Talking about the application case of rfid technology
[ad_1]
Radio Frequency Identification, RFID (Radio Frequency IdenTIficaTIon) technology, also known as radio frequency identification, is a communication technology that can identify specific targets and read and write related data through radio signals without the need to establish mechanical or optical contact between the identification system and specific targets .
Radio frequency is generally microwave, 1-100GHz, suitable for short-distance identification communication.
RFID readers are also divided into mobile and fixed ones. At present, RFID technology is widely used, such as libraries, access control systems, and food safety traceability.
Radio frequency identification (RFID) is a wireless communication technology that can identify specific targets and read and write related data through radio signals without the need to establish mechanical or optical contact between the identification system and specific targets.
The radio signal is an electromagnetic field tuned to a radio frequency to transmit data from the tag attached to the item to automatically identify and track the item. Some tags can get energy from the electromagnetic field emitted by the recognizer during identification, and do not need a battery; there are also tags that have a power source and can actively emit radio waves (electromagnetic fields adjusted to radio frequencies). The label contains electronically stored information and can be identified within a few meters. Unlike the barcode, the radio frequency tag does not need to be in the line of sight of the recognizer, and can also be embedded in the tracked object.
Many industries have used radio frequency identification technology. By attaching the label to a car in production, the factory can easily track the progress of the car on the production line. The warehouse can track the location of medicines. RFID tags can also be attached to livestock and pets to facilitate the positive identification of livestock and pets (positive identification means to prevent several livestock from using the same identity). Radio frequency identification cards allow employees to enter locked parts of the building, and radio frequency transponders on cars can also be used to collect fees for toll roads and parking lots.
Certain radio frequency tags are attached to clothing, personal belongings, and even implanted in the human body. Since this technology may read personal information without my permission, this technology will also have the risk of infringing on personal privacy.

Application case of rfid technology
RFID is a simple technology that can make any object of interest (OOI) the object of identification. Using RFID tags with unique identification codes, in addition to simply sticking the tag to the entity, it is easy to embed the tag into the object of interest (OOI) for identification. RFID is a kind of radio frequency technology, which completes the transmission through the antenna between the tag and the reader. In this way, information related to tags on the OOI can be easily obtained.
When the circuit in the RFID tag has sufficient energy, it will begin signal transmission and connection within the reader’s receiving range. This method is different from other static identification technology, it is a LOUD ID technology. This feature makes certain inventory management and positioning problems very simple, which is why RFID can be used in tracking, tracing and inventory management functions.
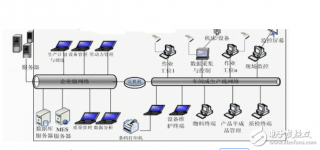
When using RFID to solve specific problems or improve specific solutions, it refers to the use of RFID application systems, including tags, antennas, and readers of the hardware part; and software application systems. The RFID tag makes the object (OOI) identifiable. The antenna and reader provide the function of identifying the RFID tag and the necessary information (physical/virtual location), and the application software is responsible for the ID information and related detection status. Use it properly. Just like any other technology, it must be perfectly combined with other integrated solutions to make sense. Therefore, special consideration must be given to the management after the program is changed in order to have the best results. In recent years, RFID technology has made some major developments and many successful cases. Although this technology can be applied to point-to-point tracking and visibility, it has not had a major impact on the logistics industry, because the technology applied in this industry has approached maturity. Although according to the law of supply and demand, the cost factor will gradually decrease; mutual interoperability will also be established by various global standards organizations, but more importantly, changes in business models, government policies, and social acceptance can achieve global tracking. And recognition. The above-mentioned non-information technology issues are quite complex. These are issues outside the scope of information technology, and they are also the biggest crux of the entire problem. Prior to this, RFID technology will continue its current development direction, successfully achieving limited applications and some close cooperation relationships, and information exchanges can be well controlled. Since 2006, Cyberport in Hong Kong, an advanced and advanced intelligent composite office building, has been using the RFID+3G facility management solution developed by the Electronic Commerce Solutions Company (EBSL). EBSL also assisted the general map of the University of Hong Kong in early 2009, importing RFID into more than 1 million books, so that students can borrow and return books by themselves, and avoid the cumbersome problems of borrowing and inventorying in the library, and provide more Serve.
