Application of RFID technology in port container logistics
[ad_1]
Since the 911 incident, ports of various countries have taken a series of anti-terrorism actions, the purpose of which is to improve the safety and efficiency of container transportation. Among them, the United States has led a number of transportation safety operations measures, such as the “Container Security Program (CSI)”, “US Customs and Trade Partners Counter-Terrorism Program (abbreviated as CTPAT)”, and “Commercial Operations Security Program (abbreviated as OSC)”, “24 Hourly advance cargo notification (referred to as ACD or AMR)” and “smart and safe trade channel” (referred to as SST) promoted by international civil organizations and many other safety protection measures. At present, a total of 38 ports in 18 countries around the world participate in the container safety plan.
In this environment, my country’s Port S uses RFID radio frequency technology, hoping to build a complete port-to-port secure channel, and become one of the international ports that join CSI with the fastest pace.
The four endpoints of a safe journey
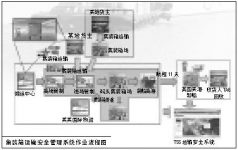
The work content of the establishment of the CTPAT/SST system includes the introduction of the TSS (Transportation Security System) transportation safety management system, the establishment of RFID wireless radio frequency hardware, and the conversion of container field operation information provided by a certain unit to the external interface information of the TSS system. Its integration.
There are 300 containers in Port S that need to be loaded with RFID electronic tags. Containers are implemented from the cargo owner’s end and the container warehousing end with two operating modes with different characteristics. All the implemented containers are loaded at the port of S port.
The system is divided into two operation modes. One is to install RFID electronic tags on the export containers of the storage and transportation center, and the other is to install RFID electronic tags directly on the export containers of the cargo owner. All containers are transported by container trucks to the container yard of Port S. The following descriptions are based on operating characteristics.
1.Storage and transportation center and cargo owner’s end
The container operation of the storage and transportation center is mainly for the cargo owner to transport the goods to the storage and transportation center. After the export goods are approved and released by the customs, the storage and transportation center will carry out the cargo packing operation and install electronic label locks on the containers that have completed the packing operation. , And start the RFID electronic tag lock with the handheld terminal.
The operating mode at the cargo owner’s side is that after the cargo owner completes the export container packing operation, he installs an RFID electronic tag on the container and activates the RFID electronic tag with a handheld terminal, and then the container transport company transports the container to the terminal container yard. After the container enters the port, the system records the arrival time of the container and the security status of the container in real time through the RFID reader, and transmits the information to the TSS system in real time.
The storage and transportation center and the cargo owner activate the RFID electronic tags with the handheld terminal and transmit the container information to the TSS system through Wireless LAN or GPRS transmission. At the same time, they must log in to the pre-set account through the network and maintain and test on the TSS system. The manifest information of the container.
2.Container loading port
After the container arrival information is confirmed by the port management system of the terminal container yard, the container monitoring operation of the container yard will be monitored by the RFID monitoring reader. When the container starts loading operations, the RFID reader installed on the bridge crane beside the ship records the time of the container loading operation, and at the same time confirms the safety status of the container to ensure that the container loaded on the ship is in the “Secured” state. After that, the container ship will go to a foreign port via the sea route.
3.Container unloading port
After the container ship arrives at the port and docks at the port, the container is transferred to the container yard by the unloading bridge crane. The local security operator uses a handheld terminal to obtain the information of the container’s arrival at the port, and then the security operator uses the handheld terminal Disable the function of the RFID electronic tag, and finally cut the RFID electronic tag from the container with a tool.
4.Consignee end
Some containers are delivered directly to the location of the local consignee. After receiving the container, the consignee directly cuts off the bolts of the electronic tag to complete the safe journey of the container.
Three-level definition of safe journey
1.Storage and Transportation Center
Above the export control lane in the container storage yard, a set of RFID triggers and RFID readers are set up. When the container equipped with RFID electronic tags leaves the yard, the RFID reader will read the container information through a wired network. The information is transmitted to the on-site work server in the information room of the container warehouse office building, and the on-site work server transmits the information back to the TSS system to start the container safety monitoring of land transportation.
2.Terminal container yard
A total of two sets of RFID readers are installed in the terminal container yard, namely the RFID arrival reader in the control center and the RFID monitoring reader in the container yard.
