Three types and six application fields of RFID technology
[ad_1]
Why our express delivery can always be accurate and correct on the route? Why is the massive amount of books in the school library managed in an orderly manner? Why can some accidentally stolen items be quickly traced back? And these have to use RFID technology, because in this In the era of the Internet of Things, it is one of the key technologies for data connection and data exchange.
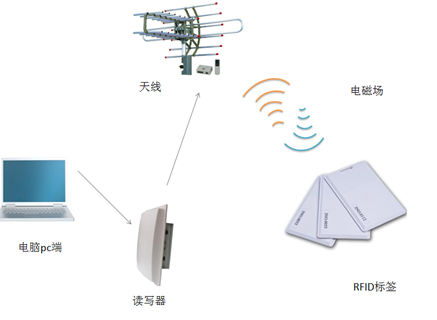
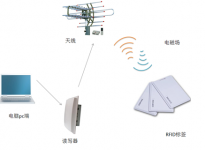
What is RFID technology? RFID, also known as radio frequency identification, recognizes and reads and writes specific target data through radio signals. It does not require mechanical contact or a specific complex environment to complete the identification and read and write data. Nowadays, the application of RFID technology that everyone talks about is actually an RFID tag, which already exists in every aspect of our lives. It works in two situations. One is that when the RFID tag enters the effective recognition range of the reader, it receives the radio frequency signal sent by the reader, and uses the energy obtained by the induced current to send out the information stored in the chip, and the other is The RFID tag actively sends a signal of a certain frequency, the reader receives and decodes the information, and then sends it to the central information system for relevant data processing. In the middle of the twentieth century, based on the improvement and application of radar, radio frequency identification technology began to lay the foundation, and then began its initial development. Until today, the application of RFID technology has a history of more than half a century. At present, RFID technology is in China. The development status of foreign countries is good, especially countries such as the United States, Germany, Sweden, Japan, South Africa, the United Kingdom, and Switzerland have relatively mature and advanced RFID systems. Launched a completely independent research and long-distance automatic identification system.
Next, the editor will take everyone to understand RFID technology:
Three types
There are three main categories of products derived from RFID technology:
1. Passive RFID products: These types of products require close contact identification, such as meal cards, bank cards, bus cards, and ID cards. The types of these cards require close contact during work identification. The main operating frequencies are: Low frequency 125KHZ, high frequency 13.56MHZ, ultra high frequency 433MHZ and 915MHZ. This type of product is also more common in our lives, and it is also a product that has been developed relatively early.
2. Active RFID products: This type of product has the characteristics of long-distance automatic identification, so it is correspondingly applied to some large-scale environments, such as smart parking lots, smart cities, smart transportation, and the Internet of Things. Their main tasks are There are microwave 2.45GHZ and 5.8GHZ, UHF 433MHZ.
3. Semi-active RFID products: As the name suggests, it is a combination of active RFID products and passive RFID products. It combines the advantages of both, and under the trigger of the low frequency 125KHZ frequency, allows microwave 2.45G to play its advantage and solves the problem of active RFID products. And passive RFID products can not solve the problems, such as access control management, regional positioning management and security alarm applications, close-range activation positioning, long-distance data transmission.
Six areas
RFID technology has the characteristics of strong anti-interference and no need for manual identification, so it is often used in some fields that need to collect or track information, including but not limited to the following seven points:
1. Warehouse/transportation/materials: Embed RFID chips into the goods, store them in warehouses, shopping malls and other goods and during the logistics process. The related information of the goods is automatically collected by the reader, and the manager can quickly query the information of the goods in the system to reduce discarding or The risk of theft can increase the delivery speed of the goods, improve the accuracy rate, and prevent the fleeing of goods and anti-counterfeiting.
2. Access control/attendance: For some companies or some large conferences, by entering their identity or fingerprint information in advance, they can identify and sign in by themselves through the door recognition system, which saves a lot of time in the middle, which is convenient and labor-saving.
3. Fixed asset management: Some places with huge assets or valuable items, such as libraries, art galleries, and museums, need complete management procedures or rigorous protection measures. When the storage information of books or valuables changes abnormally, The administrator will be reminded in the system as soon as possible to deal with the relevant situation.
4. Train/vehicle identification/baggage security inspection: my country’s railway vehicle dispatching system is a typical case. It automatically identifies vehicle numbers and information input, saving a lot of time for manual statistics and improving accuracy.
5. Medical information tracking: case tracking, waste product tracking, drug tracking, etc. are all good ways to improve hospital service levels and efficiency.
6. Military/National Defense/National Security: The dynamics of some important military drugs, guns, ammunition or military vehicles need to be tracked in real time.
Seven advantages
1. The anti-interference ability is super strong. One of its most important advantages is non-contact identification. It can work in abrupt and harsh environments. It can and has strong penetrating power, and can quickly identify and read tags.
2. The data capacity of the RFID tag is very huge, it can be expanded to 10k according to the needs of users, which is much higher than the capacity of 2,725 digits in the two-dimensional code bar.
3. It can be dynamically operated, its tag data can be dynamically modified by programming, and it can be dynamically tracked and monitored, as long as the object attached to the RFID tag appears within the effective recognition range of the reader.
4. Long service life. Because of its strong anti-interference, RFID tags are not easy to be destroyed and have a long service life.
5. Anti-collision, within the effective recognition range of the reader, it can read multiple RFID tags at the same time.
6. High security. RFID tags can be attached to the product in any form, and the tag data can be encrypted with passwords to improve security.
7. The recognition speed is fast. As soon as the RFID tag enters the effective recognition range of the reader, it will start to read the data. Generally, the recognition can be completed in less than 100 milliseconds.
Advance and retreat together
Of course, every technology has its pros and cons. The development of RFID technology to this day will also have its shortcomings, that is, the technical application of UHF frequency band is not wide enough, the technology is not mature enough, the related products are expensive, and the stability is not high. , There is no uniform standard in the world.
At present, RFID technology is closely related to our daily lives. In the current Internet of Things era, if RFID technology is perfected, RFID UHF technology is mature, and the development of RFID UHF market is widely used, then the development of the Internet of Things will also Push to a new height.
[ad_2]



