Application of RFID technology in identification management of sewage pressure pipeline
[ad_1]
I. Introduction
In March 2010, at the Third Session of the Eleventh National People’s Congress, then Premier Wen Jiabao specifically emphasized in the government work report that “we must vigorously cultivate strategic emerging industries and accelerate the development and application of the Internet of Things.” Since then, the Internet of Things technology (RFID radio frequency identification technology) has flourished and developed in full swing in China. At present, new breakthroughs have been achieved in the research and development of key technologies of the Internet of Things in my country, and they have begun to be applied in many fields such as agriculture, public safety, urban transportation, and health care. The management and application of RFID technology in underground pipeline network identification and inspection has been put on the agenda by more and more underground pipeline management departments in recent years. And it has achieved good applications in the fields of gas, tap water, and communications.
Based on real cases, this article makes a systematic introduction to the location and identification of RFID technology in urban sewage pressure pipes and later inspection management.
2. RFID working principle
RFID technology is based on a transformer coupling model (energy transfer and signal transmission between the primary and secondary) in the low frequency band, and a spatial coupling model based on the radar detection target in the high frequency band (the radar emits electromagnetic wave signals and carries the target information back to the radar after it hits the target. Receiver). In 1948, Harry Stockman published “Communications Using Reflected Power” and laid the theoretical foundation for radio frequency identification technology.
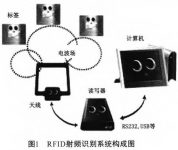
The most basic RFID system consists of three parts (as shown in Figure 1)

⑴Tag (Tag, namely radio frequency card): Composed of coupling element and chip, the tag contains a built-in antenna for communication with the radio frequency antenna.
⑵ Reader: a device that reads (and can also write in the card reader) tag information.
⑶ Antenna: Transmit radio frequency signals between the tag and the reader.
Third, the characteristics of buried RFID
RFID is divided into active card and passive card according to the power supply method; according to the carrier frequency, it is divided into low frequency radio frequency card, intermediate frequency radio frequency card and high frequency radio frequency card; according to the different modulation methods, it can be divided into active and passive; it can be divided according to the operating distance It is close-coupled card (working distance is less than 1cm), close-coupled card (working distance is less than 15cm), sparsely coupled card (working distance is about 1m) and long-distance card (working distance is from 1m to 10m. Even further).
Underground electronic signs applied to underground pipe networks are generally low-frequency, passive, and loosely coupled cards. Different from the commonly used radio frequency cards on the market, buried electronic signs need to meet the following conditions:
⑴ The structure is hard, compressive, acid and alkali resistant, and waterproof.
(2) Strong ability to penetrate obstacles, at least the ability to penetrate cement pavement.
⑶ Strong anti-interference ability, at least able to distinguish more than 8 types of underground pipeline marks of different specialties.
⑷Good confidentiality performance. Urban underground pipelines belong to the blood vessels and nerves of the city. The information attached on the RFID must have good confidentiality to prevent it from being used and destroyed by criminals.
⑸The warranty period is long, and the service life of RFID is required to be as long as the marked underground pipeline. Generally 10 to 30 years or even longer.
⑹Passive, because it is permanently buried in the ground, it is not suitable for power supply.
At present, there are mainly two mature RFID products suitable for underground pipeline marking. One is the “3M Electronic Marking System (EMS)” made in the United States; the other is the RXG.TR series pipeline electronic marker made in Beijing. The electronic logo used in this article is the RXG.TR series. Its parameters are: frequency 128KHz, working temperature -20℃~+80℃, humidity resistance 95%RH, voltage resistance ±5KV peak value, service life of 50 years, and maximum detection depth of 1.5 meters. The electronic marker detector is RXG-HandR300, and its main function is to accurately locate the location of the underground pipeline by searching for the effective range of the underground electronic marker’s magnetic field. With a GPS module, it can navigate and find the underground electronic marker buried on the pipeline.
