Optimization and Practice of Tibet Mobile’s TD-SCDMA Network
[ad_1]
1 Tibet Mobile TD-SCDMA network coverage
At present, China Mobile Tibet Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as Tibet Mobile) has 143 TD-SCDMA macro stations and 79 indoor base stations. The coverage area of Lhasa is 70 km2, and the area coverage is more than 90% of the 2G network in the same area. Covering Lhasa’s urban areas, suburbs, railway stations, and airports, mainly transportation routes, important tourist attractions, suburban population centers, industrial and economic development zones, leisure resorts, party, government and military agencies, hotels with 3 stars and above, Shopping malls, transportation hubs. The Nyingchi area mainly covers the urban area of Nyingchi and Nyingchi Airport.
2 The challenge of the plateau environment to network optimization
The Qinghai-Tibet Plateau is the highest plateau in the world, with an average altitude of more than 4,000 m. It is known as the “Roof of the World” and the “Third Pole”. Affected by the peculiar and diverse plateau topography, landforms, high-altitude air circulation and weather factors, the climate in Tibet is complex and diverse. The most obvious feature is the large temperature difference between day and night. Many people do not adapt to Tibet’s climate because of altitude sickness. It’s because of its dryness.
The influence of Tibet’s environment on network optimization can be divided into two aspects: firstly, environmental factors, including dry climate, large temperature difference between day and night, thin oxygen, and strong ultraviolet rays; secondly, human factors, including the army, more party and government agencies, and language Difficulty in communication, differences in living habits and culture, seasonal changes in the number of users, PS users are more concentrated.
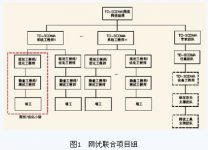
3 Organization and implementation of Tibet Mobile’s TD-SCDMA network optimization
In response to the plateau environment, Tibet Mobile decided to gather resources from all parties and set up a joint network optimization project team, as shown in Figure 1, including network optimization center personnel, branch maintenance personnel, vendor optimization personnel, vendor maintenance personnel, 2G optimization personnel, etc. See Table 1 for the division of labor of each person in the group. In response to the problems in network optimization, Tibet Mobile has adopted a thematic optimization strategy.
3.1 Indoor distribution optimization
The interference of indoor distributed sites is mainly caused by indoor equipment, which is manifested as high noise floor, difficult to make calls and low download speeds for occupying indoor distributed sites. For example, when testing the PS service in the lobby on the first floor of a certain unit, the signal strength was around -52 dBm, and the FTP download rate was low, with an average rate of 546.8 kbit/s. However, in the indoor distribution system room, the equipment of the indoor distribution manufacturer was not connected. In this case, the download rate of the tested HSDPA is normally around 1.35 Mbit/s on average. The interference power was found to be about -90 dBm through LMT. It was found that the indoor distribution manufacturer of this site introduced dry amplifier. Due to the change of the time slot switching point during the long-term use of the dry amplifier, the dry amplifier caused the donor base station. In order to avoid interference, the problem of high noise floor has been improved after processing by indoor distribution manufacturers, and the download rate has returned to normal.

3.2 Drop call optimization
(1) Sorting out the relationship between neighboring areas of the entire network
The optimization of the neighboring cell relationship of a cell is an important task, especially in the TD-SCDMA network, the neighboring cell relationship is particularly important. Due to the fact that the actual site opening and planning data are constantly changing during the project period, it was discovered through the neighbor cell tool that the neighboring cells added by some cells have nothing to do with them, and these neighboring cells need to be deleted. In view of the current terminal’s ability to demodulate neighboring cells, too many neighboring relationships will result in inaccurate demodulation of neighboring cells by mobile phones and loss of the best neighboring cells. Therefore, the neighbor cell optimization of TD-SCDMA network is a fine optimization. process. Through drive testing, TOP-N cell analysis and optimization, and legal parameter inspection of the entire network, we have added and deleted a large number of neighbor relationships, which has played a positive role in the stability of network indicators and the improvement of network quality.
⑵Analysis of interference dropped calls
Lhasa TD-SCDMA network has fewer outdoor frequency points. In order to effectively avoid the influence of the same frequency phenomenon, scrambling code planning is very important. Because the scrambling code planning of TD-SCDMA is very cumbersome, and the scrambling code automatically generated by the software is not very perfect. This needs to be discovered in a large number of drive tests and gradually improved.
The existing network has the same frequency and same scrambling code group, the interference is very serious, and it is easy to cause the same frequency to falsely high and cause call drops. We used various means to modify 15 frequency points and 42 scrambling codes to avoid the interference caused by the same frequency and the same scrambling code group to the greatest extent.
⑶ 3G/2G interoperability dropped calls
At present, some terminals have problems with the synchronization with the GSM cell when switching from 3G to 2G, which may easily cause the failure of 2G/3G handover. Therefore, it is necessary to avoid the mobile phone from initiating a different system handover. Switch to the GSM network only when the wireless environment is poor. For this reason, the following measures and principles have been adopted: For TD-SCDMA network cells that do not need to switch to the GSM network, do not initiate a different system handover as much as possible, and the 3A threshold needs to be lowered. (Reduced from -90 dBm to -95 dBm); For areas with severely weak coverage and fast fading of the TD-SCDMA signal, initiate a different system handover as soon as possible, and switch to the GSM network in advance to avoid the need to increase 3A handover due to weak coverage. Threshold value (increased from -90 dBm to -85 dBm).
⑷ TOP-N handling of abnormal call drop
The processing of abnormal call drop is mainly to deal with the call drop caused by non-wireless side in the process of analyzing the TOP-N cell every day.

3.3 Access optimization
After analyzing the reasons for the failure of RRC establishment on the entire Lhasa network in September and October 2009, it is found that the largest proportion of the reasons for the failure of RRC establishment is “no reply” (93.7%), that is, the network side sends an RRC establishment letter to the terminal. Reception timed out after the order, followed by “congestion” (6.3%), which is caused by network resource congestion. The solution to the above problems is as follows.
⑴Check the same frequency and same interference cell in the whole network
The terminal identifies the cell by the cell frequency and scrambling code. If two cells with the same frequency and the same interference are close, it may cause confusion in the terminal identification of the cell, resulting in the initial access of the terminal, that is, the failure of RRC establishment. The specific manifestation is that the terminal may be in After receiving the RRC establishment information of cell A, the information feedback is given on cell B, and the network management statistics is “no reply”. Therefore, it is necessary to investigate and analyze the same-frequency and co-interference cells of the entire network to ensure that there is no closer distance (2 Within 000 m), the same frequency and co-scrambling cell can eliminate the influence of the same frequency and co-scrambling code cell on the establishment of RRC.
⑵ Optimization of RRC connection related parameters
The optimization of RRC timer parameters such as T312 includes two parts: one is the modification of timer related parameters; the other is the improvement of SIRTarget. Due to the difference in understanding between the UE side and the system side, some UEs will add T300 to the T312 timer of the initial synchronization after receiving the “RRC CONNECTION SETUP” as the waiting time for the next retransmission, which exceeds the internal The length of the timing for the RNC to wait for retransmission causes the RRC connection failure that should be recorded once to be recorded as multiple times (up to 4 times or the successful recording of the RRC connection as a failure), so the parameters of the RRC timer need to be optimized.
⑶Troubleshooting site faults affecting RRC connection
In the third phase of the Lhasa TD-SCDMA network construction, some indoor distributed sites have introduced active dry-release antenna feed systems, and the dry-release system can easily distort the signal output by the RRU, resulting in abnormal terminal access.
[ad_2]





