Application of “Silver School Card” Mode in Donghua University Card System
[ad_1]
With the development of computer network technology, the entire society is undergoing in-depth information and network revolutions, and its application fields are becoming more and more extensive. As an important part of society, schools are gradually entering the era of digital campuses. Use computer network technology and other information technology to promote the school’s informatization level and improve the school’s management level, so as to establish a highly informatized and modern new school. The widespread application of the one-card system in colleges and universities arises at the historic moment.
In the all-in-one card system of colleges and universities across the country, there are two modes: independent issuance by schools and joint issuance by banks and schools. The advantage of the school’s autonomous card issuance model is that the school’s own card issuance is more convenient for system data processing, maintenance, expansion, etc. It has an electronic wallet but does not have the function of a bank card. The consumption data of the electronic wallet is connected to the bank through V1. The disadvantage is that It is difficult for the school’s financial service system management to meet the security strength of financial standards. In addition, the school is responsible for settlement, and the school must bear the risks of system management and operation. The bank-school joint card issuance mode is to integrate the bank card and the campus card into one card. The cardholder holds a UnionPay card with personal identification information and an electronic wallet, which is a true combination of the campus card and the bank card. . The advantage of this model is that banks issue cards. The school saves the trouble of making and issuing cards. The security of consumption data is professionally guaranteed. The bank also completes the settlement. The financial service system management meets the security strength of financial standards. The school can Focus on data processing that has nothing to do with consumption, reduce security level requirements, and reduce equipment costs. The shortcomings are also obvious. Because bank card issuing brings many inconveniences to schools, mainly due to security considerations, the bank sector is not open to schools, which hinders the further expansion of the school’s all-in-one card application, which is the time when many schools’ all-in-one card planning , The main reason for abandoning this program.
The Donghua University Card System was established in 2003 and adopted the “Silver School Card” model. Based on the successful experience of the all-in-one card system of brother colleges and universities, the school developed an all-in-one card system with its own characteristics in combination with the characteristics of Songjiang University Town, making it one of the important supporting platforms for the school’s digital campus construction.
1 Key issues in the application of Donghua University’s one-card system
1.1 Card selection
There are many types of cards used for all-in-one cards, including contact and non-contact types, among which there are also many types of non-contact cards. This system uses non-contact radio frequency card-Mifare 1 card (hereinafter referred to as MI card), mainly based on its convenience, multi-function and high security features.
1.1.1 Performance of M1 card
The M1 card is made with advanced chip manufacturing technology, built-in high-speed CMOS EEPROM and MCU, etc. The card’s operating frequency is 13.56 MHz. The reading and writing distance of M1 card is about 10~25 mm (related to the size of reader and card antenna). The M1 card has an advanced data communication encryption and two-way verification system, and has an anti-collision mechanism. It can process multiple overlapping cards within the effective working distance of the card reader antenna at the same time, and supports multi-card operation. When the card is manufactured, it has a unique card serial number (32 bits).
The M1 card communicates with the reader using a handshake half-duplex communication protocol. There is a high-speed CRC coprocessor on the card, which conforms to the CCITT standard. The communication rate between the radio frequency card and the reader is up to 106 kbit/s. The card has a built-in 8 k-bit EEPROM storage area, which is divided into 16 sectors, each sector is divided into 4 blocks, and the block is the access unit. Each sector can be individually set with its own password and access control, and managed in a variety of ways without interference. Therefore, each sector can be independently applied to an application, and the entire card is very suitable for various “all-in-one card” application systems.
The card is also built with a special mathematical operation circuit for value-added/reduced value, which is very suitable for fare collection systems such as buses and canteens. The typical ticket checking transaction time does not exceed 100 ms (0.1 s). The data on the card can be rewritten more than 100,000 times and read unlimited times; the data storage period can reach more than 10 years, and the antistatic protection capacity of the card can reach more than 2 kV.
1.1.2 The working principle of M1 card
The card is composed of a coiled antenna and a special purpose integrated circuit module. The card is passive (without any battery). Among them, the module consists of a high-speed (106 kbit/s) RF interface, a control unit and an 8k bit EEPROM. The reader sends a set of electromagnetic waves with a fixed frequency (13.56 MHz) to the M1 card. There is an IC series resonant circuit in the card whose frequency is the same as the frequency emitted by the reader. Under the excitation of electromagnetic waves, the IC resonant circuit generates Resonance, so that there is charge in the resonant capacitor. At the other end of the capacitor, a unidirectional electronic pump is connected to send the charge in the capacitor to the storage capacitor of the module for storage. When the accumulated charge reaches 2V or more, this The capacitor can be used as a power supply to provide working voltage to the module circuit, transmit data in the card or receive data from the reader.
1.1.3 Security control of M1 card
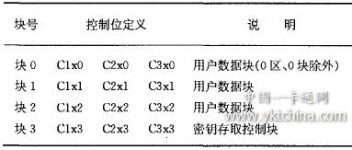
Among the 16 sectors of the M1 card, the user password and access control conditions of each sector are set independently, and their own password and access control can be set according to actual needs. In access control, each block has 3 control bits corresponding to it, which is used to determine the read and write conditions of a certain data block or control block, which is defined as “CXxy”, as shown in Table 1. Among them, CX represents the control bit number of each block (C1~C3), X represents the sector number (0~15) of a certain block, and Y represents a certain block number in the sector. For example, Clx2 is the first control bit of block 2 in X sector, and so on.
Table 1 Control bit definition “CXxy”