Four, application examples
Guangzhou sewage pressure pipes are distributed in various districts of Guangzhou, with a total length of about 40cm and a pipe diameter of 500 to 1800. The materials are steel, concrete, and glass fiber reinforced plastic with sand and so on. The main purpose is to upgrade the collected sewage to various sewage plants for treatment purposes. In order to effectively manage and inspect the scattered sewage pressure pipes, the pipeline owner entrusted our company to accurately detect all pressure pipes, and affixed metal identification plates on the detection points, and buried RXG-TR electronic signs below to establish the properties of the sewage pressure pipes. Database and electronic identification database, equipped with electronic identification detector and electronic identification scanning information transmission management system, provide the most direct and reliable first-hand information for later management, maintenance and inspection.
Before burying the electronic identification of the pipeline, the location and depth of the target pipeline must be 100% detected. This is the prerequisite for burying the pipeline identification. How to ensure that the detection of the sewage pressure pipe is 100% accurate? This is another technical topic, so I won’t repeat it here. In order to ensure that the electronic marker can be stored relatively permanently and can be read by the detector at the same time, it is necessary to install the electronic marker 50~60cm below the road surface. Before the electronic marker is installed, it is necessary to use a reader to write the corresponding pipeline information into the electronic marker. Use an electric drill to drill a small hole with a diameter of 3cm and a depth of about 60cm. First, inject cement mortar with a thickness of about 5cm, and put it into the electronic marker vertically (head up). Use the marker detector on the ground to confirm that it can be read. The information in the marker is then filled and smoothed with cement mortar. Buried density of electronic signs: In addition to characteristic points such as inflection points and tee links, one is buried at an average straight line distance of 30 meters.
5. Remote transmission technology of pipeline identification information
By writing a dedicated Android system transmission software (APK) and installing it on an Android mobile phone/PDA, the RFID information read by the identification detector is linked with the map data information in the background in real time, and functions such as pipeline identification query, positioning and monitoring are realized. The platform for pipeline identification information transmission is composed of identification detectors, PDAs, and GIS, combined with embedded systems and geographic information systems. Among them, the identification detector uses RFID to read the identification, which is an important breakthrough in the realization of the entire technology. The identification detector also communicates with the PDA via “Bluetooth” technology. The wireless network of PDA (for example: 3G, 4G) is connected with GIS, which not only realizes real-time acquisition and feedback of identification detector data, but also real-time acquisition and feedback of GIS data, so that identification detectors can communicate with GIS indirectly and in real time . So as to realize the real-time and systematic management of the pipeline, as shown in Figure 2.

The application of RFID technology in sewage pressure pipelines has made a historic breakthrough in pipeline maintenance and management, especially in pipeline inspection management. In the pipeline inspection, the inspector holds the identification detector and PDA. After each identification reading is completed, the line inspector immediately sees the pipe diameter, buried depth, material and other information of the target pipeline, and at the same time transmits the pipeline identification information to the pipeline back-end manager via the 3G network. Managers can easily and quickly inquire statistical line patrol data through GIS. In this way, not only makes the line inspection system, but also makes the line inspection management more systematic. Effectively improve the efficiency of pipeline maintenance and management.
Six, conclusion
Through the successful application of RFID technology in the detection and identification of sewage pressure pipes in Guangzhou, the author summarizes the following conclusions:
1. The RFID used for pipeline identification is different from ordinary RFID, and must have strong penetrating power and long life.
2. According to different ground conditions, different types of pipeline electronic signs should be buried to meet the detection requirements of different depths.
3. It is necessary to establish a complete back-end database and be equipped with a dedicated electronic identification reader and RFID information wireless transmission carrier, and the entire RFID management system can be considered complete.
4. Technical improvements are needed: When using RFID detectors to scan underground RFID, there should be direction arrow indication and distance display functions. When the detector is directly above the RFID, it should also have a reading depth function.
[ad_2]