Intelligent manufacturing “secret order”-the application and value of RFID technology in manufacturing and logistics
[ad_1]
In the era of the Internet of Everything, all walks of life are relying on the Internet of Things technology to “match bridges.” The RFID technology at the core of the Internet of Things is the key to data connection and communication. Why can the material distribution process be viewed in real time? Why can individual products in retail stores be quickly found and counted? Why can they be retrieved quickly after theft? For these questions, this article will answer these questions one by one, and combine the use cases to “unlock” the smart manufacturing “secret order”.

Features of RFID
RFID technology has the advantages of non-contact, large capacity, fast, high fault tolerance, anti-interference and corrosion resistance, safety and reliability. It can not only adjust the identification distance flexibly, but also read a large number of RFID electronic tags at the same time. In addition, RFID technology is penetrative and can easily identify RFID tags inside objects.
RFID implementation steps
In order to help enterprises better implement the RFID system implementation, the implementation of RFID system should be divided into the following seven steps:
1. System process design: formulate and describe the operational business process and activities of the RFID system in detail.
2. System integration framework design: determine the basic structure of the RFID system (system architecture, network topology, database structure), main functions, RFID system and MES, ERP and other system integration strategies, methods and means, information integration interface specifications, RFID System data management mechanism.
3. System function configuration: convert the originally defined function into an application software system or subsystem. Specifically, it can be divided into warehouse management, material distribution management, quality management, asset management, supply chain logistics management, supplier management, maintenance service management, product life cycle data management, etc.
4. Selection of RFID equipment: From the perspective of the production environment and the characteristics of the production system, the RFID system is selected. The characteristics of the production environment include temperature, humidity, electromagnetic radiation intensity, pH, and the texture of peripheral equipment; the characteristics of the production system include product productivity, production cycle, cost, system reliability, system real-time, system data security requirements, etc.
5. Identification point and layout design: Determine the number and specific physical location of RFID information identification points in the application scenario and determine the installation and layout methods according to different characteristics.
6. Coding format and content design: Determine the format and content of the data carried in the RFID electronic tag. The encoding content depends on the level, field and goal of the enterprise’s RFID application; the encoding format should comply with the relevant regulations of the industry and the enterprise and be compatible with barcodes or other EDI-related encoding formats of the enterprise, so as to facilitate the sharing of data within or between enterprises And integration.
7. System implementation and evaluation.
RFID investment risk analysis
RFID technology is an emerging technology in the era of the Internet of Things. The implementation and landing of RFID technology puts forward higher requirements on the recognition rate, stability, reliability, data processing capabilities, data quality, and integration of the existing system of the enterprise. Therefore, we suggest that companies need to consider the following factors when investing in RFID:

Application case analysis:
In McKinsey’s Beijing Digital Capability Development Center’s clear wheat gearbox learning factory, RFID technology use cases effectively realized the whole process tracking of the production line and optimized inventory management.
Section 1: Production line management (material assembly in the factory, customized production)

Weaknesses: In traditional assembly lines, the production tempo of different stations is not matched, and the unskilled operation of employees has always been a pain point for enterprises, and production efficiency has been greatly reduced as a result.
solution:
The UHF RFID reader recognizes the passive electronic tags of the products in the assembly line, and records the cycle time and product assembly progress of different stations. The RFID system combines the digital SOP and Andon system to guide employees in material assembly; relying on the DPM system to analyze data to obtain insights, to achieve large-scale customized production.
Effect: With the help of the RFID system, the assembly line will be able to realize the data tracking of the whole process. The data read and recorded can be insights from the analysis technology, so as to realize lean production and promote the digital transformation of the factory.
Section 2: Inventory management (providing integrated solutions for data reading, recording, analysis, and display)

Weaknesses: Gearbox factories have been facing the challenge of poor inventory management. Due to the reliance on manual operations, errors frequently occur in material picking and warehousing and outgoing, filling in forms is time-consuming and laborious, and updating information is always a step slower.
solution:
The RFID reader recognizes the passive tags on the key materials and records the material in and out information. The electronic display board displays the location and quantity information of key materials in real time. The system automatically displays location information to realize floating inventory counting.
Effect: After the introduction of an RFID system composed of RFID readers and passive tags, the electronic display board can present information in real time, thereby effectively optimizing inventory management.

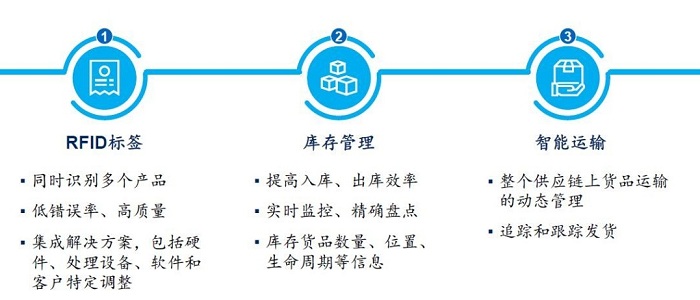
RFID technology makes it possible to visualize inventory management. Warehouse personnel can collect product information without contact, which not only greatly improves the efficiency of inventory counting, but also reduces the frequency of warehouse inventory errors. The application of RFID technology in the logistics link can also help companies realize the dynamic management of the transportation of goods in the upstream and downstream of the supply chain.
[ad_2]




