How to build a measurement standard system in the era of the Internet of Things? What is the significance of the application of the Internet of Things in the field of metrology and testing?
[ad_1]
The Internet of Things has received extensive attention and attention from countries all over the world, and is considered to be the third wave of revolution in the world’s information industry after computers and the Internet.
my country has put forward the “Perceive China” strategy, and has officially elevated the Internet of Things to one of the five major strategic emerging industries that the country will focus on.
The Internet of Things is a network that communicates and exchanges information between objects in accordance with agreed protocols, realizes the interconnection between objects and objects, as well as intelligent identification, positioning, tracking, monitoring and management.

According to different functions, the framework of the Internet of Things can be divided into four levels, namely, the identification layer, the perception layer, the transmission layer, and the application layer.
The identification layer is to obtain the identity information of the object, and its core component is RFID; the perception layer is to obtain static and dynamic information of the object through various sensing terminal devices, and its core component is the sensor; the transmission layer is to realize the communication and exchange of information. Its core component is a wireless data communication network; the application layer is to realize information recognition and feedback, and its core component is a smart chip.

The four-tier infrastructure of the Internet of Things
At present, the Internet of Things is developing rapidly, but many concepts, technologies and standard systems are under continuous exploration. Therefore, the ability to have core independent intellectual property rights and formulate core technologies and standard systems has become the key for countries around the world to seize the commanding heights of the Internet of Things industry.
Since 1999, my country has initiated research on the Internet of Things, and has made significant progress in wireless smart sensor network communication technology, miniature sensors, sensors, mobile base stations, etc., and now has a complete range of materials, technologies, devices, systems, and networks. The industrial chain is one of the few countries in the world that can realize the industrialization of the Internet of Things, and is one of the leading countries in the formulation of international standards.
For the Internet of Things to “perceive” objects, it involves the issue of measurement, and therefore it is inseparable from measurement. Measurement standards have become an important part of the Internet of Things standard system. For the Internet of Things, measurement standards are mainly centered on two aspects: One is the establishment of a measurement standard system for the four-layer core components of the Internet of Things; the other is the establishment of a measurement standard system for the application of the Internet of Things in the field of measurement and detection technology.
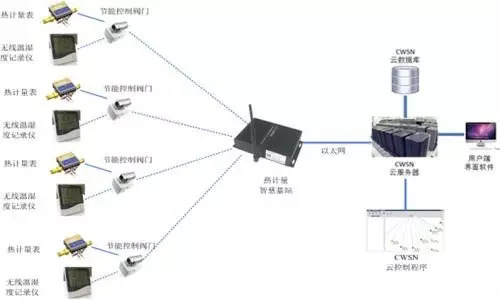
Smart heat metering cloud energy-saving IoT system
Construction of the measurement standard system for the four-tier core components of the Internet of Things
1. The standards for core components of the Internet of Things are not uniform
For the Internet of Things, the technical and standard uniformity of the core components of the four levels of identification, perception, transmission and application is the cornerstone of development.
Now, RFID, sensors, wireless data communication networks and smart chips are all mature technologies and all have their own standards. For example, in the field of RFID, there are EPCglobal (Global Product Electronic Code Management Center), Algglobal (Global Automatic Identification Organization), ISO (International Organization for Standardization), IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission), UID (Ubiquitous Technology Core Organization), etc. International standards launched by the International RFID Standardization Organization, as well as domestic standards launched by the RFID Standardization Working Group led by the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology of China.
In the sensor field, due to the numerous disciplines involved, it has been developed independently in each discipline for a long time, and there are quite different measurement, test and performance evaluation standards for sensors with different parameters.
In the field of wireless data communication networks, there are multiple wireless communication standards and protocols such as Bluetooth, WLAN, 4G, 5G, NB-Iot, and wireless ad hoc networks; as far as 3G standards are concerned, they can also be subdivided into WCDMA (European Four mainstream wireless interface standards, CDRA2000 (US version), TD-SCDMA (China version), and WiMAX. The first three standards are currently being adopted in my country at the same time.
In the field of smart chips, the diversity of standards is even more numerous.