In addition, there are also many retail RFID application cases, including the Schmidt Electronics Group Smart Retail System (SRS) and mirrors installed in the Mayen Italian fashion boutiques, which can be used to provide more information on clothing matching to savvy buyers; and The one is electric power logistics. The logistics solution under PCCW (PCCW) actually introduced the RFID sales management system to a leading home appliance and lighting company, which not only enables customers to have a simple order management model, but also improves operational efficiency and improves customers Satisfaction. PCCW (PCCW) and Hong Kong’s (Nuance-Watson) Mobile Discovery Kiosk, and E-New Technology (EBSL)’s Grand Buy Department Store E-Sample SoluTIon, are smart sales/marketing management automation service equipment that can help businesses improve Their sales or marketing capabilities. GS1 Hong Kong has just launched the ezTRACK standard as the basis for an information exchange platform to provide consumers with information inquiries and confirmations on the complete supply chain of products.
The Hong Kong government has been very supportive of RFID application research. The Hong Kong Logistics and Supply Chain Management Application Technology Research and Development Center (LSCM) was established in 2006. Its purpose is to focus on important RFID-related applications in the field of logistics and supply chain management. The development of ET I’s RAE Middle ware is sponsored by the LSCM fund and commercialized by EBSL.
Food safety is related to every citizen. It is not only a globally important issue, but also a priority for governments of various countries. In Hong Kong, most of the food is imported from the Mainland, and the governments of both sides have invested in many measures to ensure the quality of food supply. Since 2008, the Electronic Business Technology Institute (ETI) of the University of Hong Kong has been cooperating with the Shenzhen Entry-Exit Inspection and Quarantine Bureau (SZ CIQ) and the Entry-Exit Inspection and Quarantine Bureau (GD CIQ) in Dongguan to establish Information platform for vegetable and pig food safety shipped to Hong Kong. CIQ will collect and use this information to improve internal management to speed up border inspection and customs clearance procedures; at the same time, ETI will provide food safety related services, from inquiries about transportation information related to ordered products, to packaged vegetables and product recycling that supermarket customers want to buy Serve. It will also provide a message feedback mechanism to enable users to respond to abnormal food safety conditions.
This plan is very important because it will develop ways to retrieve and collect data from farms, vegetable distribution centers, food processing centers, and logistics carriers, and understand how effective RFID technology is in the process. Including the release object and the delivery method of the data, this is an important key to the completion of the plan. The value of the system is unquestionable, but whether the method is feasible, cost-effective and acceptable to the government and the industry is the most important issue of this plan. Although the plan initially focused on vegetables and live pigs from Guangdong/Shenzhen to Hong Kong, it can be extended to any food in all provinces of China and other countries. Once the food safety query and tracking is proven to be successful, combining scalability with other sensing technologies to provide the industry with food quality management services. This is the next phased plan in 2010. RFID technology has come a long way, basically it is a proven low-cost technology that can be effectively used in many tracking solutions. It is believed that the application will be popularized in the next 5 years.
RFID directly inherited the concept of radar, and thus developed a vibrant new AIDC technology-RFID technology. Harry in 1948. Stockman’s “Communications Using Reflected Power” laid the theoretical foundation for radio frequency identification RFID.

1) The history of the development of RFID technology. In the 20th century, the theory and application of radio technology is one of the most important achievements in the development of science and technology. The development of RFID technology can be divided as follows according to the 10-year period:
From 1941 to 1950. The improvement and application of radar gave birth to RFID technology, and the theoretical foundation of RFID technology was laid in 1948.
From 1951 to 1960. The early exploration stage of RFID technology was mainly in laboratory experimental research.
From 1961 to 1970. The theory of RFID technology has been developed, and some application attempts have begun. The field of RFID application is quite extensive
1. Logistics: cargo tracking in the logistics process, automatic information collection, warehousing applications, port applications, postal services, express delivery
2. Retail: real-time statistics of sales data of commodities, replenishment, anti-theft
3. Manufacturing industry: real-time monitoring of production data, quality tracking, and automated production
4. Clothing industry: automated production, warehouse management, brand management, single product management, channel management
5. Medical treatment: medical equipment management, patient identification, baby anti-theft
6. Identification: e-passport, ID card, student card and other electronic documents.
7. Anti-counterfeiting: anti-counterfeiting of valuables (tobacco, alcohol, medicine), anti-counterfeiting of tickets, etc.
