Fujian builds RFID archive warehouse
[ad_1]
Realize the modernization of warehouse management by applying RFID technology
In December 2013, the Fujian Provincial Archives “Archive Entity Security Certification Intelligent Management System” project (Phase I), which was undertaken by Fuzhou Aurora Computer Technology Co., Ltd., passed the completion acceptance and was put into trial operation. According to the authority, it can realize the functions of inventory file dynamic query, file catalog data retrieval, online file retrieval, automatic recording of file entry and exit information, automatic count of the number of files and location of the returned files, as well as real-time alarm lights for illegally retrieved files. The project (Phase I) completed nearly 100,000 volumes of archive digitization, which effectively improved the scientific level of archive storage.
In terms of file safety management, the new Fujian Provincial Archives is equipped with advanced security alarms, camera monitoring, infrared alarms, access control, patrols, automatic fire alarms and fire linkage, warehouse temperature and humidity control, communication networks, and TV broadcasts. System, intelligent dense rack and trolley track transportation system and other subsystems. However, there is room for further improvement in the safety, convenience and accuracy of the security management of archive entities. Especially when the collection of archives is gradually increasing, the need for safe, orderly and efficient archive entity management is more prominent. In response to this phenomenon, the Fujian Provincial Archives began to try to apply RFID technology to intelligently and securely manage the physical archives of the collection.
RFID technology principle and application
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) is the abbreviation of radio frequency identification technology, commonly known aselectronic labelOr non-contact card, proximity card, is a non-contact automatic identification technology. It is the most critical technology and product link of the Internet of Things, the item identification technology of the Internet of Things, and the foundation of the “things and things” interconnection of the Internet of Things. It is a communication technology that can identify specific targets and read and write related data through radio signals without the need to establish mechanical or optical contact between the recognition system and specific targets.
A complete RFID system is composed of three parts: Reader, TAG, so-called Transponder, and application software system. The working principle is: After the RFID tag is added to the magnetic field, if it receives the radio frequency signal from the reader, it can use the energy obtained by the induced current to send the product information stored in the chip (ie Passive Tag, passive tag or passive tag) , Or actively send a signal of a certain frequency (ie Active Tag, active tag or active tag), the reader reads and decodes the information, and then sends it to the application software system for relevant data processing, thereby realizing various functions. At present, it is mostly used in the intelligent construction of various libraries and archives.
In order to ensure the scientificity and feasibility of the project plan, the Fujian Provincial Archives Bureau specially invited relevant experts to demonstrate the technical plan of Fuzhou Aurora Computer Technology Co., Ltd., and concluded that radio frequency electronic technology is used in the management of archive entities, and the technology is mature and feasible. . Due to the large number of archive files, the thinner thickness, and the more serious metal interference in the storage environment, there is a high requirement for the number of readings and accuracy. Compared with high-frequency electronic tags (working frequency at 13.56MHZ, susceptible to metal interference, reading range within 1.5 meters), UHF electronic tags (labels are small in size, have a large reading range, but are easily affected by high humidity and other environments) ) Is more suitable for file entity management.
Project implementation process
1. Processing and installation of file labels
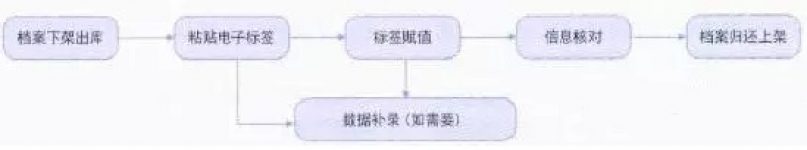
The processing and installation process of the file label (Figure 1).

Figure 1 Flow chart of file label processing and installation
File label pasting position: mainly divided into two situations, with “roll” as the unit, the label can be affixed to the inner side of the back cover (Figure 2); with “box” as the unit, sharing one electronic Labels, which can be affixed to the inside of the back (see Figure 3).

