Exploring the application of radio frequency tags (RFID) in mobile base station equipment management
[ad_1]
“Resilient network construction” that closely cooperates with market changes is the focus of mobile operators’ communication network construction; network equipment dismantling to make up for busyness and base station carrier adjustment are important means of “resilient network” construction, realizing real-time and accurate management of mobile base station equipment A major difficulty in the construction of “resilient networks”.
RFID (Radio Frequency Tag) technology is widely used in retail, medicine, transportation and other fields, and it is infiltrating into various traditional industries. At present, material and equipment management is one of the fastest growing areas of RFID technology. Many companies have adopted RFID tags and materials The integration of equipment management systems can automatically, real-time, and intelligently realize the management of complex materials and equipment mobilization. In this context, the Guangdong branch of China Mobile Communications Corporation took the lead in domestically trying to introduce RFID technology into the management of its base station communication equipment to achieve efficient, real-time, and accurate equipment transfer management.
This article will mainly introduce the ideas, technical solutions and technical difficulties of RFID used in base station communication equipment management for communication equipment management.
1. Background and significance
Every year, Guangdong Mobile has to carry out a large number of network equipment disassembly and replenishment, base station carrier adjustment work, and hundreds of thousands of new equipment are connected to the grid. The above reasons make the management of equipment transfer and asset inventory extremely difficult! The traditional manual front desk and computer backstage equipment asset management method is increasingly unable to meet the needs of the actual situation. The traditional front desk is still carried out manually. On-site inventory, hand-copying, entry, and summary are performed. After a variety of manual participation, the collected equipment asset information can be imported into the back-end computer database. A large number of manual participation in equipment asset management has caused problems such as complicated processes, long time, poor real-time performance, difficult management, and high error rate, which ultimately reduced equipment utilization and increased operating costs.
With the development of the company, Guangdong Mobile is facing the problem of how to efficiently and scientifically manage a large number of communication equipment. Therefore, Guangdong Mobile hopes to use the new technology of RFID to realize remote, dynamic and real-time equipment asset data collection, replacing the front-end manual data collection of traditional asset management methods, and better combining with back-end computer databases to form fully intelligent equipment assets. Management system, thereby greatly improving equipment utilization and reducing operating costs.
2. General introduction of technology
RFID technology is one of the fastest-growing high-tech technologies in the 21st century. With the integration of traditional networks, RFID technology shows great market application potential, and is called “Internet of Things” and “Second Generation Internet”.
RFID is the abbreviation of Radio Frequency Identification in English. Radio Frequency Identification is an automatic identification technology that began in the 1990s. RFID technology uses radio frequency to perform non-contact two-way data between the reader and the radio frequency card. Transmission in order to achieve the purpose of target identification and data exchange. Compared with the traditional barcode, magnetic card and IC card, the radio frequency card has the characteristics of non-contact, fast reading speed, no wear, no environmental influence, long life, easy to use, and has the function of anti-collision. It can handle multiple cards at the same time. card. In foreign countries, radio frequency identification technology has been widely used in many fields such as industrial automation, commercial automation, transportation control management, and asset management.
1. System composition
The most basic RFID system consists of three parts.
Tag (i.e. radio frequency card): It is composed of coupling elements and chips. The tag contains a built-in antenna for communication with the radio frequency antenna.
Reader: A device that reads (and can also write in the card reader) tag information.
Antenna: Transmit radio frequency signals between the tag and the reader.
2. Standards and classifications of radio frequency cards
At present, many companies that produce RFID products adopt their own standards, and there is no uniform international standard. Currently, several standards available for radio frequency cards are ISO10536, ISO14443, ISO15693 and ISO18000. The most widely used are ISO14443 and ISO15693, both of which are composed of four parts: physical characteristics, radio frequency power and signal interface, initialization and anti-collision, and transmission protocol. Including 13.56MHz, 800MHz, 2.4GHz and other frequencies.
RFID products currently produced are mainly divided into two categories: active (active) and passive (passive).
*Passive tags
The passive tag does not have a battery inside and can only work with energy provided by the outside world. When the electronic tag enters the working area of the system and the antenna receives a specific electromagnetic wave, the coil will generate an induced current, and then the rectifier circuit will supply power to the tag. Passive tags have a short reading distance (a few centimeters to 5 meters). Long-distance reading and writing need to increase the transmit power of the read head and increase the receiving sensitivity to be reliably recognized. Passive tags have a long life and low cost, but the price of the read head is higher.
