Cathay Pacific General Hospital applies active RFID in the operating room for full-process control
[ad_1]
Preface
Cathay Pacific General Hospital attaches great importance to patient safety and medical quality improvement, so as early as three years ago, it started to plan the operation of the entire surgical process related units e-ification, effective communication with the team, and active RFID technology as the main technology for patient identification. The coverage of the information system controlled by the laboratory is quite advanced in medical institutions in our province or the world. We named it “Operating Room-Patient Advancement Monitoring System, OR-PAMS” because of the sequential process that controls the entire operation.
About half of medical accidents are related to surgery, including errors in surgical location and procedures, errors in blood transfusion, and adverse reactions to organ transplants, which often cause major injuries and deaths of patients (Shi Chongliang, Xue Yasheng 2004). A study by the Joint Commission of Accreditation for Healthcare Organization (JCAHO) in the United States pointed out that communication problems between medical staff are the main cause of medical errors in surgery. This improves the effectiveness of communication between medical staff and reduces unexpected A medical error occurred (JCAHO, 1998).
The so-called “surgical procedure” includes pre-operative evaluation, anesthesia evaluation, pre-operative preparations, and post-operative medical care. The medical teams of various specialties provide patients with proper medical treatment before, during and after the operation. Every step will affect the life safety of surgical patients. Therefore, the improvement of surgical process management has been regarded as the focus of improving the safety of surgical patients (Zohar and Noga et al. 2007).
In the past, the use of the operating room relied on manual pen and paper operations. There was no consistent handover during the transportation of surgical patients from the ward, escort center, operating room, and recovery room, and there was a lack of integrated analysis data as a basis for quality improvement and management. . The functional characteristics of RFID not only meet the primary goal of patient safety work “improving the accuracy of patient identification”, its location tracking function also provides medical staff with real-time updated patient information, demonstrating the e-automatic efficiency and reducing the resistance to process reorganization .
According to the environment of different work sites, it is necessary to introduce UMPC (Ultra Mobile PC, ultra-small mobile computer) and other touch-sensitive handheld devices, so that colleagues are familiar with real-time input and sharing of information at the work site, and shape the safety culture of patients in this hospital Has a major and wide-ranging impact. We later included the equipment room and the central supply room into the scope of e-ization, and established a material monitoring system based on bar code technology to make the monitoring of patients, staff, and materials more complete throughout the operation process. The system was originally a Web-based design, so the expansion process is quite smooth for the information system or users.
RFID system introduction
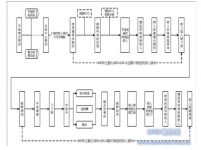
Considering that the procedure of a patient’s surgery needs to go through inspections and records by many units, therefore, after the patient is admitted to the hospital, the patient data is combined with the RFID data, written into the database for follow-up tracking, and the patient will wear it with him. Active RFID tag (radio frequency identification bracelet), after the Reader installed in a specific location, will immediately write the message record into the database, and display it on the front-end web page for users to identify and query; the RFID and system operation flow is shown in the figure 1 shown.

Figure 1. Operation flow chart of PAMS system
The scope of PAMS construction starts from the operation schedule, until the operation is completed and enters the recovery room or intensive care unit. Therefore, it needs to be partially integrated with the hospital information system to retrieve basic patient data and surgical reservation data. Including ward nursing units, surgery, anesthesiology, and escort units sharing PAMS data. After the patients are hospitalized, they enter the closely monitored surgical process.
The system and the gang knife system will link and update the surgical schedule data every three minutes. After selecting the patient, the PAMS system will automatically bring in the patient’s related surgical data. A centralized database is used as the core of the system’s operation, and the data filled in is stored in separate data tables according to the attributes of each unit’s form. The centralized database is divided into a front-end user area and a back-end database area. The front-end is a network shared browsing hospital website, using wired Ethernet as the data transmission medium, and ordinary users can operate through the hospital computer; or In response to the mobile operation requirements of clinical care and surgical procedures, it needs to be used with the lighter touch control panel of UMPC, which can be operated quickly through the wireless network in the hospital; the overall system data flow concept is shown in Figure 2.

Figure 2. PAMS overall system conceptual diagram and data flow
System hardware and software architecture
The development tools used in this system include software and hardware:
(1) Software part
The back-end database area uses Microsoft Windows 2003 as the operating platform. Because it is a Web-based website-based operating platform, users only need to operate records simply and quickly to perform electronic modules for the original complex copy work. The database part uses Microsoft SQL Server 2005 as the back-end operating platform. The RFID positioning system module uses the software Network Enabler Administrator 2.6 to set the COM of the RFID Reader on the host, the Middleware determines the strength and frequency of the reader’s received message, and the Location Calculation software uses the 3D positioning algorithm to determine the positioning point and the current position, and transfer the value After returning to the database, the front-end web program will read the positioning information.
(2) The hardware part
RFID Tag uses active RFID wristband type tags, the transmission frequency is 2.45 GHz, and the reader can receive 256 tags. In the computer part, in addition to the desktop computers of each user, the mobile hardware includes a UMPC 7-inch touch screen, which supports handwriting input, wireless Internet access, and mini-notebook computers.

