RFID technology verification test of Taiwan medical infusion preparation process
[ad_1]
With the active cooperation of Taiwan’s Department of Health, Taichung Hospital, the medical infusion concept verification has completed the performance test of RFID hardware and the prototype of the infusion RFID system with nine industry players. The Taichung Hospital was formerly known as the Taiwan Provincial Taichung Hospital. It has 560 beds and an average annual number of inpatients of 14,300. It is one of the 28 hospitals under the “Department of Health”. In 2006, it began to provide cancer patients with the service project of chemotherapy infusion preparation (formerly an outsourcing operation), and established the first central laboratory system in Taiwan Province. It also won the “National” Quality Award Organization Group Award that year.
Status description and issue analysis
At present, in the preparation process of injection drugs, the staff of the pharmacy department prints out the dispensing form, dissolves, mixes or dilutes the drugs listed in it, manually selects one by one, and records the dose of the drug that has been dispensed, fills in the stickers and labels, and fills in the drugs manually The deployment receipt and drug in-out inventory card need to record the preparation process time for chemotherapeutic drugs. The required steps are cumbersome and error-prone.
Therefore, the records of the preparation process of each chemotherapy injection, such as the name of the drug, the dosage, the completion time of the preparation, the pharmacist, the patient, and the time of administration, cannot be effectively obtained from the infusion container labeling link system that was administered in time. , Which reduces the timeliness of checking operations for pharmacists and nursing staff.
Execution
Confirm verification case
1 Application scope definition
At the beginning, the scope of verification for the application of medical infusions covered the preparation of TPN (total intravenous nutrition) and chemotherapy injections. After further communication with the pharmacist in charge, the chemotherapy injection was locked. Because TPN is mostly prepared as a solution when it leaves the factory, the pharmacist only needs to add the medicine to the special nutritional formula, which is far less harmful than chemotherapy drugs. Chemotherapy drugs are highly dangerous (because of their corrosive effects on human skin), are expensive, and require a high degree of expertise in the preparation process. Regarding the identification and verification of chemotherapy drugs from the pharmacy department storeroom, the pharmacist makes the preparation in the chemotherapy sterile preparation room, informs the ward delivery staff to receive it, and finally the nurse performs the process in the ward, and uses RFID to automatically check the receipt at the most important checkpoint. The label information is captured, compared and signed, and the dispensing process of the syringe medicine is fully recorded, and warning notifications are automatically sent.
2 Case feasibility assessment
I just discussed the preparation of chemotherapy infusion with the hospital pharmacist. When I want to use RFID to control the syringe and combine the drug barcode for drug comparison and confirmation, the pharmacist thinks it is very necessary. In addition to reducing the proportion of wrong drugs, it can also be used. Implement medical personnel to follow standard operating procedures to dispense and administer drugs. Moreover, the use of RFID to automatically capture label data, automatically complete the drug use and syringe preparation and registration operations, and save a lot of manual filling and sign-off operations.
3 executive structure
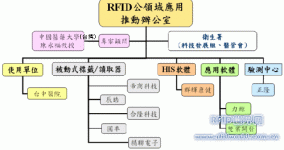
The verification team first communicated with the relevant competent units of the Department of Health (Technology Development Team, Hospital Management Committee), and selected the Taichung Hospital as the main use test unit. After an industry briefing was held in May to explain the verification content, there was a willingness with 9 companies Participating companies (5 RFID hardware companies, 3 software companies, and one testing center) work together to conduct proof-of-concept tests for medical infusion RFID applications. The empirical test execution architecture is as follows:

Figure 1. The structure of industry-university-research cooperation
Analysis and verification requirements
1 Verification context analysis
The working situation of medical infusion RFID application and a brief description of each situation are shown in the following figure:

Figure 2. RFID technology application scenario diagram of medical infusion preparation process
The process of medical infusion RFID application operation is mainly divided into three stages: preparation stage, deployment stage, and notification distribution use, as shown in the following figure:

