Application of RFID technology in the management of fast moving consumer goods supply chain
[ad_1]
The automatic identification industry in the 20th century can be said to be the world of bar code technology. Since the birth of the commodity bar code system (ie EAN-UPC system) that was promoted and applied globally in the 1970s, bar code technology has occupied the world from business to Industry, almost all data management applications from warehousing to circulation. At present, more than 100 countries and regions around the world have joined the International Article Numbering Association, more than 1.2 million companies and enterprises have participated in the global unified identification system, and tens of millions of products have used unified barcode signs. It can be said that the contribution of barcode technology to the management of the supply chain from commodity manufacturing, management and circulation is pivotal. It has laid a solid foundation for the development of modern logistics, providing enterprises with management levels, reducing management costs, and promoting the process of global economic integration. The basics.
However, with the changes of the times and the continuous updating of technology, bar code technology has been unable to meet the existing applications of enterprises. For example, in the management of the fast-moving consumer goods supply chain, due to the particularity of the industry, the commodity circulation cycle is short, and the requirements for the real-time delivery of commodity information are high. The existing barcode technology cannot obtain product information from a large number of products in a short period of time. The only way is to rely on manual one-to-one scanning.
System application solution
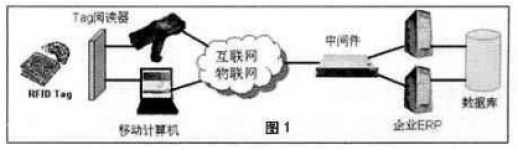
However, the RFID wireless smart tags with EPC Global as the standard are sent out through the radio waves of the wireless frequency band, which makes the automatic identification technology have a new breakthrough. In just one second, the information of 200 products can be read, and the information can be transmitted wirelessly. The Internet model is used to update data as shown in Figure 1. Such technology is integrated into the entire supply chain of enterprises, it will solve a number of product identification problems that the existing barcode technology cannot do, and establish a global logo for each smallest unit of circulating commodities, thereby achieving the entire supply chain Items are tracked and managed in real time. At the same time, the progress of the entire process of the fast moving consumer goods supply chain has been greatly improved.

Specific application links
This case introduces how to use it in the production line and the delivery link for manufacturers; how to use it in warehousing, distribution, and transportation applications in the logistics and distribution link, as well as the application of shelf management, order management, and sales management in the retail link.
A miniature radio frequency identification (RFID) tag is used on the outer packaging of each can of soft drinks. The area of the tag can be large or small, and each tag contains an electronic chip equivalent to a gravel and an antenna. The microchip in this label stores the electronic product code, namely EPC. Each can of soft drinks has a unique EPC code as shown in Figure 2.

