Animal food traceability system
[ad_1]
1 Animal food traceability system
1.1 Animal food traceability process and information model
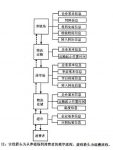
The animal food safety traceability system includes many links from “breeding farm” to “consumer”, mainly including: breeding farm, transportation and logistics, slaughterhouse, logistics and warehousing, supermarket and consumers. The matching information model is shown in Figure 1.

Figure 1 Animal food traceability process and information model
In order to ensure that consumers trace the entire process from the table to the farm, it is necessary to identify the animals with different labels in the six links in Figure 1, and manage the labeled animal food in each link and record the information in the map. .
1.2 The basic framework of the traceability system
The data of the traceability system is gradually generated in multiple links in the animal food production process, and is added to the traceability system in the corresponding links. The storage and management of a large number of multiple types of traceability information is difficult to achieve only through identification tags, and a combination of tags and data centers is needed to meet the complex needs of information management in the traceability system. Each product in the animal food processing link is uniquely identified through labeling technology, as shown in Figure 2. In each processing link, a corresponding information management platform is established, which collects the information of each product in the processing link and summarizes it in the food safety data center. In the whole process, there are special government agencies for supervision. Consumers can query all the production links and key information that the product has gone through from the data center according to the product label. Manufacturers at any link can trace the product upward and downward through the system, and the government can use the information in the data center. Establish an automated food safety monitoring platform.

2 Discussion on the application of organic RFID in animal food traceability system
Animal food involves many links such as animal husbandry, slaughter and processing, circulation and sales. The entire production process from the farm to the table is much more complicated than other foods. Therefore, the traceability information covers a wider area, a larger amount of information, and traceability. The frequency of conversion between information is higher. The use of electronic tags in the entire production and circulation links is still unrealistic based on China’s current economic foundation and industry development level. Different production links have different requirements for labeling technology, and can be flexibly selected according to needs.
2.1 Farm
After the livestock is born in the farm, the farm management platform generates a unique “production identification code” and registers the information in the food safety data center to establish a database of individual livestock information. The batch, feed, immunization, and quarantine of livestock during the breeding process are recorded in the food safety data center through the management platform. Since the two-dimensional bar code is susceptible to pollution and damage by livestock during the livestock breeding process, and the information entry link needs to register the labels of the livestock one by one, it is not suitable for multiple labels to be entered at the same time. Therefore, in the breeding process, it is suitable to use RFID tags as the carrier of the “production identification code”, and each RFID tag and the “production identification code” correspond one-to-one in the data center. Combining the breeding time of livestock and the life of inorganic RFID tags, inorganic RFID tags are used for livestock that have been bred for more than 1 year, and organic RFID tags are used for livestock that are less than 1 year. In the breeding process, organic RFID tags or inorganic RFID tags can be selected according to the needs. Although the cost of inorganic RFID is higher than that of organic RFID tags, the increased cost is acceptable for large animals due to the limited number of livestock in the breeding stage.
2.2 Logistics and transportation
In logistics and transportation, the basic information of the logistics enterprise and the basic information of the logistics are registered in the food safety data center through the logistics and transportation management platform. At this time, the RFID tag of the breeding link can still be used as the only identification for management.
2.3 Slaughterhouse
There are several production links in the slaughterhouse. The production process can be monitored according to the livestock’s identification. Each link is registered in the data center through the slaughterhouse management platform. Livestock in the slaughterhouse is slaughtered and then divided. The pre-segmentation management platform reads the “production identification code” of the meat to be divided, and generates multiple “slaughter identification codes” according to the quantity to be divided. Each slaughter identification code corresponds to the corresponding segmentation part, such as head, tenderloin, liver, etc. . The “slaughter identification code” and the “production identification code” are registered in the data center and a corresponding relationship is established. The “slaughter identification code” is then marked on the label and becomes the only identifier for a specific part of a specific livestock. Through the “production identification code”, the meat after segmentation can be traced, and the “slaughter identification code” can be traced to the animal before segmentation, which completes the transfer and transmission of traceability information from the whole animal to the meat.
After the meat is divided, each part needs a label for identification. The number of labels required is relatively large. The use of inorganic RFID tags will bring a great cost burden. Therefore, only batches can be tracked and managed. Of meat for individual tracking management. The use of very low-priced organic RFID tags or two-dimensional bar codes can solve the cost problem very well. However, the reading of two-dimensional barcodes is restricted and is not suitable for automatic reading of identification codes in multiple production links in slaughterhouses, and two-dimensional barcodes are easily contaminated and are not suitable for the needs of slaughterhouses. In view of the short duration of the slaughter process, the life span of organic RFID can meet the needs of this process. Organic RFID tags have the advantages of environmental adaptability, cost, reading methods, etc., and can play an irreplaceable role in the slaughter and segmentation links.
2.4 Warehousing logistics
Based on the analysis in 2.3, the “slaughter identification code” is used for information management in the logistics and warehousing link. Through the management platform, it summarizes basic logistics information, basic storage information, logistics temperature at multiple time nodes, storage temperature and other information to the information center, so as to realize the individualized process management of animal food in the logistics warehousing link.
2.5 Supermarket
Meat is continued to be divided in supermarkets. The supermarket management platform reads the “slaughter identification code” identified by the organic RFID tag, and automatically generates multiple identification codes according to the segmentation situation. “User identification code” and “slaughter identification code” are registered in the data center and a corresponding relationship is established. The “user identification code” is marked on the label. The number of “user identification codes” is very large. Due to cost reasons, inorganic RFID tags cannot be used, and only two-dimensional bar codes or organic RFID tags can be used. At this time, two-dimensional barcodes and organic RFID tags do not have obvious advantages and disadvantages, and can be selected according to the user’s habits.
2.6 Consumer
According to the user’s two-dimensional barcode or organic RFID tag provided by the supermarket, consumers can inquire about the product’s “user identification code” through the public inquiry system. According to the “user identification code”, the supermarket information can be queried, and it can be traced back to the “slaughter identification code”. According to the “slaughter identification code”, you can inquire about the transportation and storage information of the meat, the production information of the meat in the slaughterhouse, and it can be traced back to the “production identification code” of the meat. From the “production identification code”, you can inquire about the transportation and sales information of livestock, and various information about the breeding link. Consumers can trace the entire meat production process from the end product.
According to the characteristics and needs of different links of meat production, various labeling technologies have specific applicability, as shown in Table 2.

3 Conclusion
Organic RFID tags have the advantages of easy-to-use inorganic RFID tags and low cost similar to two-dimensional barcodes. Although they are inferior to inorganic RFID in terms of reading speed, capacity and service life, they are used in the application of animal food traceability. , These characteristics are not necessary for every link, which provides a space for low-cost organic RFID tags to play an active role.
The main links of the animal food safety traceability system include farms, transportation and logistics, slaughterhouses, logistics and warehousing, supermarkets and consumers. According to the characteristics of each link and its requirements for labeling technology, organic RFID is expected to be used in slaughterhouses, transportation and storage. Instead of inorganic RFID, organic RFID can also be used in the breeding and logistics transportation links for animals with a short breeding time, and organic RFID or two-dimensional tags can be selectively used in the supermarket link. The use of organic RFID will greatly reduce the cost of animal food traceability, thereby promoting the widespread use of animal food traceability technology.
[ad_2]