Figure 3. RFID technology application flow chart of medical infusion preparation process
2 Confirmation of verification requirements
(1) This verification is mainly aimed at the red bag of the chemotherapy syringe and the device syringe, testing the reading rate of a variety of RFID products, clarifying technical doubts, and testing whether the syringe contains liquid, which may interfere with the reading Effect. Because chemotherapy drugs are corrosive, actual drugs cannot be used in the verification process, and physiological saline is used instead.
(2) Due to the narrow on-site space of the chemotherapy preparation room, a reader with a built-in antenna in the reading device and a small RFID printer were chosen as the key considerations.
(3) Because drugs have not yet been affixed with RFID tags or even barcodes, this proof-of-concept first plans the use of barcode labels for medicine bottles, combined with RFID employee cards and patient RFID wristbands, and explores the integration of barcodes and RFID Application, the verification system is mainly to establish the use system of the syringes required by patients for chemotherapy drugs, completely record the preparation status of the syringes, and send warning messages in real time.

Table 4. Description of tested items
3 Development of verification indicators
In this proof-of-concept, the following verification indicators need to be achieved when selecting suitable tags and readers:
(1) The signing time of the dispensing form has been shortened from 2 minutes/piece for manual filling to 0.2 minutes/piece for automatic induction
(2) The efficiency of checking and checking by nursing staff has been shortened from 3 minutes/piece to 0.5 minutes/piece
(3) Change the notification from the pharmacist phone notification to the system automatic notification
(4) When reading a single label, it can be 100% identified
Prototype of implementation verification
1 The first stage basic performance test
In the first stage, a total of 6 types of HF sticker labels, 5 types of brands, and a total of 7 types of readers were tested (3 types are USB ports, 2 types use Bluetooth transmission, 1 type is PDA, and the above reader antennas are built-in. The other is RS232 / Ethernet interface, the antenna is external). The key conclusions are as follows:
When the standard ISO label is attached to the syringe, the larger the label surface, the larger the reduction of the sensing distance, which is about 15-50%.
The size of the built-in sensor antenna of the readers tested at present is not very large (most of them are the size of standard ISO cards, or even smaller), so they are less suitable for reading multiple tags at a time.
The physiological saline used in the test does not affect the RFID sensing distance.
Even if the plastic light-proof bag contains a syringe, it will not affect the induction of the RFID tag outside the bag.
It is notified that an external flat panel antenna (approximately A4 size) is used when receiving the infusion medicine. The standard ISO card-sized label can sense up to 30cm away, so it can be used to sense multiple light-proof bags.
Small labels are not very sticky (maybe caused by the curved surface of the 3 cc syringe or the label material is too hard). After standing for a period of time, the edge of the label will lift and the syringe will separate.
2 The second stage of the situational test
(1) Situational test
The situational test uses tags to perform reading tests at different moving speeds on a conveyor belt, simulating the situation where a pharmacist or nurse performs a syringe or red bag induction reading. The important findings are as follows:
The sensing distance of the tag in the moving state is generally shorter than the sensing distance in the static state.
The faster the movement speed, the shorter the sensing distance.
One of the readers (using Bluetooth to transmit data) can sense the tag and emit a “beep” sound during the dynamic test, but the test software cannot display the tag ID, indicating that the data transmission cycle takes a long time. Therefore, If this type of reader is used to read tags, it is recommended to place the identified item in front of the reader, confirm the ID display, and then perform the next reading.
(2) Verification system
While the second phase of the situational test is being carried out, the infusion fluid RFID verification system is also developed, which completes a total of six subsystems, including: 1. medication confirmation; 2. chemotherapy RFID label printing and production; 3. drug pairing confirmation; 4. . Syringe bagging operation; 5. Notification of receiving and distributing operation; and 6. Drug administration operation in the ward. The system functions are briefly described as follows:
A. Personnel authorization verification
According to the personnel operation authority, log in the system with RFID employee card induction and enter the corresponding system screen.
B. RFID label reading and printing
According to the HIS verification system, the amount of syringe used for the preparation of the medicine is generated, and the RFID label sticker is generated by the Zebra R2844-Z RFID label printer.
The clear code of the RFID tag includes the name of the drug, the total dose, the serial number of the syringe/the total number of the syringe, the medical record number, and the date of dispensing.
The clear code of the RFID tag includes the name of the drug, the total dose, the serial number of the syringe/the total number of the syringe, the medical record number, and the date of dispensing.
After the pharmacist completes the preparation of each syringe of medicine, the syringe RFID tag is sensed and confirmed. At this time, the preparation completion time (system time) is written in the RFID tag.
Scan the RFID label of the syringe before putting the syringe into the light-proof bag (red bag), and check it with the RFID label of the red bag that will be placed.
C. RFID drug delivery and application
The antenna in the storage area senses the RFID tag of the light-proof bag, and automatically sends a short message to notify the corresponding ward nursing station staff to pick it up.
The pharmacy delivery personnel or the nurses who receive the dosing use the RFID employee card to detect, record the employee code and the time of use in the RFID tag and HIS system.
D. RFID system warning
The pharmacist uses the barcode scanner to scan the barcode of the outer box and check it with the HIS system drug items. If it does not match, an immediate warning is required.
The pharmacist puts the red bag in the storage area after the preparation is completed, and the RFID antenna detects the RFID tag, and the system immediately informs the nursing station to send the staff to display the completion message of the adjustment.
Pharmacists or nurses can check the drug items, dosages, patients, and expiration dates by scanning the RFID tags with the system. If they do not match, they need to be alerted immediately.
The pharmacist reads and checks before taking the medicine. If the effect of the medicine expires, an immediate warning is required.
Nurses can read the RFID tags to view the effects of medicines, precautions for administration, and other health education information from the system.
E. RFID drug delivery and application
Requisition process
●Personnel login: The applicant uses the RFID employee card to log in to the system inductively.
●Requisition check: Induct the label information on the red bag to check the red bag to be reclaimed. If the red bag is short or the expiration date is approaching, the SMS notification will be sent immediately.
●Requisition record: After confirming that the red bag is completed without error, write the data of the requisitioner and the requisition date.
Nursing medication process
●Personnel login: The nurse uses the RFID employee card to log in to the system by induction.
●Medication check: The nurse scans the RFID tag of the patient’s wrist to bring out the information about the chemotherapy medication that needs to be administered, and then senses the label of each syringe to check the medication items.
●Clinical health education: Nurses can read RFID tags and click on drugs to display related functions, precautions for administration, and other health education information.
The following screenshots of the two main screens of the verification system:

