Application of active RFID in hospital and medical industry
[ad_1]
In the dynamic working environment of hospitals or other medical institutions, real-time and accurate positioning of important assets and personnel is often the key to the success or failure of diagnosis and treatment services. There are many examples in this regard, such as not knowing where the nearest clean infusion pump is, or when you need the most suitable doctor, but you don’t know where it is in the hospital (it’s not that doctors always carry mobile phones), etc. These important assets “Low visibility” often leads to a serious waste of time and resources. Specifically, a medical institution that lacks a highly clear asset and personnel management system will cause losses in the following areas:
Equipment loss: The annual loss of portable equipment is usually close to 20% due to misplacement, theft, etc.
Nursing staff, material supply and management, and clinicians need to spend a lot of energy every day to find the appropriate medical equipment needed
Delays in patient services: When the required doctors or equipment cannot be found in time, other staff and wards will become idle and cause the loss of opportunity to rescue patients
Failure to quickly find suitable equipment will result in the hospital having to stock too many similar materials or temporarily lease additional equipment, most of which are either idle or inefficient in utilization
For those equipment that cannot be accurately located, preventive maintenance measures are often very late, putting them at the risk of expired use or overuse
Some patients leave the ward or enter other areas without permission, causing disease threats to themselves and others
In response to the above-mentioned needs objectively existing in the medical industry, the core concept of a medical tracking solution based on active RFID technology is “advanced technology, reliable products, and a platform for medical visualization.” Based on the deep foundation of active RFID technology, Shanghai Xiupai provides complete visualization solutions for assets, patients, and staff for medical institutions at home and abroad, so as to help them provide daily operating efficiency, reduce operating costs, and improve medical service levels. In addition, the products and services provided by Shanghai Xiupai Company conform to the relevant national and industry standards. These products and services can be seamlessly connected in the basic application system of medical institutions, and can be obtained without changing the basic structure. Quick deployment and installation.
application solution
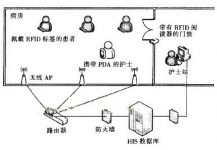
In actual use, the internal structure of the application system will be ever-changing, but the deployment method of the RFID system as a front-end data collection tool is similar: as shown in the figure below, electronic tags are generally attached to assets, objects, or persons in a variety of ways. Unique identification of identity, and may collect other relevant data (such as blood pressure, temperature, etc.) and upload it to the reader. The reader is transmitted to the background host system through wired or wireless means. After specific program analysis, relevant useful information can be parsed to stimulate the application system Follow-up control mechanism.

(1) Electronic label
In the medical industry, electronic tags are mainly used in the identification and monitoring of assets, personnel and medical items. In terms of item identification, it is mainly at the level of important medical assets and medical item packaging boxes, and the single items will still be based on barcodes. In order to realize the real-time monitoring function, the current personnel tags and most asset tags in the hospital are mainly active. In order to better demonstrate the outstanding advantages of active technology, we will use active technology and passive technology in possible application requirements. Let’s make a comparison:
In terms of wearing objects, there are mainly hospital staff tags, patient tags, and asset tags.
1. Staff tag
The employee tag is generally card-shaped and worn on the neck. It can be used as an access control by integrating high-frequency or low-frequency chips according to actual needs, that is, the dual-frequency card we usually use. In some occasions with higher security levels, biometric technologies such as fingerprints and iris can be set up to strictly manage the entry and exit of personnel.
2. Patient label
The patient tag is generally in the shape of a wristband, which can be conveniently worn on the patient’s wrist. The entire label adopts anti-tear technology, if it is forcibly damaged, it can take the initiative to report to the police. Different patient categories need to develop different label packaging styles: ordinary patients only need ordinary wristband labels, which are only used for identification purposes; some special patients also need to integrate pulse and body temperature sensors. These data will be used for hospitals to carry out related medical treatment. The service provides help; all tags can also have an alarm function, add 1-2 emergency buttons on the surface of the tag, and you can call for help at any time in case of emergencies. In addition, in the application of newborn mother-to-child identification, baby labels will adopt special clean packaging measures.
3. Asset tags
Asset tags often come in a variety of packaging styles, most of which are strip-shaped tags, which are attached to medical equipment or article packaging. Asset tags will vary according to different uses. General medical devices only need to be bound with ordinary tags for identification purposes only. Some assets that often need to be repeatedly searched and located need to be bound to tags with flashing functions with LED lights. Provide visual assistance in finding specific assets.
Some items that are more “fragile” to the storage environment, such as vaccines, plasma, etc., require active tags for real-time monitoring and continuous collection of their temperature and humidity characteristics. If a certain feature exceeds the preset range, the active tag needs to make a special identification or alarm for the batch of items. Therefore, asset tags of such materials need to integrate sensor functions.