Figure 3. Active RFID Tag (left) and Reader (right)

Figure 4. Actual erection of RFID Reader
Benefits and discussion
The operation of the operating room is similar to the flight control system. The surgical patient is transferred from the ward to the operating room until the end of the operation. The patient is moving forward dynamically, with high demand for mobility and flexibility; and medical services are highly complex and uncertain. It also needs the intervention of the medical information system to reduce the burden on staff, reduce management costs and improve service efficiency. Therefore, our hospital introduced RFID into the operating room and built a system to control the advancement of surgical patients in the operating room, integrating all preoperative, intraoperative, and postoperative resource systems to increase management efficiency, reduce the probability of errors, and improve the quality of medical services. . RFID technology has the characteristics of high-speed dynamic reading, simultaneous reading of multiple tags, large data capacity, repeated reading, thin tags and high environmental tolerance, which meets the needs of operating room process management and patient identification.
The system integrates complex and cumbersome surgical scheduling, surgical human resources, surgical instrument management, etc., so that the surgical team can be more efficient, reduce surgical operation time, patient waiting time, and improve the safety and satisfaction of patient treatment; Surgical patient process management time, including induction of anesthesia, completion of anesthesia, preparation before surgery, surgical incision of the skin, wound closure, the end of anesthesia of the patient, the recovery of the patient, and the time when the patient is discharged from the operating room. It can also be controlled at any time and managed immediately. Maintain the quality of medical care.
During the construction process, because of the many units involved, more than forty demand interviews and team meetings were held in the first half of the year. Changes in user requirements and detailed system modifications after the launch also require frequent communication. In addition to users having a deep understanding of the feasibility and convenience of the information system, the ability of the information staff of the hospital to promote cross-unit projects is also improved.
In addition to using the identification and tracking features of RFID to improve the safety of surgical patients, the PAMS system also integrates the characteristics and needs of all units in the hospital through the communication platform set up by the system itself, and improves all aspects of the surgical process. In the operation form, it is designed for different surgical characteristics in outpatient, hospitalization, emergency department and different surgical departments, so that users will not lose important information due to the short operation time; in terms of anesthesia consultation, the anesthesia visits before surgery are more important. Reach 100%; in terms of escort, patient escort needs are more specific through the use of the system interface, and the dispatched manpower is used more efficiently; in terms of surgical instruments, warnings of the effective date of the instruments, simple instrument inventory management; in terms of pathological examinations, The results of manual biopsy can be presented online in real time, reducing the time and errors of specimen transportation; for the surgical team, the record of the operation time can be instant, synchronized and consistent; in the quality index management part, it can cooperate with the Department of Health to declare and upload operations. Quality indicators can be provided to all units, departments, and even attending physicians in the hospital as a basis for improving medical quality.
Active vs passive RFID
In recent years, RFID has been widely used, and medical applications are mainly based on personnel identification and asset management. Keelung Chang Gung Memorial Hospital is the first domestic institution to report the experience of applying passive RFID technology in operating room management (You Zhangsong, Chen Zhihua, etc., 2008). This hospital adopts an active device, which is designed to operate remotely and is more convenient in terms of the function of the automatic drive system. In addition, the PAMS system is connected to the surgical scheduling system, covering the ward, escort unit, central supply room, and anesthesiology department. The important purpose is to strengthen communication between units, and it can be solved at one time in meeting the needs of users.
The OR-PAMS system uses active RFID. Because it can store more information and has a wider signal recognition range, the patient’s flow during the operation is actively recorded, which ensures the rights of the surgical patient. The application of the system also extends to equipment management, escort manpower call and configuration, real-time presentation of pathological slice tissue reports, and medical quality index management, etc. It is believed that active patient management can be achieved. In terms of cost-effectiveness, although active RFID is more expensive, RFID bracelets can be repeatedly sterilized and used to write data, and the expansion functions are also more diverse. In the medical industry that is gradually transforming and integrating information technology, active RFID is applied to patients Security will be more diverse.
Surgery patients are equipped with active RFID during the operation process. Medical staff can update the patient’s information and location in real time. The system check function improves the accuracy of the patient’s identification; the process of the patient from the ward, surgery room, and recovery room In the process, PAMS integrates the data flow of each unit, and also reduces the situation of unmatched communication and imperfect handover of medical staff; system warnings and error reminders also make patient safety maintenance more comprehensive. The establishment of the Surgical Patient Advancement Monitoring System (PAMS) replaces the paper data in the past, which not only saves manpower, but every data accessed in the database can be used for quality management analysis and improvement of surgical process safety in the future.
Many scholars questioned and discussed active RFID on patient privacy and the safety of patients (Levine, Adida, etc., 2007; van der Togt, van Lieshout, etc., 2008). The system is connected to the database through RFID, and patient data is not directly stored on the RFID wristband. In addition, in the judgment on the positioning system, the overlap of the signals may affect the accuracy of the positioning. In addition to testing the RFID power, the signal strength received by the system and determining the location of the area, this research also adjusts the time of the RFID transmission frequency to reduce the number of signals. Mutual interference. Passive RFID causes more interference to the instrument, and it is significantly higher than active RFID (EMI: 26 vs. 8). However, the transmission frequency of RFID used in this research is 2.45GHz, which is equivalent to the electromagnetic intensity of PHS mobile phones, and has little effect on medical equipment.
in conclusion
The establishment of a monitoring system for the advancement of surgical patients provides a safer medical environment and medical quality for medical staff and surgical patients; medical providers can use medical resources more effectively to improve the utilization rate of operating rooms. Because of the establishment of the OR-PAMS system, this hospital promotes cross-unit communication, and has clear benefits in promoting patient safety in the operating room. In addition, due to the establishment and online process of the complex system, the participating medical staff and information colleagues have accumulated experience in promoting large-scale projects. For the future application of information technology and RFID new technology, the development of patient-centered full medical care is provided. The foundation of organizational culture.
[ad_2]


