Use RFID technology to optimize the analysis and efficiency of warehouse logistics warehousing process
[ad_1]
introduction
With the rapid development of the international logistics industry, a large amount of information technology has been adopted to improve the service efficiency and quality of the industry, but there are still many tasks that are still mainly done manually, such as cargo inventory, inventory and data entry. Because this data collection method is difficult to standardize, it has led to a reduction in warehouse space utilization and low labor productivity, which ultimately affects corporate benefits.
As an identification technology, RFID has its unique side compared with another technology widely used in the logistics industry-barcode technology. Promoting RFID technology and letting the technology play its powerful role in promoting the logistics industry as soon as possible is a major trend for domestic logistics companies to join the application of RFID technology as soon as possible.
1 Introduction to logistics center and RFID technology
1.1 Main functions and development trends of logistics centers
The main functions of the logistics center include transportation, warehousing, loading and unloading, packaging, circulation processing, logistics information processing, etc., and the functions of the logistics center should be extended upwards and downwards according to the situation. The most important thing in the actual design is to determine how to The situation extends upwards, downwards, and the extent to which it extends. The development trend of modern logistics is:
The systematic trend of logistics;
The information trend of logistics;
Social trends of logistics centers, wholesale centers, and distribution centers;
The modernization and comprehensive systemization trend of warehousing and transportation;
The integration trend of logistics, business flow and information flow;
It can be clearly seen that the most prominent of the five major trends in logistics development is informatization.Therefore, the development trend of logistics centers is under the premise of the development of modern logistics, especially the development and application of information technology.[4].
1.2 Introduction to radio frequency identification technology (RFID) and its characteristics
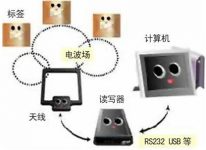
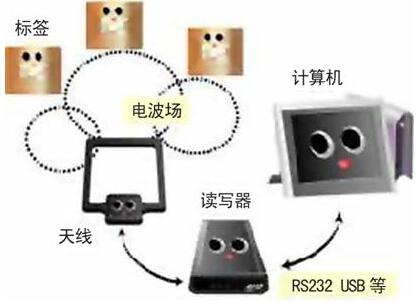
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification, radio frequency identification) is a non-contact automatic identification technology that automatically identifies target objects and obtains related data through radio frequency signals. The identification work does not require manual intervention and can work in various harsh environments. Compared with the traditional barcode, magnetic card and IC card, the label has the characteristics of non-contact, fast reading speed, no wear, no environmental influence, long life, easy to use and anti-collision function, which can handle multiple cards at the same time . RFID technology can identify high-speed moving objects and can identify multiple tags at the same time, and the operation is quick and convenient. In foreign countries, radio frequency identification technology has been widely used in many fields such as industrial automation, commercial automation, and transportation control management.
2 Analysis of logistics center warehousing process and efficiency optimization plan
2.1 Existing warehousing process:
◆Entry of warehousing plan:
The basic information of the goods entered into the warehouse includes quantity, size, weight, estimated time, etc., and some barcode sequences can also be provided;
◆Delivery vehicle registration:
This link controls the vehicles entering the receiving area to prevent overcrowding and reducing efficiency;
◆Tally:
Count the goods, record specific goods information, including scanning, palletizing, etc.;
◆Warehousing:
The goods are moved into the warehouse for storage, which requires the status of the goods, location management, mechanical scheduling, etc.;
◆Completion:
The cargo storage operation is completed.
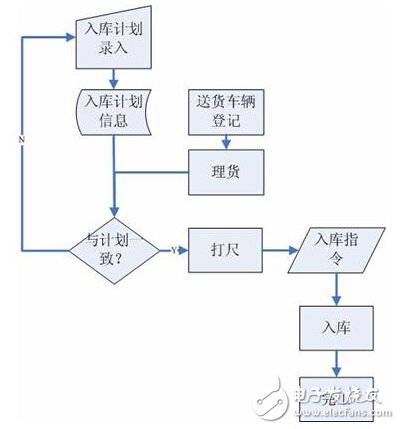
Figure 2 Flow chart of warehousing
2.2 Weak links in the analysis process
From the perspective of operating efficiency, the efficiency of data collection is very important. Barcodes need to be scanned one by one. It takes 2-3 seconds to scan one barcode on average, which will greatly reduce the efficiency;
From the perspective of accuracy, if the corresponding barcode is known in advance before the warehousing operation, it can be proofread when scanning, thereby reducing the error rate;
In order to ensure accuracy, the warehouse door should be further verified whether the passing goods have a corresponding warehousing plan, if it is, it will be released, otherwise it will be blocked, so as to effectively prevent errors.
