Application of RFID technology based on the Internet of Things vaccine safety traceability system
[ad_1]
According to a survey by the World Health Organization (WHO), more than 10% of drugs in circulation worldwide are counterfeit drugs, and more than 40% in developing countries. The global value of counterfeit drugs exceeds US$320 billion. All over the world, there are more and more medical disputes. Vaccines are vaccine-like preventive biological products used to prevent and control the occurrence and prevalence of infectious diseases. Due to the strengthening of the public’s immunization concept and the government’s policy guidance and support, my country has become the largest demand for vaccine products in the world And supply the market. However, after my country has experienced the Shanxi vaccine and Anhui vaccine incidents, more and more people hope that the vaccine can be controlled by the government and the CDC at all levels from production inspection, distribution, cold chain transportation, storage, sales, and injection. Conducted under prison camp. The anti-counterfeiting and anti-inferior measures of vaccines are urgent. In the prevention and control of counterfeit drugs, in addition to barcodes that have been standardized on drug packaging, the use of RFID (radio frequency identification) as a history of drug production has also been designated by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) as a crackdown. The counterfeit drug program allows the source and distribution channels of the drug to be verified for its legitimacy. The production history has already been applied in the food industry and it is not difficult to transfer to the medical industry. This article is the joint application of two-dimensional tags and RFID tags to realize the tracking and monitoring of the entire supply chain system of vaccines. The application of RFID technology in the Internet of Things can not only track the supply of vaccines in a complex, multi-step vaccine supply network, but also establish an efficient logistics information platform, optimize internal logistics supply and circulation processes, and improve factory production efficiency and products Quality, enhance the transparency of the vaccine supply chain, improve safety, speed up circulation, reduce logistics costs, and thereby improve the core competitiveness of the entire enterprise. Through RFID technology and Internet of Things technology, it can not only collect information on vaccine production, circulation, consumption and other links, realize full-process monitoring, establish a complete management service platform, and realize users’ traceability and inquiry of vaccine information, but also increase consumption. The safety of the vaccine obtained by the patient, effectively eliminates the harm caused by fake and inferior vaccines.
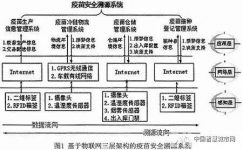
1 The composition and workflow of the vaccine safety traceability system based on the Internet of Things
The vaccine safety traceability system is mainly designed according to the four major links of vaccine production, logistics, warehousing, and inoculation. The structural design based on the three-tier architecture of the Internet of Things realizes “supervision informatization, logistics intelligence, convenient query, and source traceability” for vaccines. To ensure the safety of the vaccine supply chain, the system model is shown in Figure 1. At each stage of vaccine production, logistics, storage, and vaccination, the front-end data collection equipment is used to superimpose the information cycles of each link to form a comprehensive information document for specific vaccine products, including determining the vaccine information corresponding to the label, and Confirm the transferred photo information and all temperature and humidity information, etc. The information platform mainly includes a query and analysis module, a monitoring and traceability module, a data management module, and a logistics tracking module. The query and analysis module can provide information such as tag number, temperature, time and location.

2 Based on RFID technology in the vaccine safety traceability system of the Internet of Things
RFID is a communication technology that can identify specific targets and read and write related data through radio signals without the need to establish mechanical or optical contact between the identification system and specific targets. It can not only realize automatic recognition and fast reading and writing of the recognized object, but also recognize multiple tags and high-speed moving tags at the same time. It is quick and simple to operate and can work in various different harsh environments. It is currently the most advanced automatic Identification technology. The RFID system usually consists of a front-end radio frequency terminal and a back-end computer information management system. The radio frequency terminal is generally composed of a reader and a tag. The tag is used to identify various attribute information of the stored items; the reader is used for information collection, using radio frequency signals to identify the tag and communicate with the computer information system.