The RFID arrival reader installed in the port control center can actively read the arrival information of containers equipped with RFID electronic tags. In conjunction with the existing facilities on site, the reader is installed on an independent light pole at a height of about 5 meters above the ground. The range is 9 meters.
The RFID monitoring reader in the container yard cooperates with the straddle carrier in the yard and is respectively installed on the four units of RT1, RT4, RT5, and RT8, so as to monitor the safety status of the containers equipped with RFID electronic tags in the port.
The RFID reader transmits the read container information to the on-site work server in the information room of the office building through the port’s own optical fiber network, and the on-site work server transmits the information back to the TSS system to initiate the safety monitoring of the container for sea transportation.
3.Security status data analysis
The TSS system monitors the security status of containers with container security alarm information, which can be classified as “Tamper” (severe), “Suspect” (medium), and “Alert” according to the severity of its impact on container security. ) Three levels. If the “Tamper” message appears in the TSS system, the disposal method must be that the authorized personnel of the system directly check the container through the handheld terminal before reaching the container with the electronic tag. After confirming that the container has no abnormality, the container can be restored. Safe state. If the “Suspect” message appears in the TSS system, the disposal method can verify the cause of the container’s security alarm information through the web interface of the TSS system, and then restore the safe state of the container. If the “Alert” message appears in the TSS system, basically “Alert” will not endanger the safety of the container. The system manager must understand the reason for the activation of the message and coordinate with the relevant cooperating units to avoid similar incidents from happening again.
The 9/11 incident in the United States was an unwarned crisis and a hidden turning point. After the United States proposes CSI, it will break the traditional shipping environment and mechanism of shipping containers in the past, and the government’s contingency measures will directly affect the future container throughput ranking of Port S. Other potential ports in Asia also want to seize this opportunity. The completion of this project in Port S is expected to formally establish a safe trade channel in Asia that meets the high standards of the Container Security Program (CSI) and the US Customs Trading Partner Counter-Terrorism Program (CTPAT). The innate advantages of the geographical location and port conditions of Port S have brought about the past economic miracle of a certain city; future policies and judgments will influence the continuation cycle of a certain city’s miracle in the future.

Overseas case
South Korean government strengthens international container management
The South Korean government has been planning the “smart container” project throughout the summer last year, which was officially launched and funded in December 2004. The goal of this project called “RFID Maritime Logistics” is to enhance the efficiency and safety of international trade between South Korea and other countries through RFID technology and solutions. Smart containers equipped with smart tags and sensor equipment produced by Savi are transported from Busan Port to major ports on the west coast of the United States and Europe under the supervision of Savi’s Transportation Security System (TSS) software.
Case study
Significance of port application RFID
Approximately 5.8 billion tons of cargo, that is, 80% of the global trade volume is carried out by sea, but only about 5% of the containers will be inspected. How to protect the safety of 11 million containers transported by 46,000 sea vessels to 4,000 ports around the world? How to ensure the safety of goods and accurately control the inventory? The trick to solving all the above-mentioned problems and challenges is to make the company know everything about its supply chain. Therefore, RFID has attracted much attention in the port industry.
Problems in port applications
·Lack of uniform standards
The biggest obstacle currently restricting the development of RFID is technical standards. There are currently 117 RFID protocol standards for data exchange in the world. Excessive and excessive agreements have led to inconsistent terminology and restricted the perfection of standards in practice. More importantly, there is currently a lack of an authoritative and unified standard that the world will abide by. Related to the formulation of the standard is the dispute over the frequency band used by RFID.
·Price is still a key factor limiting the scale of RFID development
Compared with the past two years, the price of RFID tags has been greatly reduced. Nevertheless, the price of RFID tags and reading devices is still too high for large-scale promotion. And price and scale are a contradiction. Manufacturers hope to reduce costs by expanding their scale, while more users are waiting for prices to decrease before entering.
The composition of the industry chain
The RFID industry chain consists of chip design and manufacturing technology, antenna design and manufacturing technology, chip packaging technology, reading and writing equipment development and production technology, system integration and data management software platform, and application system development. In recent years, the RFID application of the customs will be widely optimistic.
[ad_2]



