The Application of RFID in the Warehouse Management System of Logistics Enterprises
[ad_1]
In the logistics industry, as the manufacturing environment changes, product cycles are becoming shorter and shorter, and the production methods of small batches and multiple varieties have higher and higher requirements for inventory management. If it is not possible to ensure timely, accurate and effective purchase, delivery and inventory control, it will cause greater losses to the enterprise. Therefore, a new inventory management system must be established. To this end, this paper designs a new logistics warehouse management system based on RFID technology. Using this technology’s features such as non-visual reading and simultaneous reading of multiple tags, several processes such as receiving, putting on shelves, picking up, replenishing, shipping, and inventory can be effectively completed, and it is used as an enterprise foundation Facility to provide a stable data stream of real-time location and status of assets, inventory, and materials, in order to further enhance the competitiveness of enterprises.

1. Introduction to RFID technology
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology is a non-contact automatic identification technology realized by radio frequency communication. At present, the use of electronic tags and RFID communication technology can realize the Internet of Things of global item tracking and information sharing. This will fundamentally improve the level of flow monitoring and dynamic coordination management of items in various links such as product production, transportation, warehousing, and sales on a global scale.
The realization of this technology includes at least two parts: radio frequency tags and readers. The RFID reader performs wireless communication with the RFID radio frequency tag through an antenna, which can read or write the tag identification code and memory data. The RFID radio frequency tag chip has an erasable and programmable read-only memory to store identification codes or other data. It can be used as an identification card for goods. It has the advantages of non-contact, long working distance, repeatable reading and writing, and identifying moving targets.
RFID systems generally consist of electronic tags, readers, application interfaces or middleware software, transmission networks, software management systems, etc. Among them, RFID middleware is a medium that combines RFID hardware and application software. Each module in the warehouse management system RFID middleware is needed to perform various operations on electronic tags.Figure 1 shows the block diagram of the RFID system
2. Requirement analysis of RFID warehouse management system
With the continuous development of the scale of logistics enterprises, the types and quantities of materials managed by warehouses continue to increase, and the frequency of in and out of warehouses increases sharply. Warehouse management operations have become very complex and diversified. Traditional warehouse management systems usually use barcode labels or manual warehouse management documents. However, these warehouse operation modes and data collection methods have been difficult to meet the rapid and accurate requirements of warehouse management, and have obvious shortcomings. In manual management, manual registration is not only easy to make mistakes, but also has low work efficiency, cumbersome warehouse operations and high labor costs; while bar code management is easier to copy, not stain-proof, and not moisture-proof, but it can only be read at close range and can only be read at a time. Read one.
Introducing RFID into the warehouse management system, using the advantages of RFID data capacity, reusability, and barrier-free reading, etc., can not only reduce labor intensity, but also greatly improve work efficiency. Therefore, the RFID-based management system can greatly simplify the inventory management of items and meet the needs of increasing information flow and increasing information processing speed.
The RFID-based warehouse management system can realize warehouse receipt management, warehousing management, warehouse transfer management and inventory management functions, which can facilitate enterprises to supervise goods, and can easily update and delete the basic conditions of materials in the warehouse. And query.
3. The concrete realization of RFID technology in the warehousing information system of logistics enterprises
3.1 Hardware configuration
The hardware of this system involves the main control computer, electronic tags, handheld readers, fixed readers, servers, etc. The server can connect the main control computer with the reader on the forklift and the handheld reader through the wireless network for data transmission. There are two main types of readers used in this article:
The first type is a handheld reader: the reading and writing distance is about 2 m, which is mainly used for operations such as warehouse storage, moving, and inventory; the second type is a fixed reader: the reading and writing distance is about 1 m, mainly used for forklifts Read the location information in the cargo label and check it with the location information on the location label.
3.2 Software design
The software part of this system adopts the Visual Basic 6.0 development platform and develops in C/S mode. The database adopts SQL Server 2000, and the connection database adopts ADO technology. The operating system is Windows 2000, Windows 2003, and Windows XP.
