Successful application case of RFID production line management system in automobile manufacturing enterprise
[ad_1]
1. Introduction to RFID system
RFID is a non-contact automatic identification technology, which automatically recognizes the target object and obtains related data through radio frequency signals, and the identification work does not require human intervention. The RFID application system has a series of advantages such as non-contact, long working distance, high precision, automatic and fast information collection and processing, and good environmental adaptability. It can not only replace the traditional manual entry method, greatly improve the operating efficiency of the enterprise, but also because of its advanced The automatic identification function can easily achieve tasks that were previously difficult to complete manually, and provide strong support for improving the competitive advantage of the enterprise and enhancing the core competitiveness of the enterprise.
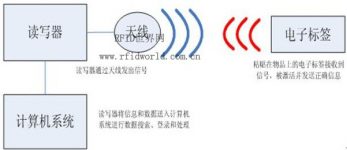
The most basic RFID system consists of the following three parts, the principle is shown in Figure 1-1:
Tag: It is composed of coupling components and chips. Each tag has a unique electronic code and is attached to the object to identify the target object;
Reader: A device that reads (and sometimes writes) tag information, which can be designed as a handheld or fixed type;
Antenna: Transmit radio frequency signals between the tag and the reader.

Figure 1-1: Schematic diagram of RFID system
An electronic tag generally stores electronic data in an agreed format. In practical applications, the electronic tag is attached to the surface of the object to be identified. The reader can read and identify the electronic data stored in the electronic tag without contact, so as to achieve the purpose of automatically identifying the object. Usually the reader is connected to the computer, and the read tag information is transferred to the computer for further processing. The RFID information processing system (ie, back-end application support software) integrates the tag data collected by the reader.
2. Current situation and demand analysis
2.1 Status analysis
The company’s bus factory is divided into 4 workshops, including welding, painting, final assembly, and completion inspection, with a workshop area of about 15,000 square meters.
At present, the collection of production line information adopts manual collection and manual input.
The accuracy of manual collection and manual input is insufficient, and there is a certain error rate.
Manual input can only be done at regular intervals, resulting in the production plan being submitted on a weekly or monthly basis, which cannot be accurate to the day.
The production data in the system cannot be updated in real time, and the lag is serious, which is not conducive to the smooth progress of the production flow and restricts the further increase of production capacity.
2.2 Demand analysis
Based on the above analysis of the current situation, our company proposes the following RFID solutions:
1,000 high-temperature, anti-corrosion RFID anti-metal tags (made in a recyclable form) are used for one-to-one identification and management of vehicles on the production line of each workshop.
Before performing each batch of production tasks, you need to initialize the information of each tag with the electronic tag issuer in the production line management system. The information corresponding to the tag should include: production line code, product code, order number, status location, plan number, product sequence Number, VIN information, etc.
The label is fixed on the vehicle on the production line with rivets or other methods. After the vehicle has passed the inspection process, the label can be removed for reuse next time.
Set up a UHF RFID reader at the welding up-line point, outer Mongolia up-line point, and welding down-line point in the welding workshop, respectively, to collect information on vehicles entering the production line of the welding workshop, and pass the information through the Ethernet network Real-time return to the background management system.
Set up an UHF RFID reader at the paint line up point and paint line down point of the paint shop to collect information on vehicles entering the production line of the paint shop, and send the information back in real time via the Ethernet network To the background management system.
Set up an UHF RFID reader at the final assembly line point, final assembly line point, and cross-check point of the final assembly shop to collect information on vehicles entering the paint shop production line, and transmit the information back in real time via the Ethernet network To the background management system.
A UHF RFID reader is set up at the qualified point of the inspection workshop to collect information on vehicles entering the inspection workshop and transmit the information back to the background management system in real time via the Ethernet network.
The RFID production management system needs to interface with the existing ERP system.
3. System composition and principle
3.1 System composition
The RFID production line management system (MES) is mainly composed of a basic hardware network platform, a hardware interface platform, a management software platform, and an ERP system interface platform, as shown in Figure 3-1.

Figure 3-1: RFID production line management system composition structure diagram
Basic hardware network platform: the data transmission network between the on-site information collection point reader device and its back-end management system.
Hardware interface platform: the part responsible for hardware control management and hardware data collection in MES software.
Management software platform: MES software is responsible for all business processing related to production execution management, which is the core part of the MES system.
ERP system interface platform: the part of the MES software that is responsible for data exchange with the ERP system.

Figure 3-2: Topology diagram of RFID production line management system
3.2 System principle
As shown in Figure 3-3, the welding upper line point, outer Mongolia upper line point, and welding lower line point in the welding workshop, the paint upper line point and the paint lower line point in the paint shop, the final assembly line point and the final assembly An ultra-high frequency RFID reader is installed at the offline point, the inspection point, and the qualified point of the inspection workshop to automatically collect vehicle information on the production line.