The M1 card has strict access control authority to the data block, which is carried out through the access control in each sector. The access control structure is shown in Table 2.
Table 2 Access control structure

Note: _b means inversion, such as C2X3_b means C2X3 inversion; B means spare bit.
The three control bits of each sector data block 0 to block 2 exist in the access control byte of block 3 in both positive and negative forms. It determines the access authority of the block. For example, it is necessary to perform decrement and initialize value operations. To verify Key A, Key B must be verified for value-added operations. The permissions of the three access control bits in the access control byte (6-9 bytes) are shown in Table 3.
Table 3 Access control authority of data block

Note: Key AlB means password A or password B, Never means no conditional realization; x=0~15, y=block O, block 1, block 2
For example, when the access control bits C10, C20, and C30 of a block 0 are set to 100, it means that the data can be read after verifying that the password A or the password B is correct; the data can be rewritten only after verifying that the password B is correct; Operations such as value addition and devaluation cannot be performed.
Based on this, through the authorization mechanism, different levels of read and write control for specific operating users are realized. Only the operating user who knows the specific password combination can update the data in the card, which greatly enhances the security of the system.
1.2 Sector planning
Although the M1 card has 15 sectors available (the 0th sector is used for the manufacturer’s code, it is not available), but for the all-in-one card application in Songjiang University Town, reasonable planning must be made for these sectors.
There are a total of 7 universities in Songjiang University Town, all of which are issued by the same bank. Each time the bank issues a card, a card number will be automatically generated. Because of security considerations, the bank sector is a black box for the school. Reading and writing the sector requires a special POS machine and special interface software, which brings inconvenience to the school’s card application expansion. If 7 universities want to have their own applications, they must have their own sectors. Therefore, the sectors must be planned reasonably. In the one-card application of Songjiang University Town, 15 sectors are divided into two parts: the first 10 sectors are bank sectors, which are reserved for bank function expansion; the last 5 sectors are school sectors, and the password of the school sector is Owned by each school. In this way, each school can carry out its own application in its own sector. Of course, if the schools get close in the future, you can open another “public sector” with a public key.
This will bring about a problem, that is, the second card issuance. Because the school’s own sector must write the card by the school itself, each card is issued by the bank once, and the school has to issue it again, which brings trouble to the actual application. Setting “shared sector” can solve this problem well. The so-called “sharing” means sharing information with the bank sector: including card number, cardholder’s name, student number, ID number, gender, department, etc. When the bank is issuing the card, copy the useful information of the bank sector to the school sector, so that the school can avoid secondary issuance of the card. The specific write sector data structure can be defined by the school. The data structure of the “shared sector” of Donghua University is shown in Figure 1. Personal number: ASC type, for example: “A20004321” = 0x65 Ox32 Ox3O Ox3O Ox3O Ox34 Ox33 Ox32 Ox3 1; Department number: ASC一>BCD type, for example: “9212o1″=0x92 0xl2 0x01, other no more details.

