Mobile Health is to provide medical services and information through the use of mobile communication technologies-such as PDAs, mobile phones and satellite communications. Specifically, in the field of mobile Internet, medical and health App applications are the mainstay. The emergence of mobile medical has changed people’s traditional medical habits in the past, making medical services within reach, and the entire medical process is no longer constrained by time and place, alleviating the problem of manpower shortage in the medical industry. At the same time, hospitals can use mobile Internet of Things technology to improve service efficiency, reduce medical errors, control medical costs and improve medical experience. In the future, PC-based medical applications will gradually migrate to mobile terminals for completion. The importance of wireless networks as a pipeline for data transmission of mobile medical services is becoming more and more obvious. A set of highly reliable, high-bandwidth, and highly available wireless networks has become one of the core indicators for measuring the level of hospital informatization.
There are four major trends in the future of hospital mobile medical services:
1) Mobile medical care: nurses use PDA to complete “three checks and seven pairs”, patient information entry, patient identification barcode recognition, medical order information query, vital signs entry; doctors use PAD, carts and other terminals to complete the check and call of basic patient information PACS information, diagnosis entry, medical advice entry, and writing medical records;
2) Medical Internet of Things: The medical Internet of Things in a broad sense can be understood as the “Internet of Things Connected”, that is, through radio frequency identification (RFID, RFID + Internet), infrared sensors, global positioning systems, laser scanners, gas sensors and other information Sensing equipment, according to the agreed agreement, connect any item to the Internet for information exchange and communication to realize a network of intelligent identification, positioning, tracking, monitoring and management;
3) Palm hospital: With the Palm Hospital APP, patients can realize functions such as appointment registration, indoor route planning, asset management, information push, recording parking spaces, wireless big data analysis, and medical process reconstruction on the mobile terminal;
4) Medical multimedia: Through a wireless network, it carries multiple services such as video, voice, image and data, such as telemedicine, PACS cart, WIFI voice phone, wireless monitoring, etc.
Customized wireless network coverage
With the explosive growth of new applications such as mobile medical, handheld hospitals, and Internet of Things technologies, traditional hospitals are forced to gradually transform into future hospitals. In the construction of the hospital in the future, the hospital will face many difficulties. The wireless network and the Internet of Things signal coverage have repeated construction lines, multiple power supply systems are required, and management costs are too high. Hospitals urgently need a new wireless platform that can carry mobile medical care while smoothly upgrading and expanding IoT applications, reducing the difficulty of operation and maintenance, and unified management of applications, equipment, and personnel on the platform.
Huawei’s medical mobile IoT solution has customized platform-level AP products for the medical industry. While meeting WIFI coverage, it supports any third-party manufacturer’s RFID, ZigBee, Bluetooth 4.0 and other functional extensions. Hospitals can make unified planning for WiFi-based mobile medical applications and Internet of Things applications, implement step by step, and smoothly transition to Internet of Things hospitals, avoiding repeated investment in the construction process. Huawei’s medical mobile IoT solution provides refined and customized wireless network coverage solutions.
In the ward, operating room and other areas through the agile distributed solution coverage, as shown in Figure 1. The whole solution is composed of a central AP and remote module RRU. One central AP can control a maximum of 48 remote modules. The central AP is responsible for functions such as spectrum analysis, roaming handover, load balancing and association control, and the remote module RRU is responsible for functions such as radio frequency control and air interface management. Features of the program:
1) Zero roaming: There is no interruption of business packet loss, meeting the requirements of mobile business continuity;
2) Dual-frequency access to the room: 2.4G, 5.8G dual-frequency dual-inflow coverage in each room, no blind spots in the signal, and signal strength better than -65db;
3) Avoid construction: The remote module is a standard 86 box size, which can be replaced and installed through the existing information points in the room to avoid drilling construction;
4) Precise positioning: room-level positioning, capable of real-time positioning of terminal equipment connected to the remote module;
5) Flexible expansion: Through the standard RJ45 interface on the remote module or the central AP, any third-party IoT and Bluetooth business applications can be expanded;
6) Simplified management: The network management takes the central AP as the node to simplify the network management topology.

Figure 1. Huawei agile distributed AP system architecture diagram
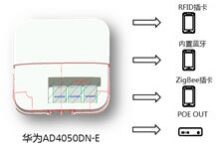
In open areas such as outpatient clinics, aisles, etc., it is covered by Huawei’s open IoT AP 4050DN-E to meet high-bandwidth and high-density access. At the same time, through the built-in three IoT card slots and the external standard POE interface , Can expand the rich Internet of things functions, as shown in Figure 2.
The value that AP4050DN-E brings to the hospital are: 802.11ac wave2: support MU-MIMO, double the performance; built-in Bluetooth: 1m precise positioning, support iBeacon and other Bluetooth-based IoT applications; 3-slot expansion: up to 3 expansions RFID or Zigbee plug-in card; POE OUT: comes with a POE power supply interface, flexibly expand the deployment of third-party equipment, such as locators.