*Active tag
The active tag has a battery inside, and the tag actively transmits signals. The reader does not need to transmit power. The tag power is generally less than 5mW. It can recognize multiple target systems at the same time, and can recognize high-speed moving targets of 100km/h. The recognition range is adjustable from 1 to 100m. The life of the active tag is affected by the battery and the cost is higher, but the price of the read head is lower.
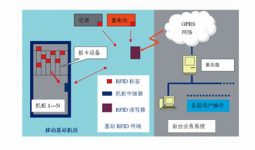
Taking into account the strong electromagnetic shielding, high power control requirements and identification distance needs of base station communication equipment, we chose active RFID tags as the application technology of base station asset management as the direction of exploration. The system structure is shown in Figure 1.

Active RFID base station monitoring equipment consists of RFID readers (including microwave antennas and read-write controllers), electronic tags installed on communication equipment (such as carrier boards), and cabinet relays on metal shielding equipment (such as cabinets) Maker composition.
The RFID reader is a read-write controller for asset electronic tags and cabinet repeaters. It is composed of encryption circuits, codec circuits, and microwave communication controllers. It uses RFID communication protocol data exchange methods and microwave wireless transmission methods. After receiving the tag information, the data can be transmitted to the background system through GPRS, wired transmission and other means to realize remote, real-time, and dynamic collection and analysis of equipment asset conditions.
Electronic tag is a mobile device identification device with microwave communication function and information storage function. The asset electronic tag itself has a unique ID number, which can be used as a carrier for asset information identification and monitoring by binding the ID number to the background data of a specific asset.
The cabinet repeater is also a mobile device identification device with microwave communication function and information storage function. In addition to the function of electronic tags, it can also be used as a shielded signal relay function.
It is planned to adopt active tags with a frequency of 2.4GHz. The radio frequency card adopts advanced embedded microprocessors and under the control of embedded software to realize functions such as sleep, wake-up, decoding, encoding, communication and information collision processing. Its characteristics:
●Read and write;
●Built-in CPU, support online download of programs;
●Intelligent two-way communication, with intelligent I/O interface, can input external temperature, humidity, access control sensor and other signals;
●With key calculation, good security and confidentiality;
●Efficient built-in ultra-thin power supply, working life of 10 years;
●High sensitivity, low emission power (0.1~1mW), only equivalent to 1% of Bluetooth power, almost no electromagnetic pollution harmful to human body;
●The communication distance is generally 1~100m, and under special circumstances, the recognition distance can be lengthened;
●Strong anti-interference, can identify more than 200 markers at the same time;
●The data transmission speed is fast, reaching 1Mbit/s.
The label is about 5*5cm in size and weighs less than 20g.
3. Technical difficulties and solutions
The main technical difficulty of the system is how to obtain the ID numbers of all communication equipment accurately, correctly and in real time in a harsh environment. Since communication equipment is mostly placed in each base station, the conditions of the base station environment and the equipment placement environment are relatively harsh for wireless electronic products, which are mainly reflected in the following aspects.
●Electromagnetic compatibility
In order to avoid the impact on the normal operation of the base station, Guangdong Mobile has strict restrictions on the use of electronic equipment in the base station. For the difficulty of electromagnetic compatibility, the following methods can be used to solve.
Staggered frequency: The frequency band of base station equipment is between 880~915MHz and 1710~1785MHz. The planned active RFID frequency band is 2400MHz, avoiding the GSM frequency band, and also has a certain protection bandwidth with the 3G frequency band.
Adopt spread-spectrum method: use spread-spectrum RFID tags to reduce the power spectral density.
Reduced power: The use of active RFID tags can greatly reduce the system power. Passive tags generate current through induction and require the reader to emit strong power. Using active tags, the power can be reduced to less than 3mW, and the use of high-sensitivity RFID readers can solve the problem of electromagnetic compatibility in the base station.
●Electromagnetic shielding problem
Many important equipment and sections in the base station need to be managed, but many equipment is placed in a metal cabinet (such as base station carrier, etc.), and electromagnetic shielding is relatively serious. In this way, the RFID tag placed in the metal cabinet cannot transmit information to the reader. The solution of using a signal repeater in the metal cabinet can solve the problem of electromagnetic shielding. In addition, through the use of repeaters, the transmit power of the RFID tags in the cabinet can be further reduced, which is expected to be reduced to within 1mW.
The repeater is about 5*15cm in size.
Four, concluding remarks
Based on the above ideas, Guangdong Mobile has begun to conduct tests and experiments on the application of RFID in the management of communication equipment, and has obtained a wealth of test data, laying a foundation for further applications. If the technology proves to be feasible, it can realize remote, real-time, dynamic, and fully intelligent communication equipment asset management after it is applied, thereby greatly improving equipment utilization and reducing operation and management costs.
[ad_2]