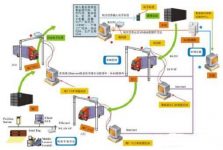
The structure of the RFID-based logistics enterprise warehouse management system designed in this paper is shown in Figure 2.
The user management module in the system can be used for hierarchical management of users. Different users have different rights. For example, the system administrator has the rights of daily management, warehousing management, query management, moving library management, outgoing management, and printing. The staff has the authority of inbound operations, query management, transfer operations, outbound operations, printing, etc.
Through material management, you can update, delete, and query all types of materials in the warehouse (including information such as names, suppliers, prices, etc.) to achieve material management functions.
Warehouse management can realize the management of receiving, warehousing, moving, exporting and inventory management of materials and goods in the warehouse, and can export the receipts of each functional module to facilitate user material management: it can also provide receiving and warehousing , Move the warehouse, leave the warehouse and inventory the details, in order to facilitate the user to inquire.
4. RFID logistics enterprise warehouse system business process
In this system, the main control system is mainly used to generate and send warehouse-in/out instructions, warehouse-moving and inventory instructions; the task of the handheld unit is to use a handheld reader to connect to the main control computer through a wired (or wireless) network to download the host Send the instructions, and complete the job according to the instructions, and then send the information to the host computer through the handheld reader.
Forklift terminal is to install a fixed reader on the forklift, so that when receiving/picking goods, use its reader to read and verify the location information on the location label and the warehousing instruction.
Electronic tags are the main components in the warehouse system of RFID logistics enterprises. Because RFID technology has not yet been popularized in various supply chains of logistics enterprises, when goods are just delivered from suppliers, they are often not labeled. To apply RFID technology to a warehouse management system, RFID tags must be used. Therefore, before warehousing, you must first make the required RFID tags. There are two types of electronic tags: one is the location label (including the location number and the information of the goods) to facilitate the management of the storage location of the goods; the other is the goods label, which mainly records various information of the goods (including the name , Quantity, type, price, etc.). The specific production process requires the use of an RFID reader to write the location information into the electronic tag, and then fix the electronic tag on the location, so that it is convenient for the administrator to use the hand-standby reader to read the location information. Because logistics companies have a large number of goods when entering and leaving the warehouse, it is necessary to make pallet labels to facilitate the management of large quantities of goods. If the quantity of goods is small, a label of the goods shall be affixed to each goods. At the same time, these labels can be reused, and when the goods are out of the warehouse, they can be removed and sent to the warehouse for reuse. The rest of the process is carried out on the premise that the corresponding electronic label has been affixed.
4.1 Inbound operations
The main purpose of using RFID technology in warehousing management is to reduce the time consumed in the goods warehousing process and increase the accuracy of the warehousing process. The specific process is as follows:
(1) When the goods are delivered to the warehouse, the staff checks whether the quantity and specifications of the goods are consistent with the purchase orders manually generated in the database. If they are consistent, they are ready to be put into the warehouse;
(2) Put the items on the warehousing pallet, and use the reader to read the goods information, so that the computer will automatically assign the location address according to the goods information;
(3) Download the location number and cargo code to the reader, and the staff will use the forklift to transport the goods to the designated location according to the warehousing instruction. After checking the position with the fixed reader on the forklift, the goods will be sent to the warehouse. (If necessary, you can also modify the goods number and quantity information recorded in the location label). If the location is incorrectly placed, the system will issue an alarm;
(4) The relevant information after acceptance is automatically identified by the RFID read-write equipment and sent to the computer management system, the inventory information in the database is updated in time, and the warehouse receipt is printed at the same time.
4.2 Outbound operations
Outbound management mainly solves the work of picking and information entry. The RFID reader can directly read the contents of the electronic tag, thereby eliminating the trouble of unpacking and checking, eliminating the tedious workload of manual entry, greatly saving labor costs, and improving work efficiency and accuracy.