(2) Reader
According to the different ways of data interaction with the background database, readers (also called information collectors) can be divided into base station readers and handheld readers.
Base station type readers are usually distributed in some specific areas, such as corridors, doorways, aisles, etc., with fixed locations as the basis for address information during background data analysis. The base station reader is connected to the antenna, searches for various data actively sent by the tag in the target area and transmits it to the background server through wired or wireless means. The reader and the antenna can be integrated into one, or the antenna can be externally installed according to the actual situation to adapt to the signal coverage in a specific environment.
Compared with base station readers, handheld readers are more flexible to use, and can be carried by staff or bound to a mobile asset as a data forwarding station. Medical staff often need to inspect the patients in their respective areas to ensure that the patients are in a normal state of care. In addition, it is very convenient to use a handheld reader to search for some important items in a large and spacious area (such as a warehouse).
(3) Application system
The hospital information system (HIS) that integrates RFID technology will significantly improve the efficiency of hospital asset operation and the level of medical services. Judging from the current domestic situation, the following applications are relatively mature:
1. Medical monitoring
In many hospitals, there are a large number of emergency patients every day, especially in some large emergency centers. When a mass accident occurs, a large number of wounded will rush into the hospital. At this time, every minute and second is extremely precious, and it cannot tolerate the slightest. error. However, the condition of each wounded person is very similar, which is easy to confuse, and the traditional manual registration is not only slow and error rate is high, it is impossible to register normally for critically ill patients. In order to quickly confirm the identity of all patients, complete the admission registration and carry out step-by-step follow-up emergency work, the medical department urgently needs an automatic identification system that can provide real-time identification and condition information of the wounded. Only in this way can the hospital staff be efficient and effective. Carry out rescue work accurately and orderly.
The specific application method is to wear a wrist tag for each patient. When the patient receives a diagnosis and treatment, the medical staff only needs to scan the tag information with a handheld reader to know the first-aid items that need to be performed, such as whether infusion is needed, the name of the drug injected, and the Specifications, treatment items that have been performed, whether there are adverse reactions, etc., all data will be displayed in front of medical staff in less than a second, so that they can check medical procedures and drug specifications and quantities. The patient tag can also store all treatment processes and medication injection records. Because RFID technology provides a reliable, efficient, and economical method of information storage and inspection, the hospital’s rescue of emergency patients will not be delayed, and there will be no misidentification of the wounded and medical accidents. In addition, in the case of transfer for treatment, the patient’s data, including medical history, type of injury, proposed treatment method, treatment location, treatment status, etc., can be made into a new label and sent to the next treatment hospital. Because the input of all these information can be completed at one time by reading the radio frequency tag, unnecessary manual input is reduced and human errors are avoided.
2. Newborn identification management application
Newborn babies have similar characteristics and lack of understanding and expression skills. If they are not effectively labeled, they will often cause misidentification, and the result will have an irreparable and huge impact on all parties. Therefore, the identification of newborns must realize the function of patient identification. At the same time, mother and baby are matched. Separate identification of infants has management loopholes and cannot prevent malicious artificial replacement. Therefore, it is best to identify both the newborn baby and its mother, and use the same code to connect the biological mother and child. Infant care is carried out between the hospital staff and the mother, and during temporary transfers, both parties should conduct inspections at the same time to ensure the correct mother-child pairing.
After the baby is born, the mother and baby should be identified in the delivery room immediately, and the mother and the baby should be transferred out of the delivery room before other patients are sent to the delivery room. The delivery room must be prepared: two non-transferable RFID tags, one for the mother and one for the newborn. The information on the label should be the same, including the mother’s full name and label number, the baby’s gender, the date and time of birth, and what other hospitals think can clearly match the biological mother and child. A device capable of clearly taking baby’s footprints and mother’s fingerprints. Appropriate forms to record relevant information and footprint data. In addition to marking, it can also fully guarantee the safety of the marked object. When someone tries to steal a newborn baby out of a hospital ward, the RFID identification device can detect it in real time and issue an alarm, and notify the security staff of the latest location of the stolen baby.
3. Application for tracking and locating important hospital assets and materials
Some large medical centers generally have huge storage bases for important medical assets and medical items. Hospital logistics personnel need to find suitable items from thousands of materials according to orders every day. The outer packaging of medical articles is usually similar, but the purpose of the inner articles is quite different. Therefore, the hospital logistics department usually needs to spend a lot of manpower and material resources to find and check these articles. Moreover, the storage of medical items must be carried out in accordance with strict storage specifications. Misplacement incidents often occur when warehouse adjustments or items are moved, causing extensive damage to items or serious drug accidents after they are circulated to the market.
