Liverpool Hospital in Australia uses RFID technology to track blood products
[ad_1]
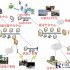
NSW Health Pathology, an Australian public pathology institution, is being used at Liverpool Hospital near SydneyRFIDThe technology tracks the entire process of blood products from storage in the freezer to use.

(SpaceCode smart refrigerator has a built-in RFID reader for identifying blood bag removal or return, operating time and personnel)
Liverpool Hospital has 23 operating rooms and 877 beds. NSW Health Pathology also operates a blood bank in the hospital to store blood and related products (plasma and coagulant).
In this solution, a SpaceCode smart refrigerator with lock is installed in the hospital operating room to identify the RFID blood products stored in it. The system can help ensure that blood is supplied to the correct patient.
Before performing a surgical operation that requires blood transfusion, the staff will take the required blood disease from the blood bank and bring it to the smart refrigerator in the operating room for use. When in use, the employee takes the blood out of the refrigerator for blood transfusion. If the blood is not used, they will be returned to the refrigerator for storage. The next day, these unused blood will be returned to the blood bank for storage.
The blood storage temperature is generally 2-6 degrees Celsius, and the highest cannot exceed 10 degrees Celsius.
Tony Greenfield, chief scientist of the blood bank of the hospital, said: “We need to ensure that the blood returned to the blood bank can be used safely, and requires the cold chain to have relevant storage records.”
Under normal circumstances, blood removed for less than 30 minutes is considered safe, and blood over 30 minutes is considered unsafe and needs to be discarded. Before deploying the RFID project, the hospital placed a register on the refrigerator for tracking.
Greenfield said: “Unfortunately, manual tracking methods are not reliable. Records are often incomplete. When records are incomplete, the blood should be discarded.”

(SpaceCode Vortex VT100 passive low-frequency RFID tag attached to the blood bag)
NSW started to use RFID technology in December 2013, marking approximately 1,000 products each year.
SpaceCode Vortex VT100 passive low-frequency RFID tags will be attached to blood products sent to the operating room. In this way, the company saves labor time and labeling costs.
Each employee distributed an employee card with a built-in RFID chip. The chip ID number and personnel information are bound to each other. When employees complete the training, Greenfield will activate the permissions to allow employees to use the RFID system.
When blood is needed in the operating room, the hospital first contacts the blood bank to select blood products of the appropriate blood type. These are achieved through the blood bank information system.
When the blood bank employees took out the blood, they attached the RFID tag to the blood bag and bound relevant information on the Smart Tracker software.
After scanning the tag with a low-frequency RFID reader, the blood bag will be sent to the operating room. The operating room staff used the ID badge to open the RFID refrigerator and put the blood bank in the refrigerator. When blood is needed, the refrigerator will prompt the employee to enter the patient’s medical record number for confirmation. Then, the employee scans the employee card to unlock it and take it out. When the refrigerator is closed, the built-in reader reads the tag, confirms the removed blood bag information and creates a record. If the wrong blood bag is removed, the user will receive a warning.

(Smart Tracker software can determine the time of blood bag removal and warn the blood bag that has been removed for more than 30 minutes)
If the blood is not used, the employee will return it to the refrigerator. The software will determine its removal time. Blood that has been removed for less than 30 minutes will be returned to the blood bank refrigerator.
Using the RFID system, the blood bank can now ensure that the blood returned to the blood bank can be used with confidence.
(Exclusive manuscript of rfid world network, please indicate the source author for reprinting!)
[ad_2]