Figure 3-3: Schematic diagram of the principle of RFID production line management system
When the car with the electronic tag passes through the information collection point of the production line, the reader will automatically collect the information of the car’s electronic tag and transmit the information to the background management system in real time. The back-end management system can realize various managements of the entire production line based on these real-time data.
4. System function
This system includes the following functions:
4.1 Production management
Arrange the production plan according to the production order, including production order import, order statistics and status information transfer, production task decomposition, automatic task assignment, etc.
Manufacture and issue electronic labels according to the production plan
Vehicle data collection at the production line collection points of each workshop. The collected data includes: production line code, product code, order number, status location, plan number, product sequence number, VIN information, etc.
The collected field data is transmitted to the background management system in real time, so that all operating information during the production process can be recorded by the system in real time
4.2 Statistical analysis
Through mathematical statistics, mathematical analysis, data mining and other methods, all kinds of data needed by the enterprise are obtained: real-time production line output, process output rate, equipment and personnel operating conditions, etc.
Automatically generate various quality reports, charts and reports such as Plato, Histogram, Xbar chart, and feed back to the online system for performance analysis and improvement
With on-site data report and query functions, to provide support for senior management’s decision-making
4.3 System Management
System backup and recovery mechanism
System operation log
Operator permission setting
Acquisition terminal configuration and control
ERP system interface rules
Data initialization
4.4 Data interface
Obtain engineering data from the existing ERP system and provide WIP information for the MES system
Provide the required data for the existing ERP system
5. Operation process

Figure 5-1: Operation flow chart
6. Equipment Introduction
6.1 Hardware
UHF RFID Reader

Figure 6-1: Physical picture of UHF RFID reader
Built-in 7dBi circular polarization antenna, system construction does not require additional antenna configuration
Lightning protection, waterproof, dustproof, anti-interference, suitable for various indoor and outdoor applications
Working frequency: 902–928 MHz (can be customized according to requirements)
Air interface standard: ISO 18000-6B/6C
Maximum stable reading distance: 12 meters or more
Write label distance: about 1/3 of the read distance
Data rate: 160kbps
Working mode: Provides two working modes (master-slave, trigger)
Frequency mode: fixed frequency/frequency hopping optional
Communication interface: RS-232/485, RJ-45
IO interface: 1 TTL input, 1 TTL output
Output power: default 1W (30dBm), maximum 33 dBm, continuously adjustable at intervals of 1 dBm
Upgrade: Support firmware upgrade and update
Power supply: +6V, 3A/DC
Adapter: 110-220V/AC
Size: 240mm×235mm×100mm
Weight: about 1.6kg
Working temperature: -20℃~+55℃
Storage temperature: -35℃~+70℃
Humidity: 20%~90%
Protection level: IP65
Shell material: ABS
Indicator light: 3
UHF RFID Card Issuer

Figure 6-2: Physical image of UHF RFID card issuer
Working frequency band: 902–928 MHz (can be customized according to requirements)
Air interface standard support: ISO/IEC-18000-6B, EPC C1G2 (ISO 18000-6C)
Reading distance: 0-1 m (related to the application environment and tags)
Card writing distance: 0-0.5m (determined by reader settings and label performance)
Antenna: built-in
Communication interface: RJ-45/RS-232
Power supply: DC5V/5 A
Power consumption: less than 9W (varies according to power setting)
Dustproof and waterproof grade: IP53
RFID anti-metal tag

Figure 6-3: Physical image of RFID anti-metal tag
Type: Passive, readable and writable
Frequency: 860~960MHz
Chip: ALIEN HIGGS2
Chip protocol: EPC Class 1 Gen 2
EPC: 96bits
Working temperature: -30℃~90℃
Storage temperature: -40℃~150℃
Weight: 20g
Size: 95*25*3.7mm
Anti-corrosion: support
6.2 Software
Hardware interface software
The establishment, control and removal of the communication connection with the reader
Reader parameter configuration and control
Reader data collection
Management software
Recording and analysis of collected data
Generate various quality reports, charts and reports
On-site data report and query
System backup and recovery
System operation log
Operator permission setting

Figure 6-5: Schematic diagram of management software
ERP system interface software
ERP system interface rule definition and setting
Obtain engineering data from the existing ERP system and provide WIP information for the MES system
Provide the required data for the existing ERP system
7. Project real picture
At present, the system has been successfully applied in Dongfeng Motor Company.



The Seventh Research Institute of China Electronics Technology Group Corporation
Address: No. 381, Xingang Middle Road, Guangzhou
Post Code: 510310
Contact: Yao Pengfei
Mobile: 15913182376
Phone: (86-20) 84119353
Fax: (86-20) 84119342
E-mail:[email protected]
QQ:398323086
[ad_2]




