RFID solution for grain storage warehouse management
[ad_1]
The increasingly fierce market competition, improving production efficiency and reducing operating costs are of vital importance to business units. At present, warehouse management systems usually use barcode labels or manual warehouse management documents to support their own warehouse management. However, the bar code’s characteristics such as easy copying, non-fouling, non-moisture-proof, and cumbersome operation, and the cumbersome nature of manual writing of receipts, are prone to human errors and losses, which make the current domestic warehouse management always have defects.
1. The problems faced by the storage management of grain storage depots
At present, most of the storage management of grain enterprises such as grain storage depots is in the stage of recording and tracking grain in and out of non-automated paper document-based systems. The following problems exist:
(1) There are many types of grains. Many different types of grains often enter the warehouse at the same time when entering the warehouse. When leaving the warehouse, each order often requires several packages of different types of grains. At this time, the method of manual counting and inbound and outbound is adopted, and the error rate is very high.
(2) When performing inventory counting, manual counting and counting is adopted, and the error rate is also very high, and it is difficult to achieve consistency between the physical object and the book.
(3) The uncertainty of human factors leads to low labor efficiency and serious waste of human resources. At the same time, with the increase in the quantity of grain and the sharp increase in the frequency of in and out of the warehouse, this mode has seriously affected the normal operation efficiency.
(4) Traditional management methods make it impossible for the grain depot’s inbound and outbound data and inventory data to be real-time, and it is inconvenient to share information resources within the unit.
The use of radio frequency identification (RFID), the latest technology product, can fundamentally solve the above-mentioned problems. The Seventh Research Institute of China Electronics Technology Group Corporation, based on radio frequency identification (RFID) technology, has developed a corresponding RFID solution for the warehouse management system in accordance with the actual situation and needs in the storage management of the grain storage warehouse.
2. Introduction to RFID system
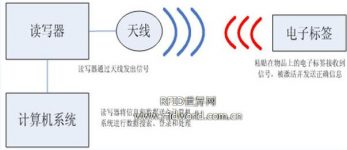
The RFID system consists of three parts: a reader, an electronic tag and an application software system, as shown in Figure 1. Its working principle is: the reader emits radio waves of a specific frequency to the electronic tag to drive the electronic tag circuit to send out the internal data. At this time, the reader will sequentially receive and interpret the data and send it to the application software for corresponding processing. .

Figure 1: Schematic diagram of the RFID system
In practical applications, the electronic tag is attached to the surface of the object to be identified, and the electronic data in the agreed format is stored in it. The reader sends out a certain frequency radio frequency signal through the antenna. When the tag enters the magnetic field, it generates induced current and sends out its own encoded and stored information. The reader reads and decodes the information and transmits it to the host application software for related processing. So as to achieve the purpose of automatically identifying objects in different states (moving, stationary). The basic principle of using RFID technology for item management is shown in Figure 2.

Figure 2: Basic schematic diagram of article management using RFID technology
Traditional warehouse management mainly uses manual or bar code identification methods, which are not only inefficient, but also prone to errors. Compared with traditional warehouse management, a warehouse management system based on RFID recognition technology has the characteristics of being able to simultaneously identify multiple targets, long reading distance, fast recognition speed, and no need for precise alignment. Table 1 is the statistics of the time spent on manual login, barcode identification and RFID identification in practical applications.
Table 1: Comparison table of the time consumed for manual login, barcode identification and RFID identification

Therefore, RFID recognition has higher efficiency and accuracy than manual login and barcode recognition. The application of RFID identification technology in warehouse management will surely greatly reduce its error rate and improve work efficiency.
3. Implementation plan
The warehouse management system based on RFID technology is a huge system, which is mainly composed of the electronic label making and attaching module, the warehouse management module, the warehouse management module and the inventory counting module. The structure diagram of its composition is shown in Figure 3.

Figure 3: Structure diagram of RFID warehouse management system
3.1 Electronic label making and attaching module
The electronic label making and attaching module is mainly composed of an electronic label making unit and an electronic label attaching unit, and its composition structure diagram is shown in Figure 4.

Figure 4: The structure diagram of the electronic label making and attaching module
The electronic label production unit is mainly to fill in the various information that needs to be stored in the card issuing software (including the type of flour, production date, batch number, etc.). After completion, the software will automatically generate a label ID number and write it into the corresponding electronic label middle. At the same time, the software will bind the ID number with the above-mentioned various information to form a record, which is stored in the database.
The electronic label attaching unit is mainly used by the production personnel to attach (hang) the manufactured electronic label on each flour packaging bag in accordance with the prescribed process.
3.2 Inbound management module
The warehousing management module mainly completes the automatic registration and other auxiliary management of the warehousing of each flour that enters the warehouse through the warehousing pipeline.
The automatic warehousing registration is mainly composed of fixed RFID readers, full coverage channel antennas, LED display panels, conveyor belts and other equipment. The schematic diagram of the work flow is shown in Figure 5.

