Application of RFID in welding production line
[ad_1]
With the rapid development of the domestic automobile industry, the diversity of automobile products and the complexity of production processes have continuously improved the means of production information management. The application of car body recognition systems in automobile production lines has made automobile production more flexible and reliable. Order production becomes possible. This article introduces the application of RFID system in welding production line in detail with the application example of Roewe 350.
The use of vehicle body recognition system (AVI) in the automobile production line can collect statistics, quality monitoring and quality information of various models of production data in real time, and transmit it to material management, production scheduling, quality assurance and other related departments in a timely manner This plays an important role in the supply of raw materials, production scheduling, sales and service, quality monitoring and lifetime quality tracking of the entire vehicle, and mixed-line production of multiple models.
There are two main vehicle body identification systems currently in use, namely Barcode and Radio Frequency Identification (RFID). Here, this article will combine the application examples of Roewe 350 to introduce the application of RFID system in welding production line.
RFID system composition
A typical RFID system includes a code carrier TAG (data carrier or data storage), a code carrier read/write (R/W) device, and an interface module (Interface).
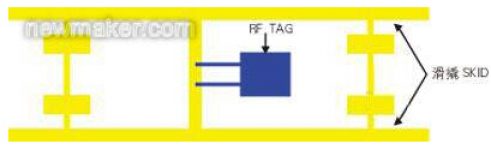
In the welding workshop, the conveying equipment is a skid conveyor (Skid-Conveyor, see Figure 1), and the code carrier TAG is fixed on the skid carrying the workpiece and runs with the workpiece from beginning to end. This actually forms a mobile database that moves with the workpiece, and the workpiece becomes a “smart workpiece” that carries the database with you throughout the production process.

Figure 1 Skid conveyor in the welding workshop
According to the process and production management needs, a code carrier reading and writing station can be set up at the starting position of the skid in the welding workshop, the fork of the workpiece logistics, and the entrance of important technological processes (such as robot welding and robot assembly). The code carrier reading and writing station is composed of a workpiece position detection switch, a code carrier reading/writing device, a communication interface module and a man-machine interface.
The process of reading the data of the code carrier is: after the workpiece position detection switch detects that the workpiece is in place, the code carrier reading and writing device starts to automatically read the data stored in the code carrier installed on the skid and transmits the data to the PLC. Display on the man-machine interface; PLC will process the obtained data information to determine the next step of the process flow.
The process of writing data to the code carrier is: after the workpiece position detection switch detects the signal of the workpiece in place, the work piece stops, and the code carrier read-write device writes the vehicle model data scanned by the previous bar code scanner into the code carrier, and The result of this operation is displayed on the man-machine interface.
Through the above read/write operations on the code carrier installed on the skid, all information is uploaded to the workshop production process monitoring system (PMC) through the PLC for further processing and calculation, so as to realize the tracking and production process of the entire workshop workpiece logistics control.
It can be seen that RFID is a decentralized data storage system. In the entire process, all or part of the workpiece information is stored in the code carrier, and the code carrier read-write device is used to read the work piece information, and then perform correlation Operation. The advantages of this method are flexible configuration, fast response speed and lower requirements for system communication. In addition, in this way, it is not necessary for all the reading and writing devices to communicate with the main database, so the failure of communication with the main database will not cause the stop of production.
RFID system performance
The following properties are generally considered when selecting a radio frequency identification system in a body shop:
1. The storage capacity of the code body
Ranging from tens to tens of thousands of bytes, the larger the storage capacity, the higher the cost; when used in the body shop, generally, the storage capacity of the download code body can meet the requirements by choosing a few thousand bytes.
2. Reading distance
The reading and writing distance refers to the normal working distance from the surface of the code carrier reading/writing device to the surface of the code carrier. Generally, when it is used on a skid conveyor, it is only necessary to select 30-150mm.
3. Data transfer rate
Including the reading and writing rate of the code carrier reading/writing device and the communication rate between the reading/writing device and the PLC.
4. Working environment
There are many welding stations in the body shop, and the welding spatter is large, so the code carrier needs to have a certain degree of protection and temperature resistance.
5. Interface form
The interface form that can be easily connected with PLC, bus, etc. should be selected. At present, there are mainly interface forms such as RS232/485 and fieldbus.
Application in welding production line
The RFID widely used in the Roewe 350 welding production line is the HMS series of American EMS company. The code body model is HMS150, the read/write head model is HF-ANT-1010-01, and the read/write head network adapter model is HF-CNTL. -DNT-01.
