A comprehensive interpretation of NFC technology, so many application areas?
[ad_1]
As the forefront of the Internet of Things information collection, intelligent identification plays a fundamental role in the realization of the Internet of Things. NFC is not only in the payment field, but also in the non-payment field with the rise of the cloud concept. People’s lives have brought great convenience, with tentacles extending to every corner of our lives.
1. Overview of NFC technology
The full name of NFC in English is Near Field Communication, short-range wireless communication. It is a wireless technology initiated by NXP and jointly promoted by well-known manufacturers such as Nokia and Sony. NFC evolved from the integration of non-contact radio frequency identification (RFID) and interconnection technologies, combining inductive card readers on a single chip The sensor, inductive card and point-to-point function can identify and exchange data with compatible devices within a short distance.
This technology was originally just a simple merger of RFID technology and network technology, and now it has evolved into a short-range wireless communication technology, and its development trend is quite rapid. NFC has the characteristics of two-way connection and recognition. It works in the 13.56MHz frequency range and has an operating distance of close to 10 cm. NFC technology promotes standardization under the framework of ISO 18092, ECMA 340 and ETSI TS 102 190, and is also compatible with the widely used ISO 14443 Type-A, B and Felica standard contactless smart cards.
2. NFC has three working modes:
•Card Emulation mode: mobile payment, ticket, channel control, toll station, parking card, etc.
•Peer-to-Peer communication mode: data exchange: fast, easy and convenient to realize the establishment, configuration and connection of equipment
• Reader mode: content distribution, information access, advertising
3. The latest NXP NFC mobile device payment solution
1. Overview of NXP NFC chip
NXP NFC chips for PN66T and PN548C2 comply with the latest NFC specifications formulated by the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI), which can provide mobile phone manufacturers and mobile operators with a fully compatible platform for launching next-generation NFC devices and services. PN66T is fully compatible with all currently released NFC specifications that connect the SIM card and the host controller interface (HCI) through the Single Wire Protocol (SWP).
In addition, NXP works closely with leading SIM card manufacturers such as Gemalto, Oberthur Technologies and Giesecke & Devrient to ensure the interoperability of SWP interfaces including MIFARE technology. PN66T is PN548C2 plus NXP’s SMART MX2 security module. The PN66T hardware pair is fully compatible with PN548C2 BGA version PIN. PN66T is the latest generation NFC full terminal solution chip.
2. Features of PN66T:
• PN66T is the only mobile application product among the security components that has passed the universal standard EAL6+ certification, providing the highest level of data protection and encryption for end users, bank card issuers and smartphone manufacturers.
• PN66T has passed EMVCo (Europay, MasterCard and Visa) certification to ensure that secure payment services can be widely deployed globally, while also ensuring interoperability with traditional and future payment infrastructures.
• PN66T can realize the integrated deployment of many applications related to transactions, including mobile payment, access control, public transportation and identity verification.
3. The following advantages of PN66T and PN548C2:
• ARM cortex M0 core
• Flexible host interface from the NFC Forum meets National Standards (NCI)
• Dual SWP interface
• Optional platform-independent software stack
• Provide GPIO PORT for external unit control
• Wider voltage connection support.
• Support safety unit control interface
• Support the latest RF protocol standards (ISO18000-3, Kovio tags, HID iClass tags)
• Support multiple RF interface protocols: ISO14443A/B, ISO15693, MIFARE, Felica.
4. Features of SmartMX P61N1M3:
• SmartMX2
• C090NV
• SPI
• JavaCard GP 2.2 OS
• MIFARE
• DESFIRE
• CC EAL6+ /EMVCO
• Multiple Applets
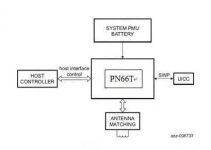
5. NFC PN66T/ PN548C2 hardware circuit block diagram:

The NFC electronic wallet function uses mobile devices such as mobile phones as the transaction platform. The two parts, the PN66T NFC controller and the built-in security module, realize the mobile device payment and data exchange functions.
NFC-SWP software architecture block diagram:
Standardize the software architecture of NFC-SWP terminals and the functions of each unit

NFC and SIM card security module interface circuit, NFC IC with SWP one-line interface can realize data communication with NFC-SIM card, the current NFC mobile payment solution led by China Mobile.
Fourth, the advantages and disadvantages of NFC payment
●Advantages: Compared with the traditional short-distance communication payment, NFC payment has the advantages of security and faster connection establishment. The payment distance is less than 10 cm, which can avoid mutual interference between devices. In addition, the time to establish a connection is less than 0.1 second, which better guarantees the security of user payment and has a lower cost.
● Disadvantages: The popularization of NFC requires a large number of hardware devices to support, and the premise for mobile phone manufacturers and financial institutions to deploy a large number of hardware devices is to have a large enough market. In addition, this payment method is also faced with issues such as who’s standard to use, what to do if the user’s mobile phone is lost, and how to set the payment limit.
Five, NFC technology applications and scenarios
NFC devices can be used as contactless smart cards, smart card reader terminals, and device-to-device data transmission links. It has a wide range of applications, and NFC applications can be divided into four basic types. For applications such as access control or traffic/event ticket checking, users only need to bring the device storing the ticket or access code close to the reader. It can also be used for simple data capture applications, such as reading URLs from smart tags on posters.
Contact and confirm. In applications such as mobile payment, the user must enter a password to confirm the transaction, or only accept the transaction.
Contact, connect. Connect two NFC-enabled devices to perform peer-to-peer network data transmission, such as downloading music, exchanging images, or synchronizing contacts.
Contact, explore. NFC devices may provide more than one function. Consumers can explore and understand the functions of the device and find out the potential functions and services of the NFC device.
1. NFC is used for payment and ticket purchase, for example: China Merchants Bank’s Yixantong, etc.
2. NFC for smart media. For phones equipped with NFC, using its reader/writer function, users only need to touch smart media to get rich information or download related content.
3. NFC is used for electronic tickets. Electronic tickets are access rights stored electronically. Consumers can purchase this right to gain admission to entertainment venues.
4. NFC is used for connection and as a wireless activation device. Consumers want wireless connection to be simple and convenient, but the convenience and mobility promised to consumers have not yet been fulfilled.
Due to the high security of NFC payment, this technology is considered by the industry to have great development prospects in fields such as mobile payment. As a mature payment technology, NFC has been applied in many fields. According to industry insiders, once the industry standards for mobile payment are unified, NFC payment is likely to become the mainstream mobile payment method in the future.
[ad_2]