Figure 5: Schematic diagram of the work flow of automatic registration of warehousing
When the flour affixed with the electronic label passes through the storage pipeline and is ready for storage, it will pass through the conveyor belt installed at the outlet of the pipeline. At this time, the reader uses RFID to identify the flour through a fully covered channel antenna installed next to the conveyor belt. After the recognition is completed, the reader will display the important information represented by the electronic tag (such as the type of flour, etc.) on the LED panel, and at the same time start the voice prompt. In addition, the reader will transmit the warehousing information to the back-end database for update at the same time. At this point, the automatic registration of flour storage has been completed.
In addition, the use of on-site handheld RFID readers can also achieve other auxiliary management of storage. For example, query the storage history records of specified types of flour, automatically generate and print storage records reports of specified dates, etc.
3.3 Outbound management module
The outbound management module is mainly to complete the accurate and automatic outbound registration and other auxiliary management of various types of flour required by the customer according to the specific requirements of the customer’s bill of lading.
The outbound automatic registration is mainly composed of fixed RFID readers, handheld RFID readers, full coverage channel antennas, LED display panels, conveyor belts and other equipment. The schematic diagram of the work process is shown in Figure 6.

Figure 6: Schematic diagram of the workflow for automatic registration of outbound
The warehouse staff first use the handheld RFID reader to handle the outgoing tasks. When processing, the staff only needs to select the outbound task to be processed on the handheld (After the sales department has processed the customer demand, an electronic sales receipt will be generated and automatically sent to the back-end server; the warehousing department can receive the sales receipt in real time , After the processing is completed, the corresponding outgoing task will be formed, and will be automatically sent to the background server for the handheld device at the work site to query and download), after confirming, the handheld will automatically download the outgoing task to the warehouse exit through the background server Fixed reader. After the download is complete, the fixed reader will display the quantity of each type of flour that needs to be out of the warehouse and the quantity that has been out of the warehouse on the LED panel. The schematic diagram of the work flow of this part is shown in Figure 7.

Figure 7: Schematic diagram of the process of handling out-of-warehouse tasks using a handheld RFID reader
The warehouse staff transports the corresponding flour from the wooden platoon to the conveyor belt according to the quantity of each type of flour that needs to be out of the warehouse displayed on the LED panel. The flour will enter the warehouse out of the warehouse along with the conveyor belt through the fully-covered channel antenna. In this process, the reader uses the full coverage channel antenna to perform RFID identification on the flour. After the recognition is completed, the reader will sound the type and quantity of the flour read, and increase the quantity of that type of flour that has been out of the warehouse on the LED display panel. When the outbound quantity of a certain type of flour meets the outbound task requirement and the outbound quantity of all types of flour meets the outbound task requirement, the reader will respectively voice prompt the on-site staff. Moreover, when the outbound quantity of all types of flour meets the outbound task requirements, the reader will automatically send the outbound data to the background database for update, and will prompt on the LED display panel that the outbound task has been completed. At this point, the accurate and automatic outbound registration of flour is completed.
In addition, the use of on-site handheld RFID readers can also achieve other auxiliary management of the warehouse. For example, query the historical records of the designated types of flour out of the warehouse, automatically generate and print out-of-warehouse record reports on the designated date, etc.
3.4 Inventory Checking Module
The inventory counting module mainly completes the counting and counting of various types of flour stored in the warehouse. It is mainly composed of a cart-type RFID reader. The schematic diagram of its work flow is shown in Figure 8.

Figure 8: Schematic diagram of inventory counting workflow
The warehouse staff pushes the cart-type RFID reader to walk around in each channel of the warehouse. The reader can accurately count the quantity of various types of flour stored in the warehouse, and send the data to the warehouse via GPRS. The background database is updated. At this point, the inventory count is complete.
4. The benefits of the system
(1) The traditional and original mode of relying on manual counting for warehousing management and inventory inventory management has been changed, and the error rate has been greatly reduced.
(2) Greatly improve the work efficiency of on-site staff, reduce the labor intensity of on-site staff, and realize “request labor from science and technology”.
(3) Make the warehouse entry and exit data and inventory data have strong real-time, accuracy and interconnectivity, which is very convenient for the sharing of internal information resources of the unit.
(4) The warehousing management system incorporating advanced RFID technology will greatly improve the modern and informatized image of the enterprise unit and win a higher reputation.
5 Conclusion
The warehouse management system independently developed by the Seventh Research Institute of China Electronics Technology Group Corporation introduces advanced UHF passive RFID technology, which has the advantages of high reliability, high efficiency, and user-friendly interface. The operation and use of the system will greatly reduce the error rate of warehouse management and inventory management, greatly improve work efficiency, improve the real-time and accuracy of data, and will greatly improve the modernization and informatization image of enterprise units. Win a higher reputation in China.
The Seventh Research Institute of China Electronics Technology Group Corporation
Address: No. 381, Xingang Middle Road, Guangzhou
Post Code: 510310
Contact: Yao Pengfei
Mobile: 15913182376
Phone: (86-20) 84119353
Fax: (86-20) 84119342
E-mail:
[email protected]
QQ: 398323086
[ad_2]