Figure 1 Shared sector data structure
1.3 System architecture and data operation
The all-in-one card system is based on the campus network and is separated from the public network of the campus network by dividing the virtual subnet of the all-in-one card. The routing function is cancelled between the virtual network and other virtual networks and connected to the campus network through a firewall, thus logically Separated from the campus network. The dedicated physical channel guarantees the security of each part and each level of network connection and information transmission.
The data flow of bank card issuance, card loss report, and card replenishment is run in the one-card system through the data synchronization mechanism. The entire synchronization system is centered on a shared database and is used as an authoritative data source to synchronize personnel and organizational data to various application systems to maintain the consistency and unity of personnel data and identities among various application systems.
At present, the personnel data of Donghua University comes from the two departments of the Personnel Office and the Academic Affairs Office, which manage the data of faculty and students respectively. The card management center also obtains the data of the personnel applying for the all-in-one card service from these two departments, and then transfers these data to After being reviewed by the card center, it will be submitted to the bank via FTP. When the bank completes the card activation, the bank returns the account opening information and blacklist to the card management center (including card loss report and card replacement information). After the data synchronization service obtains the user’s various change information and the blacklist information sent by the bank, it will synchronize the corresponding information to each application system according to the needs of each application system, such as library, computer room, etc.
Canteens, supermarkets, bookstores and other places with consumer POS machines are equipped with a PC. The consumption data is collected by the PC and uploaded to the bank’s dedicated server through the bank VPN. At the same time, the bank blacklist is downloaded to each POS terminal. The statistics, settlement, maintenance, and security of consumption data are all done by the bank. The bank transmits the consumption data of cardholders and statistical reports of various merchants to the school. The structure of Donghua University’s all-in-one card system is shown in Figure 2.

Figure 2 Donghua University All-in-One Card System Architecture
2 Successful application and shortcomings of Donghua University’s one-card system
At present, the system is applied to more than 20,000 students and more than 2 faculty members in the school. Cardholders can use this card as an ordinary UnionPay card to deposit or withdraw money at any bank or ATM/CDM. Parents of students can also credit their living expenses in the student’s account in a different place. Cardholders can use the self-service card placed on campus. The transfer machine or manual recharge machine transfers the money in the savings account to the e-wallet for consumption. You can swipe your card at any POS machine in Songjiang University City, borrow books from the school library, swipe your card, and perform various Attendance, access control, students can also perform physical exercise compliance tests, and teachers can also swipe their cards to take a shuttle bus. In short, as an effective identification of the identities of teachers and students, the all-in-one card integrates the functions of student card or work card, bank card, library card, medical card, dining card, computer card, etc., so that “one card in hand, universal on campus, “Passing” has been realized, bringing great convenience to the teachers, students and staff of the whole school.
At the same time, the program also has shortcomings. Mainly manifested in: bank card issuance and reissuing time is relatively slow, and inconvenient, it is not as fast and convenient as the school’s own card issuance; the realization of the data synchronization mechanism, there are some problems, such as the synchronization of data monitoring, fault tolerance and so on. The former problem can be minimized by coordinating with the bank to shorten the time for card issuance and reissuing, and reduce inconvenience; the latter problem can be solved by continuously improving the system design.
3 Conclusion
Donghua University has made a reasonable plan for the sectors of the safe, convenient, and multi-functional non-contact RF M1 card. By setting up a “shared sector”, it has expanded the application of the “Silver School Card” mode card; stable and secure system architecture, Ensure the normal operation of the one-card system; through the synchronization mechanism of card data, the campus one-card system becomes the basic platform for the school’s digital campus construction, which plays an important role in the school’s information construction.
About the Author:
Jiang Tao 1969-), male, from Danyang, Jiangsu Province, master of engineer, research direction for all-in-one card construction and management. E-mail:[email protected]
Donghua University Information Office Jiang Tao Liu Suping Pu Fang
references
[1] Huang Liping.On the Operation Mode of “Campus All-in-one Card” and the Realization of Network Security[J]. Educational Information (Digital Campus), 2005, (4): 34-35.
[2] Ma Xiuli. Analysis of Technical Features and Application of MIFARE 1 Non-contact IC Card[J]. Golden Card Engineering, 2005, (2); 46-50.
[3] Song Guangwei. Implementation of One Card System of MIFARE 1 Contactless IC Radio Frequency Card[J]. Modern Electronic Technology, 2005, (11): 27-29.
[ad_2]