However, if these mature standards are to be applied to the field of the Internet of Things, there are still many problems. This is because the Internet of Things requires unified technologies and standards between all layers of the framework to realize the connection between things. Just as the Internet has effectively solved the unified TcP/IP transmission protocol, router protocol, terminal architecture and operating system and other standardization issues in the world, it can reach the current level of development. If the Internet of Things lacks a unified national and international standard system during the development of the Internet of Things, the standards developed or adopted by various enterprises and industries will inevitably have inherent problems of poor compatibility. As a result, a large number of small private networks will be formed. Networks cannot be connected, and cannot be connected and connected. Therefore, economies of scale cannot be formed, a complete business operation model cannot be formed, and popularization to the general public cannot be achieved.
2. Construction of the measurement standard system for core components
In the construction of the four-layer core component standard system of the Internet of Things, the role of measurement is to form a complete set of measurement and evaluation standard systems, which can perform various parameters of core components such as RFID, sensors, wireless data communication networks, and smart chips. Comprehensive measurement, comprehensive testing of the adopted protocol, and evaluation of the reliability and accuracy of the entire system. Form a complete measurement and test technical standard specification to provide measurement guarantee for the comprehensive deployment of the Internet of Things.
The Internet of Things is not an independent product, nor is it that an enterprise or an industry can do it independently. It involves all walks of life in the whole society and needs to integrate multiple resources to achieve it. This requires the support of national industrial policies and administration. The management department takes the lead, according to the actual situation of my country’s social and economic development, integrates existing standards in the fields of RFID, sensors, wireless data communication networks and smart chips, and forms a core standard with independent intellectual property rights, so that it can be in the wave of IoT development Occupy the commanding heights and gain the right to speak internationally.
The establishment of a standard system for the application of the Internet of Things in the field of measurement and testing

Energy metering IoT application solution
1. Difficulties facing the measurement and testing industry
In the field of metrology, measuring instruments for work objects have distinct characteristics of periodic verification/calibration. For measurement instruments under mandatory state management, re-inspection shall be conducted in accordance with the legal cycle; for non-mandatory measurement instruments, the user can perform re-inspection according to the legal measurement cycle or a cycle determined by the enterprise itself.
For each measuring instrument, within the effective service life, it often needs several to dozens of measurement verifications. At the same time, due to the fact that the working measuring instruments are installed at the site of use, are large in size and not easy to move, etc., they often need to provide on-site measurement services by the metrological verification agency.
The existence of these two situations causes the metrological verification agency to complete a large number of on-site metrological tasks each year, resulting in the following four problems:
(1) The metrological verification personnel spend a lot of time on their way, which greatly reduces the work efficiency. There is a dilemma that the metrological verification task is too late and the effective working time cannot be arranged reasonably;
(2) On-site verification requires working equipment such as standard measurement instruments. Considering the stability, accuracy and safety of standard measuring instruments, it is not easy to use convenient transportation methods such as consignment and express delivery, and can only be carried with them. This results in measurement personnel who need to carry a large number of instruments every time they go out. Equipment to increase work intensity;
(3) The verification objects are scattered all over the country, and each group of verification personnel needs to carry working equipment. Therefore, the metrological verification agency must be equipped with a certain number of the same type of measurement standard. This not only increases the pressure on the operating cost of the metrological verification agency, but also is not conducive Reasonable use of equipment results in waste of resources, and also gives rise to a series of problems such as equipment management, maintenance and depreciation;
(4) The metering verification service charge items include the travel cost of the metering verification personnel. Sometimes the verification cost of a simple measuring instrument is far less than the travel cost. Increasing the economic burden of enterprises, leading to the phenomenon of “do not want to be inspected, unwilling to inspect, and evade inspection”.
2. The significance of the application of the Internet of Things in the field of measurement and testing
As we all know, measuring instruments are metrology tools, and the accuracy and reliability of their instruments and equipment directly affect the accuracy of measurement parameters.
In the four areas of trade settlement, medical and health, safety protection, and environmental monitoring, measuring instruments are directly related to major issues such as national economy and people’s livelihood, personal safety, and social stability. The “Measurement Law” clearly stipulates that mandatory periodic measurement should be carried out. However, under the current regulatory system, the verification of measuring instruments relies more on the voluntariness of enterprises, and government functional departments and related measurement verification agencies lack effective supervision measures and means to supervise the measuring instruments in use by enterprises.
