The Application of RFID Technology in South Korean Army Logistics
[ad_1]
1 Introduction
“Without innovation in the logistics industry, there will be no innovation in military logistics.” The view of Shinseki, the Chief of Staff of the South Korean Army, has elevated logistics innovation to a priority. Take a divisional unit of the Korean Army as an example. When the grassroots needs supplies. Replenishment requirements are reported to the relevant departments of the division’s first-level units through 5 levels, and then each level goes through a 3-step processing procedure. The replenishment materials finally reach the soldiers through a 7-step allotment process. That is to say, during the entire supply process, 71 to 72 steps are required for military supplies to reach the soldiers from the division one unit. In addition, although the superiors promised to ration the materials, the warehouse currently has insufficient inventory, and the inability of automatic replenishment of materials will result in inability to supply in time. Unlike military officers in higher-level departments, it is impossible for grassroots departments to know the delivery time of supplies, which also prevents timely supplies of supplies. Because there is no automatic system in the division, logistics supply department, and logistics command department. Therefore, it is very difficult to understand the demand information of supplies. In order to solve this problem, the South Korean military promotes the use of RFID tags in the new military distribution system.
2 Logistics Information System
2.1 Overview
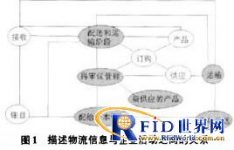
The production process is enough to obtain raw materials, produce goods, and sell goods for profit. The activities at each stage are inseparable from personnel, raw materials and funds. As raw materials are finally converted into products, physical distribution will be carried out. The logistics information system is to provide support for physical distribution activities. The physical distribution process is closely related to all the activities of the enterprise. In other words, the logistics information system is a system that facilitates physical distribution. The system uses all the information about distribution. And to process and transmit this information. Figure 1 describes the relationship between logistics information and corporate activities. Since the logistics information system of small and medium-sized enterprises is also closely related to non-distribution activities, they should not only handle distribution activities, but also production activities to promote the integration of the system with other supply activities.

2.2 The purpose of logistics information systems and distribution services
The goal of logistics information system planning is to improve customer service levels and reduce distribution costs. These two goals are in conflict. There is a balanced relationship between them. Customer service includes commercial distribution services and physical distribution services. Of course, these two goals are closely related to a certain extent, which is why the balance between them is troublesome. At the same time, sales and distribution is a kind of goods flow that starts with an order contract (either verbally or in writing). It starts from understanding the requirements of the orderer and ending with the delivery of the goods to the correct place.
2.3 The role of RFID in the logistics information system
RFID technology was first applied in the military field, and currently the most representative of the highest level of RFID technology application is the US military. The US military’s application of RFID technology stems from the needs of modern warfare. During the 1991 Gulf War. The United States shipped about 40,000 containers to the Middle East, but due to unclear markings, more than 20,000 of them had to be reopened, registered, sealed, and put into the transportation system again. This kind of label is also further used in the FMCG (Fast Moving Consumer Goods) supply chain. Because RFID technology and wireless barcodes can reduce costs in many areas (such as sales chain management and air/postal distribution), they have attracted more and more attention. .
3 Logistics management of the Korean Army
3.1 Classification by type
Military supplies can be classified by number, characteristics (consumables and non-consumables), unit price, etc. In addition to these classification standards, classification by type is also common. Below we focus on the method of classifying the supplies according to their use and nature. This classification method classifies the supplies into X-levels. Level I supplies are food, including staple food and non-staple food; Level II supplies are equipment, including clothing, personal equipment, combat uniforms, combat boots, engineering spades, helmets and other items: Level 111 supplies are fuel, including fuel and Gasoline; Grade IV supplies are building materials. Including wood, cement, plywood, paint, iron nails and other materials; Class V supplies are munitions, including guns, bazookas, and artillery; Class VII supplies are equipment for combat missions, including rifles, tanks, and automobiles; VIII Class-level supplies are medical supplies, including various medical equipment and medicines. Grade IX supplies are parts of machinery and equipment, including bolts, nuts, engines, tires and other materials; the remaining materials are classified as grade x supplies.
3.2 Classification by function
Military supplies can also be classified by function. It can be divided into 9 categories: firepower equipment, transportation equipment, special weapons, communications and electronic equipment, aviation and maritime equipment, general equipment, supplies, munitions, and medicines. Firepower equipment includes firearms, monitors, artillery measuring equipment; transportation equipment includes various vehicles and their parts and components; special weapons include anti-aircraft artillery, anti-aircraft missiles, anti-tank weapons, and surface-to-ground weapons: communications and electronic equipment include wired/wireless communications Equipment, detection equipment, radar, and camera equipment; aviation and maritime equipment includes aircraft, ships, and airborne and shipborne equipment; general equipment refers to equipment used in infrastructure, energy supply corridors, inland water transportation, and service industries.
4 South Korean Army Logistics System
The logistics system of the South Korean Army is divided according to the delivery method of the enterprise. First, supplies can be sent directly to munitions units or demand units that need them. Or first deduct the munitions unit and then go to the combat unit that needs these items. For consumables, the demanding unit can compile a report based on the demand for non-consumables of the unit, and temporarily request rationing from the superior.
This method may be a waste of time. Because the munitions department is responsible for distribution, it needs to have an accurate list of items to serve on time. Introduce an RFID technology as shown in Figure 2 to the logistics system.
Through the rapid delivery and precise management of materials, budget waste can be prevented and other resources can be saved.
In addition, although a department promises to ration supplies, the warehouse currently has insufficient inventory. The inability to automatically replenish materials will result in a substantial reduction in effective supply. Unless the logistics officer supplements the fallen supplies. The demand unit is different from the superior department because there is no automatic system between the division, logistics supply command, logistics department, and combat unit. They do not know the supply schedule of materials, which makes it difficult to receive supplies. Using RFID technology can solve this problem and establish a network between the Ministry of National Defense, the logistics department, and the material supply department.

5 Conclusion
Nowadays, the popular e-commerce, automatic transportation system using intelligent traffic control and tracking technology is also applied to the enterprise distribution system of Internet service. With the development of enterprise distribution systems. Military distribution systems will also use these cutting-edge technologies. The logistics system needs to react to various situations in advance, which will cause a waste of time and budget. In order to solve this problem, this article analyzes the logistics system using RFID technology. But there are also shortcomings, because the application of RFID technology in the logistics system is not mature, and there is not enough data to prove the effect of the system.
At present, many logistics companies are actively adopting RFID systems, and there is reason to believe that RFID technology will be widely used in military logistics in the near future.
[ad_2]