Figure 2 Huawei’s open-mount IoT AP 4050DN-E
Rich mobile medical IoT applications
The architecture of the mobile medical Internet of Things is shown in Figure 3. It consists of 6 parts:
1) Label: Any product that can identify the identity, status, location and other information of an object can be called a label, including barcodes, two-dimensional codes, passive RFID, and various active IoT tags. Active IoT tags can support various signal formats, such as RFID, Bluetooth, ZigBee and WIFI.
2) Reader: The reader device can carry out two-way data transmission with the tag, such as the scanning gun of passive tags, the infrared scanning of medical PDA, the reader of active tags, and the tag trigger to obtain the position.
3) Network: Internet of Things data can be uploaded to the upper application server through network devices such as APs and switches. The transmitted data is divided into two types, one is location information data, and the other is business content data.
4) Positioning server: The uploaded position information type data is processed by a positioning server based on WIFI, RFID, and Bluetooth to complete applications such as position recognition and indoor positioning and navigation. Of course, two or more signals of WIFI, RFID, and Bluetooth can also be used for comprehensive positioning.
5) Internet of Things application: The uploaded business content type data is collected and processed through the Internet of Things application software, compatible with different protocols of multiple application vendors.
6) Medical application system: The ultimate goal of mobile medical IoT applications is to complete a variety of medical application tasks, and finally connect data with medical business systems such as EMR and HIS. At the same time, some applications also need to be completed in cooperation with other application systems in the hospital. For example, baby anti-theft will trigger an alarm and access control system after an unauthorized tag crosses the electronic fence, and locate the baby’s location with the help of the whole hospital monitoring system.

Figure 3 Mobile medical IoT architecture diagram
Huawei’s mobile medical IoT solution builds a medical IoT ecosystem through platform-level IoT APs, and fulfills Huawei’s dream of “Fully Connected Medical” by expanding the capacity to carry the infinite requirements of future hospitals for IoT applications. The construction content of the medical Internet of Things commonly has the following 8 directions, as shown in Figure 4:
1) Baby anti-theft: Through the matching function of the mother and baby tags, prevent the baby from holding the wrong phenomenon. Through the cut alarm of the baby’s wristband, the electronic fence function of the positioning trigger of the entrance and exit of the department, and the automatic lock function of the door to prevent the baby from being stolen.
2) Asset management: Identify the location and working status of valuable assets through active asset tags. On the one hand, it can realize asset inventory and quickly find the location of assets. On the other hand, it can count the income created by the equipment over a period of time through the working status of the equipment.
3) Medical waste tracking: The path of the medical waste truck is set in the hospital. When the waste truck is prevented from entering the unauthorized area, it will be linked to the alarm to remind. At the same time, the entire process of medical waste treatment can be tracked through the GPS IoT module.
4) Indoor navigation: Find the indoor location through the indoor navigation function, plan the path for medical treatment, and save time for medical treatment. At the same time, combining medical big data analysis and registration queuing information, optimize and reconstruct the medical treatment process and shorten the medical treatment time.
5) Ward monitoring: Real-time monitoring of patient vital signs information through vital signs tags, and upload to the business system as required for automatic recording.
6) Wireless infusion: the infrared sensor is used to prevent the needle from leaking during the infusion, and the infusion is automatically closed; the gravity sensor is used to monitor the liquid flow rate and remotely control the infusion pump; when the infusion is completed, it can be linked to call the nurse station.
7) Behavior analysis: In nursing homes, the sleep quality of the elderly can be monitored through the Internet of Things tags, and real-time warnings when the elderly fall down; in mental hospitals and infectious diseases, prevent patients from going out without authorization.
8) Supply system management: Through the passive IoT tags, the disinfection supply process and drug statistical management can be traced back.

Figure 4 Construction content of medical Internet of Things
The future hospital mobile medical Internet of things construction
As IoT hospitals involve a large number of business categories and a long construction period, not only the adjustment of the overall platform architecture of the hospital, but also the adjustment of the national medical policy is required, so the construction process needs to be gradual and planned. Therefore, it is necessary to make a unified plan during the construction process and complete the construction step by step.
1) In the first stage, the overall plan for the construction of the hospital’s wireless network, try to achieve dual-frequency signal coverage without blind spots, and the overall coverage strength is better than -65db. At the same time, it is possible to conduct IoT application trials in a small number of areas in accordance with the hospital’s own construction needs.
2) The second stage is to open up the data channel between the internal and external networks to realize data sharing inside and outside the hospital. For example, telemedicine and vital sign sensors are used in hierarchical diagnosis and treatment, combined with regional medical platforms and residents’ health files, to give play to the value of building a comprehensive mobile medical IoT hospital.
Concluding remarks
Over the past 20 years, Huawei has worked hard to make the world more stable and reliable; now, Huawei’s mobile medical IoT solution serves as a medical data fusion platform. In medical institutions, various application systems are interconnected through the medical network to achieve efficient business collaboration; among medical institutions, through the WAN for interconnection and collaboration, the sharing of medical and health resources is realized; in the future, Huawei is committed to building a better fully-connected healthcare The internet. Huawei Agile Network leads technological innovation and provides reliable, secure, and convenient operation and maintenance medical network solutions. Help the medical industry to communicate and share, promote medical business and management innovation, transform medical service models, and jointly build a better fully connected medical care.