2.3 Links that need to be modified and optimized
◆The warehousing plan link:
Connect with customer data, unify standards, and obtain relevant barcode numbers or RFID in advance to improve the efficiency of subsequent operations.
◆The actual warehousing information collection link:
Use RFID batch identification to improve the efficiency of the collection process;
◆Data inspection of the warehouse door, check whether there is any mistaken storage operation, and prevent such errors from occurring:
Read the RFID information of the goods at the warehouse door, and there is a corresponding release in the warehouse plan, otherwise the alarm is issued.
2.4 Design specific optimization measures
◆Establish RFID database:
In the case of non-uniform standards, customers should be asked for their opinions and try to unify standards with long-term stable customers.
◆Place RFID tags on the goods:
The ideal situation is that manufacturers place RFID tags in advance when they produce goods. If not, they can temporarily affix or hang the RFID tags made by the warehouse during the collection of goods data.
◆Use smart tray:
The manufacture of plastic pallets is a good example of RFID PCB applications. Before the ultrasonic welding stage of the plastic pallet manufacturing cycle, the PCB is placed in the plastic pallet. In this way, PCB turns the pallet into a “smart pallet”, and data can be read and written to the pallet in the entire logistics chain.
◆Install RFID read-write device in Kumen:
Taking into account the operating efficiency and operating environment, a gate-shaped RDID antenna reader can be used, so that the goods can be directly entered when entering the warehouse without stopping to scan, thereby improving its efficiency.
◆The library management personnel are equipped with handheld RFID readers:
In this way, it can be used to find goods and inventory goods. The warehouse management staff can walk around the warehouse to know the storage situation of the goods clearly.
2.5 Warehousing process after design optimization
◆Introduction of warehousing plan
The basic information of the goods to be put into the warehouse, including quantity, size, weight, estimated time, RFID information of each goods, and delivery truck information, are directly imported into the database.
Improvements: Try to avoid manual input links to reduce the error rate links; use the electronic and automated methods of cargo data to improve data operation efficiency and help improve the overall process efficiency.

Figure 3 Improvement of manual entry method
◆Delivery vehicle registration
Delivery truck registration, check whether there is a warehousing plan, and directly call out if there is.
◆Tally warehousing
Use RFID batch identification technology to collect the cargo information, compare it with the warehousing plan information in the database, and if there is no abnormality, the goods will be checked into the warehouse. When passing through the warehouse door, the system automatically collects it through the door-shaped antenna reader. The RFID information of the moving pallet and the RFID information of each item placed on the pallet are recorded in the database in real time, and the storage is completed.

Figure 4 Logistics tray
RFID tag and antenna placement:
There are two ways for the tray: surface fixing and embedding. Surface fixing means fixing on the outer surface by pasting, etc., and embedding means placing it inside the wooden pallet.The antenna of the reader can be made into a door-shaped antenna according to the shape of the door to ensure that the goods can be read and written smoothly when passing through the door.
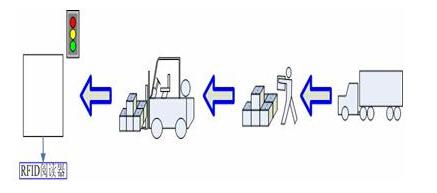
Figure 5 Schematic diagram of RFID cargo storage
Goods identification process: After the goods are unloaded from the truck, they are placed on the pallet. When the forklift transports the pallet with the goods to the door of the warehouse, the reader can read the RFID information of the pallet and the goods on it in batches. The coding category of the goods is different, and it can be distinguished which is the pallet information and which is the cargo information. The reader transmits the collected data to the information system processing unit to determine whether the goods have a storage plan, and if not, an alarm is issued to prohibit the goods from entering the storage. On the contrary, let the goods enter the warehouse smoothly. Figure 6 reflects the three relationships between the cargo pallet and the reader.
The state A is: the goods with RFID tags are placed on the pallets with RFID tags, and they are in the state when they are approaching the door of the warehouse on the way to the warehouse. When the distance between the pallet and the warehouse door is reduced to a certain extent, it enters the effective reading and writing range of the RFID reader.