8. Asset management: all kinds of assets (precious or large quantity, high similarity or dangerous goods, etc.)
9. Transportation: high-speed non-stop, taxi management, bus hub management, railway locomotive identification, etc.
10. Food: freshness management of fruits, vegetables, fresh, food, etc.
11. Animal identification: identification and management of training animals, livestock, pets, etc.
12. Libraries: bookstores, libraries, publishing houses, etc. 13. Automobiles: manufacturing, anti-theft, positioning, car keys
14. Aviation: manufacturing, passenger ticket, luggage and parcel tracking
15. Military: RFID for identification and tracking of ammunition, guns, materials, personnel, trucks, etc.
Application in animal husbandry
1. Install electronic ID cards for cattle
The first step in RFID-based cattle breeding and tracking is to install an electronic ID card on the cattle and establish a permanent digital file for each cattle to uniquely identify the attributes of each cattle. The basic methods of installing electronic tags for animals include: collar type, ear tag type, injectable type and pill type electronic tags.
2. RFID-based cattle farm management system
Write livestock information into the chip, including: livestock owner-owner’s name, gender, animal type, characteristics, immunization, vaccine type, manufacturer, production batch number, vaccination method, vaccination dose, immunization quantity, and immunization personnel’s name, etc. , The owner needs a handheld data collector and can obtain information about the livestock. According to the regulations of the Ministry of Agriculture of China, the cattle coding format is: 2-×××××× (county-level administrative area code)-×××××××× (identification sequence number). Other countries should be modified according to the local code. The specific operation process is: in the daily management of animal husbandry, the owner only needs to carry a wireless handheld terminal to read the animal ear tag to be followed, and the relevant information of the animal can be displayed on the handheld terminal. Owners can feel this information to deal with their daily diet, medical history, reproductive history, immunization records, etc. accordingly. Fast and convenient, saving a lot of time. There is no need to look up the original acquisition file card. At the same time, the data can be transferred to the back computer, and the livestock file can be established in the back computer. Professionally record the detailed information of each livestock through the computer. No need to worry about illegible records or missing file cards. At the same time, the department and relevant leaders can check the situation of any ranches, stalls, and livestock instantly through the Internet to achieve information transparency. 3 RFID-based precision feeding subsystem for dairy cows
The digitization of fine aquaculture is based on a database system. In a distributed network environment, users of various business units can obtain and update data, store and manage data, extract and analyze information, and form basic data through the basic data warehouse mechanism of digital agriculture. Sharing and information mining. The knowledge and experience of precision breeding experts are abstracted, a data model is established to guide dairy cow breeding, and the feedback formed in the breeding practice is used to adjust the model. The logical structure of the digital system for fine dairy cattle breeding is divided into three layers: data layer, service layer, and application layer. The data layer is composed of digital agriculture basic data warehouse (including metadata database, image database, comprehensive feed nutrient database), sensor information database (including radio frequency sensor data, video surveillance data, etc.), expert model database and other database groups. The service layer is composed of a digital agricultural precision breeding support platform and an information sharing and exchange platform, including computer network systems, communication systems, monitoring systems, display systems, and operating systems. The application layer mainly includes a variety of application systems, as a client to call database server information and services. 4 RFID-based meat tracking system
RFID technology can be applied to the entire process of animal husbandry food production, including feeding, epidemic prevention and sterilization, product processing, food circulation and other links. Standardized technical regulations and quality supervision measures are fully introduced to establish a “farm to table” food supply Chain tracking and traceability system.
(1). The government takes the lead in building a meat food supervision platform to realize the information access and sharing of related enterprises and departments in all links of the supply chain, and realize end-to-end monitoring from the source of production to the retail link.
(2). In the cattle breeding link, RFID technology and supporting auxiliary methods are used to realize the whole feeding and tracking, realize the integration with the back-end livestock production management system, and realize the docking with the livestock quarantine and inspection system of the competent department of the industry. At the same time, the relevant information is input into the meat food. Regulatory platform.
(3). In the beef transportation link, crossing monitoring systems are deployed on different transportation nodes through RFID technology and supporting auxiliary means to realize the monitoring of the entire transportation process, and provide activities such as pig quarantine inspection and transportation disinfection. At the same time, relevant information is input into the meat food supervision platform . (4).Cattle slaughter link, passed
RFID technology and supporting auxiliary methods realize the verification and confirmation of the health status of cattle, integrate the back-end management system of the slaughterhouse, and at the same time, input relevant information into the meat food supervision platform. (5). In the beef processing link, RFID technology is used in conjunction with bar code technology to realize the correlation between cattle information and beef information. At the same time, relevant information is input into the meat food supervision platform. (6). In beef wholesale and retail links, RFID technology is used to accelerate the efficiency of logistics links, and bar code technology is used to trace its source information to strengthen its market transaction management. At the same time, relevant information is input into the meat food supervision platform.
[ad_2]



