Ping An Bank “Supply Chain Finance + Internet of Things Technology”
[ad_1]
1. Case background
In recent years, due to the slowdown in macroeconomic growth and the weakening of commodity prices, commodity industries such as steel and coal have fallen into adjustments. The trust among banks, borrowers, and loan regulators has dropped sharply. The traditional commodity financing business models that banks have used for many years, such as warehouse receipt pledge and interconnection and mutual insurance, have been challenged unprecedentedly. Deterioration of industry credit has led to companies. Generally caught in financing difficulties. However, objectively, the real economy still has a huge demand for bulk commodities. Ping An Bank’s plan is ahead of schedule during the downturn in the industry. United Perception Group has introduced sensing devices and intelligent supervision systems such as sensing covers and other Internet of Things sensing devices to rebuild mutual trust between all parties in the pledge of movables. The movable property financing business is recovering steadily, and ultimately hopes to use the Internet of Things technology to reinvigorate the trillion-level blue ocean market of commodity financing.
2. Case analysis
(1) “Supply Chain Finance + Internet of Things Technology” Operation Mode
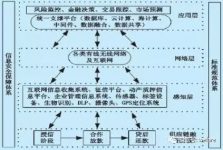
The “supply chain finance + Internet of Things technology” model mainly uses GPS, biometrics and other means to identify, locate, track, monitor and other systematic and intelligent management of movable property inventory, and then conduct data aggregation and analysis to enable customers and supervision Participants such as parties and banks can fully perceive and supervise the existence and changes of movable property from the two dimensions of time and space, and conduct risk monitoring and market forecasting. This kind of supervision of movable property without missing links greatly reduces The risk of chattel pledge. The specific operation mode of supply chain finance and Internet of Things technology is shown in the figure below.
Figure 1 “Supply Chain Finance + Internet of Things” model

As of the end of 2016, Ping An Bank has deployed a “supply chain finance + Internet of Things technology” model in multiple fields such as steel and automobiles. The following is a selection of more well-developed and typical models of automobile production and sales supply chain financing business for analysis.
(2) Analysis of financing business of automobile production and sales supply chain
1. Business process
(1) Develop the “movable property pledge identification and tracking system”. The “Mobile Property Pledge Identification and Tracking System” consists of an interactive smart RFID tag with anti-disassembly function installed on the vehicle and a (2.4G) RFID card reader and wireless camera installed in the parking lot. The RFID card reader is responsible for identifying, supervising and assisting positioning of vehicles with RFID tags in the management area. The wireless camera is responsible for managing the video recognition and auxiliary management of the vehicle. The transmission control system is composed of a wireless local area network responsible for local data transmission and control and a 4G mobile network responsible for remote data transmission and control. Together, the acquired data information is safely transmitted back to the supply chain financing bank. In the security application system, the CA certification center of the head office of the financing bank is responsible for the issuance, management, and cancellation of digital certificates of commodity electronic tags and other system equipment (card readers, cameras, wireless transmission control equipment), and the legality of electronic tags and system equipment Perform authentication and realize encryption and decryption of data transmission to ensure the security of the entire system. The above system can be connected with the existing “credit ledger system” to realize real-time tracking of movable property pledges.
(2) Sign a cooperation contract (agreement). The Supply Chain Finance Bank signed the “Entrusted Agent Payment Contract” with the brand car manufacturer; signed the “Loan Contract” and “Auto (Moveable Property) Pledge Contract” with the brand car dealer; signed the “Automobile” with a national logistics company that has a strategic partnership (Moveable Property) Pledge Service, Freight Outsourcing Contract.”
(3) Issue a digital certificate and confirm the sales contract. The CA certification center of the head office of the financing bank will issue digital certificates to brand car manufacturers and brand car dealers. When a brand car dealer submits a purchase contract to a brand car manufacturer via the Internet, it will use the digital certificate in hand for signature and encryption; when the brand car manufacturer receives the purchase contract, it will use the digital certificate in hand for verification and signature confirmation , To complete the signing of the supply and marketing contract between the two parties. After the financing bank receives the supply and marketing contract containing the signatures of both parties, it will verify the signatures of both parties through the CA certification center of its head office to confirm the authenticity of the transaction contract.
(4) Carry out on-site pledge operations of cars. Brand car manufacturers submit complete product information and sales contract information to the supply chain financing bank after completing product production. After receiving the above information, the supply chain financing bank uploads it to the CA certification center of its head office together with the car pledge information, and independently generates a corresponding electronic label for each pledged vehicle. The CA certification center transmits the electronic label information to the cooperative logistics company. After the latter completes the update of the electronic label and the information of the smart identification sensor device, it will install the “smart label” on the car to be shipped to the 4S shop at the brand car manufacturer , Thus completing the on-site pledge operation of the car. Then the logistics company notified the supply chain financing bank via the Internet, and the supply chain financing bank immediately activated the “movable property pledge identification and tracking system” to scan the pledge and confirm the status of the pledge. After confirming that they are correct, the supply chain financing bank will issue loans to brand car dealers in accordance with the “Loan Contract”, pay the brand car manufacturers in accordance with the “Entrusted Agent Payment Contract”, and in accordance with the “Auto (movable property) pledge service, freight The “Outsourcing Contract” stipulates that the logistics company is required to transport the car (collateral) to the brand car dealership agreed in the contract.