1. System overview
The system uses Rockwell Guardlogix 1756-L62S as the main control unit, Rockwell 2711P-T12C4D2 as the data operation man-machine interface, and HF-CNTL-DNT-01 forms a relatively independent Devicenet network through the 1756-DNB module of the PLC. The identification system PLC transmits all the information of the identification system to the skid conveyor system PLC, the welding station robot and the workshop PMC system through the industrial Ethernet to realize the management of the production information of the entire welding workshop. The process of Roewe 350 data transmission system is shown in Figure 2.

Figure 2 Flow chart of Roewe 350 data transmission system
2. System hardware composition
(1) The car body recognition system PLC completes the internal control of the car body recognition system through the Devicenet network, and transmits relevant data and car body information to the skid conveying system and the control system of each area through the industrial Ethernet, and participates in the control of the corresponding area , And at the same time transmit this information to the monitoring system of the central control room for display and printing.
(2) On-site reading and writing station (R/W Station) Each on-site reading and writing station is equipped with a touch screen (HMI) and interface module. The touch screen mainly completes the car body sequence number, skid number, car body color, whether it is sunroof and model Information writing, reading, display and modification. The interface module (HF-CNTL-DNT-01) mainly processes the information to be written or read by the read-write head HF-ANT-1010-01, and sends this information to the CPU of the PLC through Devicenet for processing. The reading and writing stations set up on site mainly include:
UB60 read-write station: set the initial station on the car body to the skid, when the detection switch detects that the car body is in place, the read-write station only performs write operations, and writes the vehicle model information transmitted by the PLC in the engine compartment area into the TAG ; The model data of the engine compartment is the data obtained by manually scanning the bar code of the model. The scanned data is transmitted to the control PLC in the engine compartment area through the Ethernet, and the PLC in the engine compartment area writes this data in the UB60 station through the Ethernet. In the prying code body.
UB70, 80, 90, MB20, 30, 40, 50, 90, 130, 140, 160, 180 and 190 reading and writing stations: these stations are all robot welding stations. When the car body is in place, the reading and writing station will read Skid the vehicle type information in the code body, and transmit the read result to the control PLC of the station. According to the different vehicle type information, the PLC then controls the robot to call different user programs through the Ethernet, thereby realizing the mixing of multiple vehicle types. Line production.
UB120 reading and writing station: this station is an inspection station, with the functions of out and in. When entering a car body again, manually write the model information on the HMI, and the reading and writing station will write this information into the code carrier; during normal production, considering that the roof of the MB10 station needs to be assembled, it needs to be identified as a sunroof It is still not a skylight, and combined with the beat and other reasons, the UB120 reading and writing station also needs to perform the reading function, and the UB120 station will also perform manual scanning again to compare the scanned data with the data read by the read-write head. Ensure that the data will not be wrong to ensure the correct assembly of the MB10 station.
MB110, 120 and 240 reading and writing stations: these 3 stations are all lift stations, and the car can be temporarily taken off the line at the lift, or the car body can be temporarily inserted on the line. Therefore, these three stations are equipped with When the writing station is temporarily inserted into the car body on the line, the car body information is first input into the control PLC on the HMI, and the PLC controls the read-write head through Devicenet to write this information into the code carrier of the skid.
(3) Code carrier (RF TAG) The code carrier adopts HMS150 with protection class IP65, and the code carrier is installed on each skid. All the information of the stored car body is recycled in the welding workshop along with the technological process.
In addition, some production line RFID systems use read-only code carriers. This system operates similarly to barcode recognition systems, but the accuracy of data reading is higher than that of barcode recognition systems, and it is more able to withstand harsh environments. The advantage is that the system cost is lower than that of a readable and writable identification system. According to statistics, due to environmental factors and maintenance conditions, the accuracy of barcode recognition system data reading is less than 90%, while the RFID system can almost reach 100%.
Concluding remarks
The application of the car body recognition system on the car production line makes it possible to make car production flexible and to order production. The car body information file will also accompany the whole process of a car from manufacturing to sales to after-sales service. Production management and after-sales service provide strong basic data, and provide first-hand information for lifetime quality tracking and accident analysis of the entire vehicle. At present, major domestic automobile manufacturers (such as Shanghai-Volkswagen, Shanghai GM, and FAW-Volkswagen, etc.) are using body recognition systems in their main production workshops such as welding, painting and final assembly.
[ad_2]