The emergence of the Internet of Things has provided help in solving this problem. The application of the Internet of Things technology in the field of measurement and detection has the following advantages:
(1) To dynamically track and supervise the use of compulsory verification measuring instruments. It breaks through the restrictions of time, region and personnel, and is conducive to the implementation of laws and regulations on the mandatory management of measuring instruments;
(2) Real-time collection of information such as the performance and parameters of measuring instruments can fundamentally change the traditional verification mode of predetermined cycles, which is conducive to the realization of dynamic management of measuring instruments used in work, and the formation of a scientific verification mode for prior quality management , Effectively avoiding the mismatch contradiction between the agreed verification period and the quality status of measuring instruments, saving operating expenses for the enterprise, and improving the efficiency of the use of measuring instruments;
(3) It is conducive to the realization of intensive management of measuring instruments, promoting the development of outsourcing service models of measuring instruments, forming a working mode in which measurement and testing institutions provide enterprises with one-stop services, allowing enterprises to devote greater energy to their main business superior.
3. Construction of a standard system in the field of measurement and testing

In the process of measuring and testing services, the core technical means is value comparison, and the core concept is value traceability.
According to the current technical standards for measurement and testing, measurement and testing institutions use measurement standard instruments that are at least one order of magnitude higher than those used by the enterprise for on-site measurement value comparison. For comparison between national measurement standards or international measurement standards, the entire comparison chain must meet the principle of value traceability. Therefore, the legal basis for the current metrological testing technology reference, that is, metrological verification regulations and metrological calibration specifications, are compiled accordingly.
The Internet of Things transcends the limitations of time and space, and realizes the interconnection between working measuring instruments and measuring standard instruments, eliminating the need for on-site comparison between the two. In this way, part of the current metrological verification regulations and metrological calibration specifications are obviously not applicable, and there is a lack of guiding operating clauses. In particular, how to realize the problem of value traceability in the metrological standard system is particularly important.
The following takes the measurement and detection of the gauge block as an example to illustrate the above problems. According to the current metrological verification regulations and metrological calibration specifications, the working quantity block and the standard measuring block are compared on the spot, and the test conclusion of the working quantity block can be given. In the Internet of Metrology, the work volume is in the enterprise site, and the standard volume is in the measurement and testing organization. Firstly, the parameters of the working meter should be read through the measuring device, and then transmitted to the measuring and testing organization for comparison with the parameters of the standard meter. This kind of operation process is not reflected in the current measurement standards, so the inspectors have no basis for operating instructions. The more important thing is how to obtain the parameters of the working quantity block and the standard gauge block, which involves the accuracy and reliability of the traceability of the quantity value, which requires the support of relevant measurement standards.
In the development of the Internet of Things, the four core components of RFID, sensors, wireless data communication networks, and smart chips at the four levels of identification, perception, transmission, and application involve the issue of how to accurately and reliably obtain and evaluate the value. Need to be clarified in the relevant measurement standards. At the same time, these four core components all have the problem of inconsistency in current standards, which has brought inconsistencies in standards for the full realization of the Internet of Things.
The concept and technical application of the Internet of Things is feasible and necessary in the field of metrology and inspection, and it can effectively solve the development bottleneck problem currently facing the field of metrology and inspection. However, due to the obvious differences between the cross-regional detection methods of the Internet of Things and the current on-site comparison methods, the current measurement verification procedures and measurement calibration specifications are obviously insufficient in operation guidance, and the standard system for value traceability needs to be renewed. consider.
The standard system of the Internet of Things is still in the stage of gradual development and is far from mature. Whether it is the construction of a system of measurement standards for the core components of the Internet of Things or the construction of a standard system for the application of the Internet of Things in the field of measurement and testing, it is a huge system project that cannot be completed by an enterprise or an industry alone, and requires the support of national macro policies. And guidance requires the leadership and leadership of national-level functional departments, mobilizing the forces of the whole society, and pooling their efforts to complete the construction of a measurement-related standard system and lay the foundation for the arrival of the Internet of Things era.
[ad_2]



