Introduction to the application of barcode (magnetic card) system in hospitals
[ad_1]
|
This plan is to allow the hospital to use additional equipment with barcodes (magnetic cards) on the original basis to improve work efficiency, minimize errors, increase benefits, and reduce the occurrence of medical accidents. |
|
Advantages of using barcodes for management in hospitals: |
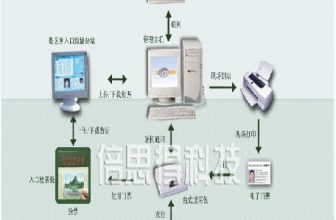
| 1. General outpatient application: (1) Registration office When a patient enters the hospital to register, he will register with his ID card, and the system will instantly generate an “identity registration card” with his ID number. The card will have: ID card number, barcode corresponding to the ID number, patient’s name, gender, birth Basic information such as year, month and day. In order to ensure the uniqueness and versatility of the patient’s barcode, the ID number is set as the basis of the barcode (if the patient does not have an ID, the system will automatically generate a number that is different from the ID number). As the specific information of patients in the hospital often changes, one-dimensional barcodes are recommended for barcodes. The material of the “identity registration card” can be made of durable and thick PET for long-term use. The main function of the identity registration card: After the patient has registered the personal information for the first time, there is no need to enter it again next time, which will increase the registration speed; after the patient has registered, barcodes can be used for all subsequent activities in the hospital Confirm the identity and record it in the computer for later recall; (Two), consulting room When a patient goes to the doctor to see a doctor, the doctor can use a networked terminal to read the barcode on the patient’s registration card with a barcode scanner, and then query the patient’s medical history and previous examination records; when the patient needs a biopsy, take a sample from the doctor After that, immediately printed labels with the patient’s name and bar code are attached to the specimens. Such labels will be more concise than the existing paper-wrapped method and can reduce the error rate. (The same method is also used when collecting specimens in the laboratory.) (3) Pricing and charging office Scan the patient registration card, read the barcode, charge and send the confirmation data to the laboratory or pharmacy. (Four), laboratory After receiving and inspecting the specimens in the laboratory, use the scanner to scan the patient’s barcode into the computer, first confirm the receipt, and then enter the test results on the automatically generated test form (which already contains the patient’s data) and print it out. The test results can be queried on a networked computer, so this single submission is for reference and retention of patients. (5) Pharmacy After receiving the confirmation payment information from the charging office, the pharmacy starts to dispense the medicine, and affixes a label indicating the patient’s name and the method of administration on the package of the medicine (for the patient to confirm and prevent errors), and then the medicine will be displayed on the display screen after the medicine is dispensed Notify the patient to get the medicine. After scanning the barcode information of the patient registration card to confirm the identity, the medicine is given to the patient to leave. |
| 2. Hospital application plan: When the patient goes through the admission procedures, if the existing registration card is presented to the admission office, the staff only needs to scan the bar code on the card to call up the patient’s previous data and complete the input of the patient’s information without repeating the input. Visible numbers and barcodes are printed on the patient’s wristband at the same time, which is convenient for identification and data inquiry in the hospital. |
| 3. Surgical application plan Mainly used for patient identification. Before the patient goes to the operating table, the nurse is responsible for scanning the patient’s barcode and confirming it by the computer, so that the procedures for confirming the patient’s identity can be implemented more easily without errors. |
[ad_2]