Figure 2 The label pasting position in the file dossier

Figure 3 The label sticking position in the file box
2. Processing and installation of shelf label
Rack label installation: first install the label to the appropriate position of the file rack, and then write the information (including the name or number of the rack label, and the corresponding name or number of the rack position) on the rack label through the RFID read-write device, and then load the rack The bit label is associated with the corresponding file. The shelf labels are divided into layer labels, cabinet labels, row labels, and warehouse labels. Each label corresponds to a different range and is placed in a different position.
3. Installation and debugging of equipment and software
Equipment installation is divided into the installation and debugging of workstations, RFID tag desktop reading and writing equipment, security doors, and RFID mobile workstations. The equipment is normally powered on, the information interaction with the computer is normal, and the information reading and writing functions of the RFID electronic tags are normal. The local area network connection is stable, and the signal detection and recognition function of the RFID electronic tag is normal. The file entity security certification intelligent management system software runs stably and smoothly, the man-machine interface is friendly and correct, and the work flow is clear and clear.
Introduction and characteristics of functional modules
1. Main functional modules
(1) File query positioning
Currently, the system supports query fields: file number, title and document number. Through retrieval, the files that meet the conditions are displayed on the screen in the form of a list. When the staff selects the required file, the system will automatically locate the storage location of the file in the warehouse, and display the serial number, column number, row number, and shelf where it is located. Information such as the tag number, and its location can be visually displayed on the two-dimensional graphics of the warehouse to guide the staff to quickly find the target file, which greatly facilitates the administrator to find the file.
(2) Outbound and warehousing registration
Simply swipe the outbound or inbound file at the RFID desktop reading and writing device, and the system automatically recognizes the file information without manual input. In the state of setting files out or in, the system automatically completes the registration of file information, makes effective reminders for files that have been misread or not read, records the operation time, and generates a log for easy viewing in the future. The staff can quickly register the file information out and in the warehouse, especially for the relatively large number of files. The efficient registration method makes the work more effective.
(3) Warehouse inventory
The inventory work is mainly realized by RFID mobile workstations. The information in the shelf tags and electronic tags is read through wireless signals, and checked with the system database. The system screen displays the file list corresponding to the current shelf, such as file number, title number , Whether it is out of the library, and whether it exists, the system automatically matches various information.
If there are files that have been put in storage, but have not been registered for storage, the system will issue a reminder and the staff can restore their status to storage. The inventory system not only enables quick inventory, but also realizes the sorting of files in the wrong frame, so that the inventory and sorting of files in the wrong frame can be handled satisfactorily in one link.
(4) Security door monitoring
When the archive file passes through the security door, the system automatically obtains the identification number by identifying the wireless signal. After matching the database information, it is judged whether the file has been authorized and the warehouse registration is carried out according to the normal procedures. Otherwise, the system will send out an audible and visual alarm, which effectively guarantees the safety of archives and avoids human error to the greatest extent.
(5) Utilization management
Process management for lending and return. The borrowing applicant sends an application through the system, and the application information is communicated to the leader for approval. If agreed, the warehouse manager will adjust the papers, and the system will record the borrower and file information. When returning, the system ends the entire utilization process after verifying the accuracy of the returnee and document information. In this way, the process of file utilization and return can be monitored, and responsibilities can be refined to individuals.
(6) Warehouse situation management
You can view the current occupancy rate of the shelf space of the warehouse and the unused shelf information, so as to facilitate the overall planning of the warehouse use.
(7) Utilization statistics
Automatic statistics on the lending and utilization of files, including information such as the amount, category, file number, and channel used. The staff can choose the time period by themselves, 1 day, 1 month or 1 year. The system can also automatically generate and print reports for the statistical data, which greatly saves the time of manual statistics.
(8) Guide to file listing
The system provides two guide modes for the shelf: input the file number of the file to be shelf, the system displays the storage location of the file; the file is recognized on the RFID desktop read-write device, and the system automatically displays its storage location.Display shape of storage location
The format includes text and two-dimensional graphics, which is the same as the display mode in the “Query Positioning System”. Shorten the shelf time and improve work efficiency.
2. Main features
The positioning speed is fast, which effectively solves the technical problem of quickly finding a file in a large number of archives, and improves the efficiency of file search; fast inventory speed, based on technical advantages, can quickly read multiple target signals from a long distance to achieve high-speed inventory ; Real-time tracking, rapid registration of files in and out of the library, real-time control of file utilization; strong control of missed and misreading functions, because the reading rate of RFID tags cannot reach 100% at a time, the system is based on the workflow and technology The angle realizes the reminder and filtering of missed and misreading, which effectively solves the problem of misreading of labels; comprehensive management, from data collection to shelf, from retrieval application to storage, all links are coordinated, and process-based electronic control is realized. , To achieve scientific and information management; log records, make corresponding information records for each management process and link, generate logs, which are conducive to inquiries and experience summaries; to ensure safety, it can completely prevent unapproved or authorized But unregistered files are taken out of the warehouse to ensure the safety of files.
Trial operation status and future goals
Through trial operation at the Custody and Utilization Office of Fujian Provincial Archives, the various functional modules of the project system are operating normally; the performance of hardware equipment is stable, and the software interface is good; it is convenient and fast to use in file search, storage and exit registration, and inventory. Improve work efficiency and improve the level of file safety management. After the commissioning of the dedicated business network in the library is successful, the Fujian Provincial Archives plans to expand the scope of operation of the project to the daily work of various business offices in the library to further summarize experience.
Information technology continues to develop, and archive management technology is also constantly improving. The Archives of Fujian Province will continue to explore and practice, advance management with technology, gradually realize automation, digitization, and intelligence in archive management, promote the improvement of the informatization level of the entire archive management, and bring the level of archive management and service to a new level.
[ad_2]