(5) Real-time monitoring of cars in brand car dealers. According to the specific conditions of the parking lot of the brand car dealers, a national logistics company with a cooperative relationship will first install wireless (2.4G) RFID card readers and wireless cameras on the premises. After the car arrives at the parking lot, the logistics company will park the car in a location that can be covered by wireless (2.4G) RFID card readers and wireless cameras, and transmit the information of the received goods to the supply chain financing bank via the Internet. After receiving the information, the supply chain financing bank activates the “movable property pledge identification and tracking system”. The UHF card reader and wireless camera installed in the parking lot capture the information, confirm the pledge for the first time, and update the location information of the movable property pledge. It also launched the real-time monitoring service of the “Pledged Movable Property Recognition and Tracking System”, and regularly provided the latest data of the pledged property (automobile) of the movable property to the “Credit Ledger System” of the financing bank.
(6) Supervise and urge repayment. When the car leaves the monitoring site or the car dealer disassembles the interactive smart RFID tag, the “movable property pledge recognition and tracking system” defaults to the brand car dealer having completed the sale of the vehicle, and then sends the information of the vehicle sold to the financing bank through the Internet. The financing bank prompts the auto dealer to repay part of the loan in accordance with the time and amount stipulated in the “Loan Contract” and the “Auto (Moveable Property) Pledge Contract” signed with the brand car dealer. After the brand car dealer has returned part of the loan, the bank issued an instruction to the cooperative logistics company, requesting the logistics company to take back the wireless UHF card reader in accordance with the “Auto (movable property) pledge service, freight outsourcing contract”, and release the pairing through special equipment. Supervision of vehicles, while updating the information on the “Credit Ledger-Movable Pledge Status”.
2. Business innovation
Commercial banks have established “CA Certification Center” and “Interactive Smart Electronic Labels” with professional Internet of Things technology manufacturers to provide digital certificates (digital certificates for individuals, devices, etc.) issuance and management, as well as a full range of security services such as security authorization and document encryption .
3. Identification of emerging risks in supply chain financing under the Internet of Things financial model
Judging from the current development, the role of the Internet of Things in the field of supply chain financial services is still tending to develop in a favorable direction, but this does not mean that there will be no risks in the future development process. Traditional supply chain financing risks under the Internet of Things financial model are controlled to a large extent, but at the same time, various new risks will inevitably arise. According to the hierarchical structure of the Internet of Things finance, emerging risks can be divided into three categories: perception-level risks, network-level risks, and application-level risks.
(1) Perceived risk
The accuracy, completeness, and comprehensiveness of the information collected by the perception layer are the main concerns of its risks. Therefore, the inefficient operation of various information sources and the failure or failure of related detection equipment will directly lead to the occurrence of risks. According to the three stages of supply chain finance, relevant data of the borrowing company needs to be obtained during the credit granting stage. The possible risks are: unreliable e-commerce data, incomplete platform data, and inaccurate market information. The cooperative lending stage mainly occurs in the pledge acceptance stage, and may face risks such as: the risk of quality inspection equipment failure, the risk of untimely and inaccurate monitoring, the risk of untimely response, the risk of loss of goods, and the risk of delivery failure. In the post-loan repayment stage, in addition to the risks in the cooperative lending stage, there are also risks of untimely tracking of financing projects and incomplete collection of market information.
(2) Network layer risk
The network layer mainly uses Internet technology to transmit the data obtained from the perception layer over long distances. Due to the incomplete related technologies and standards, many risks have arisen. The main risks faced are: information leakage risk, information delay risk, information encryption risk, information loss risk, information asymmetry risk, IoT standard risk, malicious interference risk, network instability risk, these risks will cause the application layer to fail to obtain timely Comprehensive, accurate, and objective data information has a major impact on subsequent data processing and scientific decision-making.
(3) Application layer risk
The application layer processes the acquired data and provides services such as risk monitoring, financial decision-making, transaction tracking, and market forecasting. The risks at this level are mainly the risks arising from the cooperative operation of the participating parties and the possibility of disrupting the state of cooperation. They mainly include: business secret leakage risk, intellectual property protection risk, data mining efficiency risk, data fusion risk, and cooperation risk of all participants. , Internet of Things management risk, socio-economic risk, policy and regulation risk, organizational management risk.
Four, banking business marketing advice
Through the above analysis of the “supply chain finance + Internet of Things technology” model, banks should pay attention to the following points:
(1) Improve IoT technology
As a “visual tracking” technology platform, the Internet of Things can effectively help banks and customers to track and supervise the operation and income of related financial service products in a timely manner. It can formulate scientific research in the first time according to the operation of the market. Management and operation actions, thereby reducing the income risk caused by market fluctuations in the process of financial services. However, judging from the current technological level, while the Internet of Things brings convenience to supply chain finance, it also has a lot of technical risks. Therefore, banks should focus on improving the Internet of Things technology in the future.
(2) Pay attention to the technical level of related equipment
At the perception layer, the failure of related detection equipment may cause problems such as unreliable data and loss of goods. Therefore, while applying the Internet of Things technology, it is necessary to strictly limit the technical level of its related equipment to minimize the risk at the perception layer.
(3) Horizontal expansion of the covered industries of IoT finance
In 2016, Ping An Bank continued to use the automotive industry as a breakthrough point, gradually covering the Internet of Things movable property financing to non-ferrous metals, energy, building materials, mining products, agricultural products and other industries, striving to create a “Internet of Things + Supply Chain” commodity finance paradigm . Therefore, other commercial banks can cooperate with large-scale production companies, trading platforms, and warehousing and logistics companies in many fields to cover “Internet of Things + Supply Chain” finance to multiple industries.
[ad_2]




