RFID Asset Management-RFID Asset Visualization Management System
[ad_1]
1 Introduction
1.1 Project background
Hangzhou Dongshi Technology RFID visual asset management system is an informatized, intelligent and standardized system for unified management and analysis of RFID assets based on mutual 3D technology, cloud computing, big data, RFID technology, database technology, AI, and video analysis technology. .
With the rapid development of the high-tech information industry and the formation of global economic competition, management work such as improving production methods, improving operating efficiency, reducing operating costs and improving service quality has become the top priority of all companies. Under the current management model, in the process of transferring information on asset changes, it is believed that the distortion and lag of information caused by factors have caused the account to be inconsistent, resulting in a large number of idle and wasteful assets, which seriously affects the authenticity of financial reports. As a bridge between the physical world and the existing IT system, barcode technology can effectively integrate the daily asset management activities with the asset management system, so as to achieve the synchronization of physical information and system information. Therefore, it has become possible to establish an asset management system based on barcode technology to realize automatic management.
As an important part of corporate assets, fixed assets constitute corporate value together with corporate funds and intangible assets. The proportion of fixed assets in the total value of corporate assets varies according to different industries, ranging from 20% to 75%. As an integral part of enterprise management, due to the high value of fixed assets, long service life, scattered use locations, etc., it is not easy to achieve one-to-one correspondence between accounts, cards, and objects in actual work. Work such as change, replacement, loss, inventory cleanup, etc. brings a certain degree of difficulty. It has a direct and close impact on data report statistics, asset structure analysis, asset appraisal and corporate listing and reorganization based on it, and has important practical significance for the rapid development of enterprises.
1.2 Introduction to RFID
RFID is the abbreviation of Radio Frequency Identification, which is a non-contact automatic identification technology. RFID can be traced back to the Second World War (around 1940), when the main function of RFID was to distinguish between enemy and British aircraft. In recent years, with the development of large-scale integrated circuits, network communications, information security and other technologies, as well as the promotion of the world’s number one retailer Wal-Mart and the U.S. Department of Defense, RFID has been rapidly applied to smart grids, transportation, logistics, medical and health, Fine agriculture and animal husbandry, finance and service industry, industry and automatic control, smart home, environment and safety inspection, public safety, national defense and military, smart city and other industries and fields.
RFID is to automatically identify target objects and obtain related data through radio frequency signals, and is mainly composed of electronic tags (Tag), readers (Reader), and antennas (Antenna). The tag is composed of a coupling element (also called an antenna) and a chip. Each tag has a unique electronic code (EPC), and the chip can store a specific serial number and other information. The reader is the connection bridge between the tag and the software system. On the one hand, it reads the tag information, and on the other hand, it communicates the reading result with the software system. The antenna exists in the tag and the reader, and is responsible for the data transmission task from the tag chip to the reader to the software system.
RFID technology is divided into low frequency, high frequency, ultra high frequency, active, etc. according to the frequency band. RFID technology has non-contact, fast scanning, high identification efficiency, not easy to damage, suitable for harsh environments, convenient operation, and fast reading and writing speed. Large amount of information storage, one card for multiple uses, anti-collision, good security and encryption performance, reusability, tracking and positioning.
1.3 Project objectives
The use of advanced Internet of Things technology, through the use of RFID technology, etc., realize the management of asset addition, allocation, maintenance, scrapping, and inventory, and improve the accuracy of asset management system data. The main goals are as follows:
·Improve the timeliness and accuracy of system data
Many aspects of traditional management use manual registration, which is easy to make mistakes; due to manual failure to register in time, the system data is not accurate enough.
· Quick inventory to improve the efficiency of asset inventory
The data in the process of entering and leaving the library adopts RFID technology, which can be scanned quickly to improve management efficiency.
·Provide leaders with a basis for decision-making analysis
The data can be analyzed online or generate reports for leaders to make decisions and analyze.
·Asset visualization
RFID equipment monitors the asset location in real time, displays the asset location in real time, and replays the track of the asset location.
2. Overall system design
2.1 System application architecture

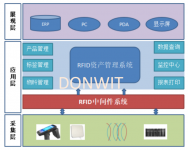
The system application architecture is divided into three logical levels: acquisition layer, application layer, and presentation layer.
·Acquisition layer: readers (desktop readers, fixed readers, etc.) read the electronic tag data, and then transmit it to the RFID middleware system through the network and other methods.
