Application of RFID-based Intelligent Bus Dispatching Management System
[ad_1]
1. System Overview
1.1. System background
With the rapid development of my country’s economy and the trial implementation of smart city policies, the scale of urban construction is expanding day by day, and urban traffic problems have become increasingly prominent, which has become one of the key issues that have severely restricted the development of many large and medium-sized cities. Vigorously and prioritize the development of public transportation, realize digital and intelligent urban traffic management, improve the efficiency of public transportation operation management and social service levels, and conform to the current development trend of modern large cities in China.
1.2. Status Quo and Analysis
The urban public transportation system basically still adopts the manual dispatching method of “fixed departure and stuck at both ends”. Dispatchers cannot understand the status of operating vehicles in real time, and it is difficult to take dispatching measures in a timely and effective manner. Bus dispatching is in the status quo of “invisible and inaudible”, with greater blindness and lag. As a result, the driving speed of public transportation vehicles is reduced, the driving interval is not balanced, and the phenomenon of “crossing” and “large gaps” often occur, which seriously affects the service quality of public transportation passenger transportation. People waiting for the bus cannot know the running status of the bus they are waiting for in time, and do not know how long they will have to wait for the bus to be taken.
The bus dispatching management system is the core component of the intelligent transportation system. It adopts advanced information and communication technology to collect dynamic and static road traffic information and conduct real-time analysis. According to the analysis results, the vehicle’s driving route, travel time, and To make full use of the limited traffic resources, improve the efficiency of the use of vehicles, but also to understand the operation of the vehicles and strengthen the management of the vehicles. RFID technology, as an effective means of information collection in the traffic dispatch system, will play an important role in the traffic dispatch management system.
2. System Introduction
2.1. System Principle
Use willRFIDTechnology, electronic map and wireless network technology to build a public transportation management system can realize long-distance bus collection information without stopping; automatic and accurate display of entry and exit information. Make the bus dispatching system accurately grasp the real-time dynamic information of buses entering and leaving the bus parking lot. Through the implementation of this system, the management level of buses can be effectively improved. The collected data can be researched and analyzed by computer, and the rules of vehicle operation can be grasped, the loopholes in vehicle management can be eliminated, the intelligent management of buses can be realized, and the image of the city can be improved. Thereby improving the management level of urban public transportation operation and dispatch.
Intelligent bus dispatching includes the management of bus terminals, bus stops, and bus driving routes.
Bus terminal management
The reader is installed at the entrance and exit of the terminal. When the tag is read, the information of the tag is obtained for back-end comparison, which can control barriers, etc., to realize remote identification of entering and leaving the bus terminal.
Bus stop management
The reader is installed near the platform. When the bus enters the station, the tag is read by the reader, and the data is transmitted to the dispatch center through wireless or wired means.
Bus route management
Readers are installed in overpasses, viaducts and other locations. When the bus passes through this section, the information from the tags read by the reader will be transmitted to the dispatch center to monitor the correctness of the bus route.
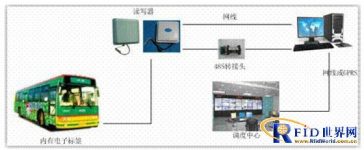
2.2. System topology diagram

|
Figure 1 Topology diagram of terminal management |
2.2.1. Bus terminal management
Each bus will be issued with a tag with a globally unique identification code and registered by the system. When the bus enters the parking lot, the tag on the bus will be automatically obtained by the reader installed at the entrance and transmitted to the background computer for processing. The background computer records and processes this information, records the vehicle’s entry time and vehicle-related information, and the background determines which parking space the vehicle should be parked in, and feeds this information back to the LED display at the entrance. Through the LED display, the driver can know which parking space should be parked and some additional information, such as the next trip time (this time is the result of automatic calculation by the background computer) and so on. When the bus leaves the field, based on the same working principle, the back-end system records the time and other information of the field and writes the records into the back-end database.
2.2.2. Bus station management

When the long-distance reader installed at the bus station receives the signal of the tag, the reader sends the tag signal to the designated data processing terminal through the network cable (or GPRS), and judges that the bus is entering the station; when the reader cannot read When the signal of this tag is taken, it is judged that the bus is leaving the station; the judgment result can be connected with the in-bus broadcast system to control the voice broadcast, and then the bus door opening and closing signal can be used to accurately determine the status of the bus has stopped and will leave the station.
2.2.3. Bus route management
When the bus travels through the overpass where the reader is installed, the reader reads the tag information and transmits it to the dispatch center for processing to determine whether the bus deviates from the driving route, traffic conditions, etc., effectively realizing remote monitoring and dispatching.
2.3. System structure
2.3.1. System composition
The intelligent bus dispatching system based on radio frequency identification technology provides relevant data for bus scheduling, dispatch monitoring and passenger information services by collecting the location information of operating bus vehicles. Its composition mainly includes front-end information collection unit, bus dispatching center, and terminal There are three parts of the service unit, and the frame structure is shown in Figure 3.

