Singapore Tan Tock Seng Hospital uses RFID to automatically record patient temperature
[ad_1]
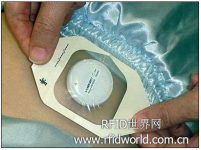
Tan Tock Seng Hospital in Singapore first adopted RFID technology to track and locate 1,200 inpatients in 2007. Now, the hospital has expanded the application of this system, sticking a 3 cm wide active, UHF label on the patient’s abdomen to monitor body temperature and detect serious infections.

ThermoSensors that are pasted on the patient’s abdomen to monitor body temperature
According to Yong Keng Kwang, deputy director of nursing at the hospital, Tan Tock Seng is the busiest hospital in Singapore, with more than 1,200 inpatients at any time, and the daily utilization rate of hospital beds is 90%.
“We believe that real-time patient tracking can help improve the efficiency of bed allocation and communication between different departments, and speed up the admission process of patients,” Yong said: “In the past, bed allocation relied heavily on the three-way communication between the bed management department, emergency room, and intensive care unit. After the adoption of RFID, the information exchange between these three departments has been automated, and verbal communication has become less.”
In 2007, Tan Tock Seng chose Singapore company Cadi Scientific to implement this patient tracking system. Cadi Scientific can provide local technical support, which is very important for the application of new technologies. The hospital uses 556 Cadi SmartNode RFID readers, and 868.4 MHz, battery-powered SmartTags are embedded in the patient identification wristband to track patients moving in the hospital.

SmartTags tags
The hospital has benefited a lot from this system. Yong said that the system has improved staff’s work efficiency, communication efficiency, bed utilization rate and reduced patient waiting time.
“For example, when a patient is discharged from the hospital, the bed management department will be notified in real time, and the bed will be cleared within 30 minutes. The emergency department can also better prepare for patient transfer. When the patient undergoes an operation, the monitoring nurse will understand the patient At the location of the anesthesia recovery room, the patient’s family will be notified of the end time of the operation in time,” Yong explained.
Due to the successful application of the tracking system and the fact that patients have already adopted RFID tags, hospitals have begun to consider other applications of the RFID system.
According to Lim Soh Min, director of Cadi Scientific, the hospital has expanded this system last month and enabled wireless temperature sensors to realize paperless data on vital characteristics such as pulse, respiration, body temperature, and blood pressure. The company’s new RFID tag ThermoSensors can monitor the body temperature of patients and track their location. 300 patients from Tan Tock Seng Hospital participated in the application test of tags in different scenarios.
“The results show that the accuracy of the ThermoSensor is comparable to that of ear thermometers, underarm or oral thermometers, and the accuracy is within 0.2 degrees Celsius,” Lim said.
This system can automatically perform temperature measurement, and the data is continuously downloaded from the SmartNode reader to the server. Through Cadi’s SmartSense Enterprise software, all information is automatically plotted on the paperless case, so that doctors, nurses and different departments can better share patient information.
The new wireless temperature monitoring system improves patient care. Nurses can immediately detect whether the patient has a fever without affecting the patient’s rest. This also reduces the workload of the nursing staff and allows them more time to complete other tasks, such as feeding or managing the isolation of the patient.
[ad_2]