In the vaccine production information management system, a reader is used to collect the electronic tags affixed to the vaccine production packaging boxes, and the collected electronic tag information is stored in the computer information system. Through the Internet of Things technology, it can be tracked anywhere. Vaccine packaging boxes with RFID tags. Figure 2 shows the application of RFID in the vaccine production information management system.
In RFID technology, electronic tags are composed of coupling elements and chips, including microprocessors, E2PROM, and transceiver circuits, which store detailed product information. The electronic label of each product is unique, contains encryption logic, and cannot be modified or imitated. The RFID reader/writer emits a certain frequency radio frequency signal through the antenna. When the electronic tag enters the working range of the reader, due to electromagnetic induction, the antenna will generate an induced current, so that the electronic tag gains energy and is activated, thereby sending it to the reader Send the encoded information stored by itself. The reader decodes the received information and sends it to the back-end computer information management system. The computer judges the legitimacy of the label according to logical operations, and makes corresponding processing and control for different settings. The computer information management system is networked with various monitoring points through the Internet to set up an information platform, and the flow of products can be monitored and inquired through the information platform.
3 RFID design and application
At present, RFID technology has not yet issued a unified global standard, and the standards of each country are different, leading to the coexistence of multiple global standards. However, with the large-scale application of RFID in the global logistics industry, some RFID international standards formulated by ISO have been widely recognized by various industries around the world. This article uses passive RFID electronic tags, supports ISOI8000-6C (EPC GEN2) international standard protocol, the working frequency is between 860~960MHz, different working frequencies need to design different antennas, the following mainly introduces the RFID antenna design and application .
3.1 RFID antenna design
The most difficult part of RFID technology is the design of the antenna. The larger the antenna area does not mean the greater the induction intensity. In order to obtain the best measurement results, the size of the device must be known, and then the size of the antenna can be determined. The antenna is a sensitive object. The resistors, capacitors, inductors and other components used to make the antenna must have high precision, otherwise the antenna production may fail. The equivalent circuit of the antenna is shown in Figure 3.
The performance of the antenna is mainly related to the size of Rant and Lant. When calculating the quality factor Q of the antenna and the antenna tuning, the capacitance Cant of the coil can be ignored. The estimation formulas for several important parameters of the antenna are as follows:
Among them: L1 is the length of one turn (turn) of the wire loop; D1 is the diameter of the coil or the width of the conductor; N1 is the number of turns of the coil;
K is the coefficient of the antenna (1.07 for loops and 1.47 for squares).
The size of the antenna capacitance Cant is related to the size of the coil of the fabricated antenna, which can be directly measured with an instrument.
Quality factor:
(Generally it is recommended that Q=35 is more appropriate), where: ωR=2π·fR, fR is the working frequency of RFID, because the RFID of this system can work between 860~960MHz frequency, there will be conflicts with domestic mobile phone GSM900 applications, so use At that time, only 860-870MHz is used as the RFID operating frequency range.
According to the above two formulas of Q and ωR, the resistance of Rant resistance can be directly calculated.
3.2 Application of RFTD
In terms of the current development status of my country’s medical logistics, it is still impossible to use RFID tags to identify each vaccine to achieve vaccine tracking. Nowadays, two-dimensional bar codes are mostly used in combination with RFID tags, and two-dimensional bar codes are used to record vaccine information, so that each vaccine has a uniquely identified retail package, and then RFID electronic tags are used to identify the vaccine’s production logistics packaging and record the packaging box. The internal vaccine information can realize the traceability of the vaccine supply chain and the traceability function of the problem vaccine.