State B is: cutting the gate antenna of the RFID reader placed at the entrance of the warehouse during the movement of the goods. At this time, it has entered the effective reading range of the reader, and the reader will return the identified information to the database, which will be analyzed by the warehouse check module Deal with it, and prompt the error situation through the alarm method.
C status is: the cargo information has passed the inspection and is being delivered to the designated location.
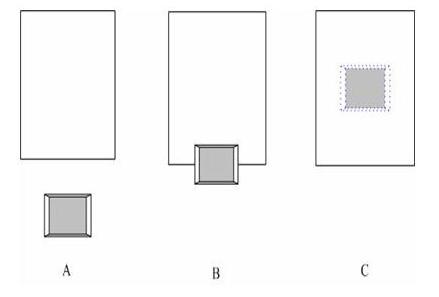
Figure 6 The goods pass through the RFID reader at the warehouse door
◆Completed
The new process is more effective for the larger the quantity of goods, and the system will automatically calculate whether there are overflows and deficiencies when the goods are put into storage. There are two judgment methods according to the process design:
Inspection before storage: The goods are palletized centrally on the platform, and then the RFID information of the goods is read with a handheld reader, counted, and compared with the storage plan. If it does not match, the alarm will be reported.
Statistics after warehousing: The goods are palletized and warehousing, and the goods are identified, compared and counted during the warehousing, and finally the overflow and shortage are counted.
The latter is more efficient, and the effect will be better if it is adopted when the warehousing plan is relatively accurate.
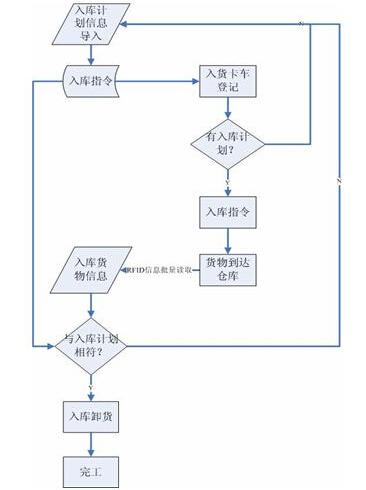
Figure 7 Improved warehousing process
3 Process comparison and summary before and after RFID technology optimization
3.1 Comparison of warehousing process
Compared with the warehousing process before optimization, the optimized warehousing process is more prominent:
The manual entry plan is changed to the method of electronic data import, which reduces the links of manual entry.
The process of scanning goods one by one is reduced, and the method of RFID batch identification is changed. This method is particularly suitable for large quantities of goods.
If a single piece is in the warehouse, it can also be realized that the reader can automatically identify and record the goods when the goods pass through the warehouse door.
The basic information of the goods, including size, color, model, etc., can also be obtained from RFID storage, eliminating the need for inspection at the warehouse door.
Added the function of checking at the warehouse door. This is a problem that the previous barcode management process is not easy to handle, because if you want to use barcode management to check, you must stay at the warehouse door for enough time to scan and check, and doing so will undoubtedly increase the work. Time and lead to reduced work efficiency. Now using the RFID system, using its characteristics that can be identified in motion, it is easy to achieve the goal of inspection and verification at the warehouse door.
Due to the limitations of barcodes, surface contamination, temperature and other factors will affect its accuracy, and RFID itself is not affected by such factors, and can be built-in, which increases its stability and reliability.
3.2 Summary and Outlook
From the results of analysis and optimization of the warehouse logistics warehousing process, basically due to manual data collection, multi-tag batch reading, data collection in motion, reading distance, etc., it can be improved by introducing RFID technology, and there are further The possibility of optimization. At the same time, it should be noted that in order to make good use of this technology, the handling of some key issues is very important.
After the optimized process obtained from the above work, full use of the characteristics of RFID technology has played the purpose of improving work efficiency and quality from multiple links, and achieved the expected goal. If it is adopted on a large scale, the effect will be more obvious, and the economic benefits of the entire industry will be considerable.
It is recommended that the warehousing and logistics center consider its own situation and external environment to adopt RFID technology as soon as possible to improve operation efficiency and quality, achieve the goal of strengthening management and improving services, and will have a profound impact on enhancing corporate image and expanding business areas. At the same time, it is also hoped that more relevant manufacturers will also develop more cost-effective RFID products as soon as possible to promote the rapid development of the logistics industry.
[ad_2]



