee technology.
[ad_2]