During operation, the operator generates a sales order according to the warehouse management system software in the host, and downloads its related cargo code and corresponding location and other data to the reader, and the operator can follow the reader’s prompts to reach the designated location.
Then, take the specified quantity of goods from the storage location and place them on the shipping pallet, and rewrite the pallet label and the number of items in the storage location label. When the goods are delivered to the exit, the reader can read the information of the goods and compare it with the outbound instruction. If it is not in compliance, a warning will be given and manual inspection will be carried out: if it is in compliance, the warehouse information will be read in and out of the computer through the reader, and the warehouse out list will be generated. Finally, remove the cargo label so that it can be reused.
4.3 Move the library
When the delivery of a batch of goods is nearing completion, the inventory is running low, or the next batch of bulk goods has been notified that the warehouse needs to be moved or moved, if the manual method of moving the warehouse is used, it will often lead to The goods are inconsistent with the storage location, which is not conducive to the next picking, and brings great inconvenience to the warehouse management. If RFID technology is adopted, the computer system only needs to issue instructions to the reader in the operator’s hands. After seeing the instructions, the operator can locate the corresponding goods and quantity to move the goods to the corresponding target library; after completion , You can modify the label information and send back the corresponding data to the system computer.
4.4 Inventory check
The role of inventory is to ensure the consistency of the physical inventory and the records in the information system. The traditional inventory method requires manual counting of the quantity of goods, which not only increases the strength of the operators, but also greatly lengthens the inventory cycle, which is not conducive to grasping the inventory situation. Even if the goods are missing or stolen, they cannot be discovered in time. However, with RFID technology, only the operator needs to carry a handheld reader into the warehouse area, and after traversing all the locations in turn, the corresponding item number, item name, item location bar code and item can be placed on the location. Inventory results such as the number of products are transmitted to the system management center, and various inventory reports are generated as required.
The inventory method using RFID technology can not only reduce the work intensity of the operators, shorten the inventory cycle, improve the real-time performance of the data, understand the inventory situation in time, make a reasonable purchase plan, but also find the errors in the operation process in time to ensure the materials Security.
5. Application effectiveness
Applying this warehouse management system to logistics enterprises can achieve better results, mainly as follows:
(1) Using RFID technology can read a large number of tags at one time, thus eliminating the tedious workload of manual entry, greatly saving labor costs, and improving work efficiency;
(2) The location label and cargo label can record the change information of the goods (type, location, name, quantity, etc.) in time, reduce human errors when entering the goods, and improve the accuracy of operations such as personnel, exit, removal, and inventory Rate;
(3) Due to the improved reliability of storage and other operations, many unreasonable orders have been avoided, and the operation cycle of supply and rationing has been greatly improved;
(4) Increase the throughput of warehouse products and reduce operating costs;
(5) The use of radio frequency technology can greatly improve the efficiency and accuracy of the picking and distribution process, and accelerate the speed of distribution.
6. Conclusion
This article applies RFID radio frequency technology to the warehouse management of logistics enterprises, and on this basis, develops a set of intelligent warehouse management systems that can be used by logistics enterprises. This system can automatically inspect and register the entry and exit of warehouse goods, understand inventory information, and grasp the current location of various materials in the warehouse, which not only saves the cumbersome steps of manual entry, but also greatly reduces the risk of improper operation. Mistakes made. Compared with barcode tags, RFID readers can read a large number of tags within a certain range at one time, thereby reducing labor intensity and greatly improving efficiency; at the same time, it is small in size, large in storage, and can be remotely identified, which is very suitable Use in a variety of complex environments. The application of RFID radio frequency technology to the warehouse management of logistics enterprises improves management efficiency as a whole, brings direct economic benefits to enterprises, and also helps to enhance the core competitiveness of logistics enterprises.
[ad_2]