The use of RFID tags with LED lights will make this search and verification process extremely fast and accurate, and the tags themselves can carry item-related information, which can increase the speed of the entire verification process by about 20 times. In addition, if some items are misplaced, the system can remind the warehouse manager to adjust the storage location through flashing LED lights.
4. Hospital contact history tracking control application
Combining the infectious disease epidemic tracking control system and the medical hospital contact history RFID tracking control system, epidemic prevention and government units can instantly and accurately grasp the dynamic information of the entire processing process, thereby preventing the recurrence of nosocomial infection control problems similar to the atypical pneumonia epidemic .
Home quarantine and infectious waste generated in medical hospitals, at the same time that the health unit issues the home quarantine notice, the global positioning system is used to track and control the transportation of special garbage trucks throughout the whole process, and the relevant units can instantly grasp the whereabouts of the garbage trucks, and when abnormalities occur It can be corrected immediately to prevent spreading. Most importantly, transparent dynamic tracking information can eliminate people’s doubts.
5. Management application of pharmaceutical supply chain
In the medical field, a large number of errors in prescriptions, drug delivery, and medication take place every year, leading to many medical accidents, a large number of lost hours and legal proceedings. According to statistics, the losses in these areas are as high as 75 billion US dollars each year. Improved drug tracking methods may help hospitals save costs and curb the proliferation of counterfeit and substandard drugs, which currently account for 10% of the global drug market.
Smart tags, or radio frequency identification (RFID)-through the use of such tags, physical objects can be identified at any point in the manufacturing and distribution process. RFID will play a key role in eliminating the usually slow and inefficient sales and distribution processes. It will help pharmaceutical companies prepare for the future and enable them to produce a wider variety of more complex products in small batches. . It can also monitor drugs at all nodes in the supply chain, including accurate target batch delivery, thereby helping pharmaceutical companies meet increasing regulatory requirements.
Judging from the above application situation, the application of RFID in the medical industry has surpassed the concept of fast search and location. The hospital HIS system integrating RFID technology will integrate all the assets of the hospital into an organic whole, providing patients with fast, efficient and reliable service.
Program features
Long distance: It can be recognized within 80 meters, and there is no need to manually approach and swipe the card or pass in a designated area to recognize, and realize automatic recognition.
Large flow: extremely high anti-collision performance, adopting a variety of anti-collision schemes, which can support more than 200 people or objects entering and exiting at the same time.
Supports high-speed mobile reading, and the moving speed of the target person/item can reach 200 km/h.
Two-way high-speed data exchange can be realized between the identification card and the card reader.
High reliability, working temperature -40℃~85℃, waterproof and shockproof.
High anti-interference: There are no special requirements for various interference sources on site, and the installation is convenient and simple.
There is no need to apply for and pay for the ISM microwave frequency band that is open worldwide.
Ultra-low power consumption: safer and healthier for the human body.
Required product introduction
1. Active electronic label card
2. Reader (card reader)
3. Handheld reader
Attachment: Introduction to the application status of RFID in the medical industry in various countries
All over the world, medical disputes have set off a peak in the past few years. According to a survey by the World Health Organization, more than 10% of the drugs in circulation worldwide are counterfeit drugs, and more than 40% in undeveloped countries. The global amount of counterfeit drugs exceeds 320 billion. In addition, the problem of mis-dispensing drugs also plagues the medical industry. The United States causes millions of dollars in losses each year, and the United Kingdom causes 72,000 deaths each year. The number of medical appraisal commissions from its health department in Taiwan has changed from In 1987, the number of 147 cases rose all the way, and by 2001 there were 406 cases. In 2005, the number remained high. The main reason is that the highest proportion was 24% of malmedical problems, followed by surgery-related problems, accounting for 15%. Obviously, the solution to the problem of drug identification is urgent.
As far as the application of RFID in the medical field is concerned, drug identification has already accounted for the largest proportion of applications. Drug control in medical hospitals has the so-called “three readings and five pairs” method. For the confirmation that the location changes, the five pairs are compared with five data items such as patient, time, drug name, dosage, and route. These five pairs of three readings can be used to improve the accuracy of RFID.
For example, after a doctor writes a prescription, the prescription information is loaded on the RFID tag and handed over to the patient to collect the medicine. On the other hand, the doctor’s prescription data will also be transmitted to the pharmacy at the same time. When the pharmacist dispenses the medicine, the RFID system on the medicine box will Proactively remind the medicine whether the medicine is correct or not. When the medicine is prepared, the RFID system on the counter will again compare whether the RFID label data of the medicine recipient is consistent with the medicine.