·Application layer: build production management, maintenance, query and other applications based on the RFID middleware system.
· Presentation layer: Users can log in to the system through ERP systems, computers, handhelds, display screens, etc.
2.2 Electronic label scheme
Since the warehouse is full of metal items, it is recommended to use RFID anti-metal tags.
3. System function introduction
3.1 Daily asset management functions
It mainly includes daily work such as adding, modifying, exiting, transferring, deleting, and taking inventory of fixed assets.
3.2 Monthly Fixed Assets Report
Query classified statistical monthly (annual) reports according to conditions such as unit, department, time, etc., increase fixed assets monthly report this month, decrease fixed assets monthly report this month, fixed asset depreciation monthly report (annual report), and provide printing functions.
3.3 Comprehensive Query of Fixed Assets
You can query the status of a single or a batch of fixed assets. The query conditions include asset cards, custody status, valid asset information, department asset statistics, exit assets, transfer assets, historical assets, name specifications, start and end dates, unit or Department.
3.4 Inventory function
Check the data in the barcode handset with the data in the database, and process the normal or abnormal data to get the actual situation of the fixed assets, and generate the inventory profit schedule, inventory loss schedule, and Inventory summary table.
3.5 System maintenance function
·The system administrator shall check the asset classification code table, exit method code table, purchase method code table, storage place code table, department code table, custodian table, and unit name table. Perform operations such as adding, modifying, and deleting;
Provide the function of the operator to modify his own password;
·The system administrator can freely set the operation authority of each subordinate operator to the function.
3.6 Security Management Function
Provide various security management methods;
·Password management function: maintain account numbers and passwords;
·Authorization control function: divide users into different levels to determine the user’s authority to use the system, and determine different operations according to different authorities.
3.7 Asset theft prevention
Carry out regional alarm for illegally entering and exiting assets to prevent asset loss.
4. System process design
4.1 Overall process
This project mainly manages the items in the warehouse. The management of large items in the warehouse to single items (the items are directly labeled); the management of small items to the category (a RFID tag is attached to each type of item turnover box) The main process is as follows :
4.2 Function introduction
4.2.1 New assets
The addition of assets is actually the entry of asset information. In the entry process, a desktop reader or handheld is used to initialize the tags, and the device details are registered in the background. We register detailed product information (site name, asset barcode, model, etc.) in the background. name).
4.2.2 Asset Requisition
When the asset is requisitioned, the RFID handheld device is used to scan the asset tag and fill in the recipient and the department.
4.2.3 Return of assets
When assets are used, RFID handhelds are used to scan asset tags and return the assets to the warehouse.
4.2.4 Asset allocation
The process of asset allocation needs to move the equipment from one place (room A) to another place (room B). In this process, it needs to go through two registrations of the reader. If a fixed reader is installed in the workshop, it can be collected automatically, or a handheld reader can be used. The specific process is as follows:
4.2.5 Asset maintenance
Scan the assets that need to be repaired, and the scanned assets are recorded as assets being repaired. After the repairs are completed, warehousing scans are performed.
4.2.6 Asset retirement
Obsolete assets are found at the asset obsolescence point: prepare the equipment for obsolescence and turn on the switch of the reader to make the reader in the state of reading tags. Take out the end-of-life equipment and confirm that the label is read correctly. Turn off the reader switch, and the scrapped equipment will be removed from the reader.
4.2.7 Inventory management
The general business process of inventory is as follows:
· The planning department issues an inventory notice and prepares for an inventory
· The warehouse manager receives the order, finds the corresponding location, starts the inventory, turns on the handheld, and scans the product RFID tag information
· Scanned data is automatically transmitted to the warehouse system via wireless
· After the system receives the collected information, it compares it with the book data in the system to determine whether the results are consistent.
· If unanimously confirm the inventory is completed
· In case of inconsistency, an alarm will prompt to find out the difference between the physical and system data, confirm it manually, and process the difference result
4.2.8 Asset theft prevention
When an asset enters or exits the workshop gate illegally, the RFID system automatically collects asset information, generates an alarm, and manually assists in finding the cause.
4.2.9 Asset trajectory tracking
Through real-time tracking of the position of the electronic tag, the movement track of the electronic tag is automatically generated and displayed in a graphical form.

4.2.10 Asset visualization
The large screen displays real-time asset status, utilization, alarm handling, etc.
[ad_2]