Figure 4. The medication confirmation system screen

Figure 5. The screen of the ward dosing system
3. The third stage of on-site import test
The on-site introduction test is carried out in the chemotherapy preparation room on the first floor of the Taichung Hospital (On-site introduction observation instructions will be held on 11/18). However, due to the narrow on-site space of the chemotherapy preparation room, light and easy-to-carry reading devices are selected; Especially in the operation process in the sterile room, try not to let the pharmacist hold the reader to sense the label of the syringe, but fix the reader on the table so that the syringe is close to sense the record. For the small screen of UMPC, the original design verification system is adjusted to enlarge the display fonts and data fields, so that the operator can easily read important data. When designing the interface, it is not necessary to use the keyboard for input actions, but to click on the screen. The way.

Figure 6. The configuration diagram of the flow line and hardware facilities of the chemotherapy deployment room
Evaluate verification effect
After verification, we have analyzed the improvement of operational benefits that can be obtained after the introduction in the hospital as follows:

Table 5. Hospital operation benefits
conclusion and suggestion
The verification test confirmed that RFID technology has management benefits in the application process of chemotherapy infusion (identification of syringes and red bags). In addition to integrating RFID and barcode technology, as a phased solution, it simplifies the manual and paper record processing mode and reduces the risk of negligence. In the standard process of checking infusion solution preparation and requisition, by sending warnings in real time, the probability of medication error can be reduced; and the management of infusion operation and requisition can be strengthened to improve operational efficiency; it is also linked to the drug graphic database to ensure The correct medication can strengthen the energy of health education and consultation. Limited to manpower and material resources, this proof-of-concept is only for technical feasibility and preliminary benefit discussions. In the future, development and testing of recyclable RFID tags will still be needed; in terms of external antennas, manufacturers in the province still need to invest in design , To produce antennas with excellent reading performance and stability; hardware manufacturers can also enhance existing barcode and RFID reading devices to provide more complete and high-performance solutions.
[ad_2]