In addition, in the prevention and control of counterfeit drugs, in addition to barcodes that have been standardized on drug packaging, the use of RFID as a history of drug production has also been designated by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) as a plan to combat counterfeit drugs, allowing the source and circulation of drugs Channels have been able to verify its legitimacy, and production resumes have been applied in the food industry, so it is not difficult to transfer to the medical industry.
RFID is also used as the control of special drugs. For some drugs, the reader on the pill box has its limitations. The approved label must be read before the pill box can be opened. The drug cart used by nurses to patrol the room, An RFID system has also been built. With RFID, the nurses’ medication use can be controlled and recorded. The patient’s medication time will also be recorded in the RFID system, which will be used as a basis for future medical treatment or judgment evidence in case of disputes.
In addition to the establishment of RFID systems in hospitals to control drugs, it also extends to other applications, such as asset management, waste tracking, identification of operating personnel, etc. These applications have been introduced before, and let’s look at cases in other countries. Possible applications of RFID in the medical industry.
In terms of application classification, drug control is still the main medical application of RFID in various countries, including South Korea, India, Italy, the United States, and the United Kingdom. South Korea is mainly used to combat counterfeit drugs. Its Unimed Pharma uses RFID tags. It is expected that 1 million labels will be used each year. The RFID anti-counterfeiting drug project in South Korea has been effective since it was launched in September 2004. In 8 weeks, 13,500 drugs were shipped, Tracking and tracing, and then we will learn from the project and expand the application.
India’s RFID drug control was born in response to Wal-Mart’s requirements. The leader is Ranbaxy PharmaceuTIcal, India’s second largest pharmaceutical company, which has built RFID tags on anesthetics and analgesics and used RFID to check the preservation of medicines. When the expiration date is approaching, the reader will warn the manager and send the goods back to the manufacturer for destruction. Next, Ranbaxy PharmaceuTIcal is expected to integrate ERP, WMS and other systems.
The Spallanzani Hospital in Italy implanted the RFID chip into the patient’s body. The system is manufactured by VeriChip for reader manufacturing and system integration. The chip is 11 mm in size and uses a frequency band of 125-135KHz. It is implanted into the patient’s arm fat layer. After that, it can be used for 20 years. The program is approved by the US FDA to grasp the patient’s medical records and medication status. When the patient has an emergency, the medical team can read the patient’s condition for diagnosis and treatment at the first time.
RFID is widely used in the medical industry in the United States. In addition to drug control, there are already application examples in the management of nurseries, the protection of elderly people with dementia, patients in the emergency room, the control of blood transfusion bags, and the management of assets. In addition, A special example is the process control of dentures and specific tooth molds. The American system integrator Dental@xUSA puts the RFID chip into the tooth mold. During the manufacturing process, the specifications of the gum will be recorded in the chip, and every part of the manufacturing process Steps such as the use of material, color, material batch number, manufacturing date, etc., will be written into the chip. In order to protect the patient, when the tooth mold is manufactured, the data in the chip will be blocked and transferred to the smart card held by the patient Or other written media, as long as the reader can read the data of the tooth model in the future, so that the quality of the denture and the tooth model can be effectively controlled.
Make good use of RFID to control the quality of blood transfusion and sample blood
France applies RFID to blood transfusion bags. In order to ensure that the quality is not prone to adverse changes, the blood must be kept at a certain temperature. Therefore, French Blood Agency Chemovigilance cooperated with the system manufacturer Technopuce. This application must combine the RFID chip with a temperature sensor. After the blood is drawn, the chip and sensor are attached to the blood bag. During transportation and storage, the temperature measured by the sensor will be recorded in the chip. The blood can be read through The device sees all the temperature records to judge the quality. In addition to France, KSW Microtec in Germany also uses the same system.
The United Kingdom also applies RFID to blood bags, but not for blood transfusion, but for identification. Portsmouth General Hospital attaches RFID tags to both blood samples and blood bags to reduce the incidence of accidental blood bag collection. It can reduce labor costs. Portsmouth General Hospital believes that if the United Kingdom can fully implement the mechanism, it can save 1 billion euros in annual costs. In addition, British public hospitals also use RFID systems for asset management, which will change the past official document and paper operations. , Use RFID to manage the rental of various equipment.
Japan uses RFID for observation of test tubes. Hitachi designs the antenna on a silicon chip. No additional antenna or chip is needed. After the RFID chip is set in the test tube, it is placed in the test tube box. The bottom of the box layer is equipped with a reader. This scans the test tube conditions and reduces the time for manual observation. This system is currently still in the experimental stage. The 96 test tubes have a reading time of 20 seconds, and 10 seconds will be the goal.
[ad_2]