When the beverage is filled on the assembly line, the RFID tag reading equipment located at each position of the assembly line will automatically issue data reading commands and accept the information fed back by the tags. These data are collected and recorded by the production control system, and further incorporated into the enterprise production management system to realize automatic counting and establish a product tracking database. At the end of the assembly line, canned beverages are packed into the packaging box, and there is also an RFID label on the packaging box. When a box of beverages is packaged, the production control system will drive the RFID label printer (a special type of writing to the electronic chip). The printer that enters the data usually has the function of the existing barcode printer at the same time), write the detailed information of the packing box (transportation barcode, product production date, etc.) on this label, and store the data in the enterprise production management system at the same time . These boxes are placed on pallets when they are stored in the warehouse, and each pallet also has an RFID tag.
There is an RFID reading device above the doorway of the shipping platform. When the pallet passes the doorway, it reads the radio waves emitted by the device and activates these tags. At this time, these tags “woke up” and began to send their own EPC. Like a good kindergarten teacher, the reader only lets one tag “speak” at a time. It will quickly open and close these tags in turn, until it has read all the tags. As far as the current mature technology is concerned, every second, the RFID reading device can successfully read 200 RFID tags as shown in Figure 3.
This is the content of one of the tags: EPC: F127.C238.DF1B.17CC
This information is first transferred to the software system, and then the object analysis service system (ONS) on the local area network or the Internet is used to retrieve the goods related to the EPC, just like registering on the Internet. The role of ONS is to integrate the software in the software system. The data is stored in the corporate database and retrieved on the Internet of Things. The data of each product will be stored in a physical markup language (PML), similar to the current popular XML, which can perform some common enterprise tasks.
The tag reading device is connected with the system, and the received EPC data is passed to it, and the system is driven to perform subsequent work at the same time. The system can send queries to the Object Name Service (ONS) database via the Internet (Internet of Things), which is like a reverse phone number lookup service, that is, provides an address based on the received number;
The ONS server matches the EPC code with the server address that stores a large amount of information about the product. These data can not only be used by software systems around the world, but also can be automatically supplemented by the software system;
The PML (Physical Markup Language) server stores the complete data about the factory’s products. In this example, it recognizes that the received EPC code belongs to a certain company’s canned beverage Cherry Hydro. Since the software system knows the location of the reader that issued the query command, it now also knows which manufacturer produced the can. If a product quality problem occurs, this information can be easily traced back to the source of the problem. , In order to achieve product tracking.
Now, the whole package of soft drinks is delivered to the distribution center, and the RFID reader located at the gate of the unloading area starts to work to read the EPC codes of all the drinks in the boxes. Since RFID can be collected in a non-contact manner and can even be read through the packaging box, the real inner packaging product information and quantity can be obtained in the unloading area without unpacking inspection. The data obtained by the tag reading device is transferred to the software system. In the entire Internet of Things, the location information of the beverage changes accordingly as shown in Figure 4.

After the business processing of the distribution center, the goods are delivered to the retail outlets. On the shipping platform, the EPC tag is read once. When entering the warehouse of the retail point, the EPC tag is read again. These two reading processes The accuracy of the logistics and transportation process will be verified, and the new location information will be reflected on the Internet of Things as shown in Figure 5.

After the beverage is delivered to the warehouse, the commodity inventory information of the retail point changes immediately. In this way, the computer system of the mall can realize the real-time monitoring of the soft drink inventory and ensure the safe stock of the commodity.
Similarly, RFID tag reading equipment is also integrated on the shelves of the shopping mall. When the staff replenish the shelves, they use a handheld reader to record the beverage information into the corresponding shelf inventory. At this point, if a customer purchases 6 cans of beverages, the shelf will send a message to the shopping mall’s replenishment system, and the system will determine whether to place an order based on real-time inventory information (the number of commodities on the shelf and in the warehouse); if The inventory of goods on the shelves is reduced to a certain level, and replenishment information will be sent to the staff.
RFID technology can also facilitate customers. Customers don’t need to wait in line for a long time for checkout payment, just push the selected items through a door equipped with a tag reading device. The reader on the door can identify the items in the shopping cart and automatically complete the checkout through the EPC of the goods. Customers only need to swipe their payment card or credit card to leave.
Beverages are bought home and put them in the refrigerator. At this time, the label reader on the refrigerator will also automatically record these commodities to form a small inventory management system; when the can of beverage is taken out of the refrigerator, it will It is considered that it is drunk, and the refrigerator inventory will change at this time. This inventory management continues until the next time you shop, the refrigerator will provide a copy of its “out of stock list.”
Finally, the beverage can completed its mission and was sent to the recycling center, where the RFID tags were automatically sorted and classified into the corresponding reuse category.
Basic system configuration
Electronic label for commodity packaging: smart label in sticker mode, 915MHZ, ISO18000-6/EPC standard, pasted on a fixed position of the commodity.
RFID equipment required: a dual-standard compatible reader that supports the EPCGlobe standard, and has a network interface; a fixed reader; a handheld terminal.
Software system: label issuing system (including device drivers), verification system, local database system and local ERP system.
Other equipment: on-site computer and wireless Internet equipment.
[ad_2]