1) The front-end information acquisition unit is used for data communication between the on-board electronic tag and the bus station reader;
2) The bus dispatch center is used to analyze, process, and forward the data collected;
3) The terminal service unit is used to realize the issuance of dispatching commands and the issuance and query of vehicle operation information.
Data collection part
Install integrated readers on the flyovers, advertising poles, telephone poles near the platform (for easy access to electricity and lower investment) or above the platform, as well as the entrance and exit of the bus yard, to read the traffic of vehicles passing through the station or entering and leaving the venue. The data (vehicle identification code) stored in the electronic tag is shown in Figure 4.
Data transmission part
Upload the collected data to the bus dispatch center in real time via wired network cable or wireless GPRS.
Data processing part
Through the analysis and processing of the uploaded data by the dispatch center server, the integrated and intelligent monitoring, dispatching and management of operating vehicles are realized.

2.3.2. Functional composition

Figure 5 Information flow chart
Through the monitoring and management of the bus terminal and bus station, the intelligent bus dispatching can be effectively realized. As shown in Figure 5, there is vehicle information in the electronic tag. When the reader reads the electronic tag, it can obtain the current time, bus license plate number, and type; the dispatch center analyzes and calculates the information transmitted by the reader , It can effectively monitor the vehicle location, driving speed, and traffic flow status; the dispatch center sends the latest bus information to the electronic display board of each station, which shows the estimated time of the bus arrival at the station, the distance to the station and the current status of the traffic flow, and judges whether there is an increase, Reduce the number of vehicles, or increase or shorten the interval between departures, and implement the dispatch of buses in the bus station.
3. System flow
1) When the bus is approaching the station, the RFID reader installed at the station receives the signal sent by the electronic tag attached to the bus, and it is judged as the entry stage. GPRS will transmit the vehicle information, arrival time and other information to the bus The station dispatching center updates the LED display content of the station signs at each station at the same time.
2) After the bus leaves the station for a certain distance, it no longer receives RFID signals. The RFID signal from presence to absence can be identified as the inter-station driving stage. According to the code of the station just left, the next station number is judged, the corresponding information is calculated, and the next station sign LED is displayed.
3) During the course of the bus, when passing a certain route monitoring point, the reader/writer at a certain position of the overpass or route receives the RFID signal, and can judge whether the driving route is correct, the road condition, etc.
4) Repeat steps 1) to 3) when entering the next station.
5) The bus dispatch center can know the current status of the bus according to the process of 1) to 4), and at the same time can make reasonable dispatch according to the status of the bus.
4. System Installation

|
Figure 6 Example diagram of terminal installation |
The reader’s tag reading distance is limited to less than 10 meters, and the speed of the vehicle should be less than 60 km/h. The electronic tag should be installed behind the windshield of the car or in a suitable place in the car. The reader/writer of the bus terminal is fixed on the side of the aisle or suspended on the top of the passage with a stainless steel column. The reader/writer of the bus station is installed on the utility pole near the platform (for easy access to electricity and lower investment) or above the platform. The installation can be based on Adjust the actual situation on site to the best height and angle from the ground.
If UHF tags are used, they can be installed on the upper right corner of the windshield or on the top of the back of the bus; if they are usedActive tag, The label can be installed in a certain position in the bus, but it must be ensured that it cannot be shielded by the iron box.
5. System Features
5.1. Wide range of applications
The main disadvantage of the inductive buried coil is that it can only collect traffic flow information but cannot identify and track specific vehicles, so its application range is limited. The RFID technology just makes up for this shortcoming of the buried coil.
5.2. The signal is stable
When GPS satellite positioning encounters many high-rise buildings and dense road sections, the signal is severely weakened. When there is no signal when the viaduct or tunnel is blocked, the GPS system signal will be unstable or even unable to work normally. The active reader/writer has a stable distance and is not easily affected by the surrounding environment. Moreover, the active tag can effectively break through the shielding effect of the automobile’s explosion-proof metal mesh, and smoothly exchange data with the reader. Of course, RFID technology is inferior to GPS in terms of flexibility, but it is sufficient to meet the industry needs of public transport under the characteristics of fixed lines and fixed stations.
5.3. Low cost
Compared with GPS requiring expensive on-board equipment, a system based on RFID technology can move the main identification and communication equipment from the vehicle to a fixed ground data collection point. Because the number of collection points is far less than the number of vehicles that need positioning services, the required investment in the traffic information collection network is much less than the investment in installing GPS equipment for many vehicles.
5.4. Strong anti-interference ability and fast response speed
Self-developed unique data processing technology, accurate and fast identification card, effectively solve the problem of co-frequency interference, solve too many cards at the same time, reader data conflicts cause misreading, missed reading of the identification card, resulting in inaccurate feedback information The exact question.
5.5. Avoid human operation loopholes
The management of the entire process eliminates human intervention, minimizes the operating cost of the system and reduces the inevitable losses caused by manual operations.
Applications:
Shenzhen Bus Company

[ad_2]