The application of RFID tags enables vaccine manufacturers to establish a unique EPC code in each packaging box. It is considered to be the only effective way to identify all objects. Although the EPC code can only record limited identification information, it has a corresponding back-end database. As a support, you can quickly query the information about each package of the vaccine. When the vaccine is out of the warehouse, the RFID electronic tag will be tracked to ensure that the logistics, storage, and vaccination of the vaccine can be monitored during the distribution process. RFID will curb the emergence of fake and inferior vaccines, prevent the loss of vaccines, accelerate the turnover of vaccine stocks, and increase the speed of vaccine recalls. The use of RFID technology in the logistics link can record the storage temperature, transportation vehicle, vehicle location and transportation time during the cold chain transportation of vaccines. The recorded information can be communicated with the logistics company’s local area through GPRS wireless communication or on-board wired network. The database communicates, so that the four major links of vaccine production, logistics, storage, and vaccination can be linked together, and the source of problems in each link can be found in time.
4 Problems to be solved when using RFID technology
The use of RFID technology brings many benefits to the vaccine safety traceability system, but there are still some problems in the entire system due to some internal reasons.
4.1 Cost issues
The price of RFID is an important reason that affects the large-scale application of its technology. RFID tags are relatively expensive, and if they are widely used like the current QR codes, the cost is bound to rise. For this reason, this system uses the advantage of RFID that can be tracked and located, and it is only used on vaccine packaging boxes and transportation vehicles. Therefore, if you want to promote RFID technology to various fields, only when its cost is further reduced can the advantages of its technology be truly realized.
4.2 Electromagnetic interference problem
As we all know, mobile phones can interfere with the work of many electronic devices, such as medical equipment and aircraft radars. The frequency range used by RFID is 860~960MHz, which conflicts with the frequency used by mobile phones, so it will also cause electromagnetic interference to electronic devices. This system uses 860~870MHz as the working frequency. According to a scientific research published in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA), RFID can cause serious electromagnetic interference to medical equipment. Researchers at the center tested 41 medical devices on 868MHz passive tags. In 123 tests (average of 3 tests per piece), a total of 34 electromagnetic interferences were recorded, causing some medical devices to stop working. This shows that RFID technology will produce the same radiation to electronic equipment as mobile phones, which is a potential problem. Although it will not prohibit the application of RFID technology to the medical industry, it should be paid attention to.
4.3 Standard formulation and implementation issues
RFID standards are roughly divided into four categories: technical standards (such as symbols, radio frequency identification technology, IC card standards, etc.), data content standards (such as coding formats, grammar standards, etc.), and consistency standards (such as printing quality, test specifications, etc.) And application standards (such as shipping labels, product packaging standards, etc.). At present, the frequency used by RFID technology is difficult to be unified, radio frequency identification readers and tag technologies cannot be integrated and applied, and an international standard acceptable to the world has not yet been formed, so it cannot be popularized. The RFID technology of the vaccine safety traceability system needs to be used in the four major links of production, logistics, warehousing, and inoculation. Only when the same frequency is used in the four links, the RFID hardware equipment and software system can be unified, and the entire system can be closely linked. The formation of a complete and safe vaccine industry chain is conducive to the promotion and use.
4.4 Information security and privacy issues
The RFID electronic tag adopts the database information sharing mode. The information in the database may be infected with viruses during the reading and writing, transmission process and Internet access, and there may be potential safety hazards of illegal reading and modification of tag information, and there is no need for RFID The data can be read by contact, and there may be disputes about infringement of personal privacy rights. Information security and privacy issues require government assistance. The government should increase investment in talents, policies, and funds in the research and production of RFID technology to solve the technical problems of RFID information security, and it can be increased through legislation. The protection of user privacy rights will gradually resolve information security and privacy issues.
5 Conclusion
The application of RFID technology introduced in this article in the vaccine safety traceability system, the entire supply chain adopts the same frequency range and forms the same standard system. Each vaccine packaging box has a unique EPC code to further strengthen vaccine anti-counterfeiting measures, use RFID technology to collect information in various links, grasp the flow information of the product in real time, and realize product quality traceability, to combat counterfeit and inferior vaccines , It is of great significance to protect the health of the people, and it also lays the foundation for further application in the pharmaceutical industry in the future, and even the comprehensive promotion of fast-moving consumer goods such as food, tobacco and alcohol.
[ad_2]



