RFID intelligent archive warehouse management system
[ad_1]
1. Demand analysis
In recent years, my country’s archives industry has made considerable progress. The scale of archives industry has expanded, and the number has increased day by day. The types of archives have become increasingly diversified, and the amount of information has expanded rapidly. However, the problems caused by traditional file management methods and technologies have become increasingly prominent:
(1) The traditional manual file cataloging process is cumbersome and inefficient, and the organization time is long
(2) The order of file storage is easy to be disrupted and difficult to find
(3) The types of files are complex and time-consuming to look up
(4) The inventory operation of archives is unscientific, and most of them stay on the inventory of archive boxes
(5) The management of invalid files is lagging behind, and a large number of redundant files are formed, which increases the management load and cost.
In view of this status quo, technical upgrading and transformation of archives management is imminent.As a new generation of material tracking and information identificationRFID(Radio frequency identification technology) The rapid development of technology has brought the possibility of automation and intelligence of file management, which has the unparalleled superiority of other methods.

2. The advantages of applying RFID technology to file management
1. Non-contact data collection
2. Fast scanning, large amount of one-time data processing
3. Large label information capacity and long service life
4. Data access password protection, high security
5. Strong anti-pollution performance and durability
6. Small size and diversified shapes
7. It can be reused to facilitate the update of information
8. Penetrating and barrier-free reading
9. The label has EAS anti-theft function
3. Introduction to RFID file intelligent warehouse management system
The archives management department can use RFID technology in three aspects in the archives management process.
1. Statistics of physical files
Install RFID tags in the archive file to enter the case number, catalog number, title of the file, the number of files in the file, and storage location, etc., and transmit the information to the server through the wireless network, which is managed by special software After processing, a database is formed. The staff can use the intelligent archive rack automatic collection inventory system when counting the archives, without checking each case file.
2. Management of physical files
By installing an intelligent security detection door at the entrance of the archives warehouse, real-time collection of label information can alarm the unauthorized archives, and record and count the authorized archives.
3. Correspondence with digital archives project
The label information can be connected with the file management software through the interface program, and the files that need to be adjusted can be retrieved through the file management software, and the warehouse staff can directly and accurately adjust the files through the terminal. Cooperate with the intelligent file shelf to realize the automatic opening of the file shelf. The access control system that reads the tag information ensures that the files will not be taken out of the file lending room.
4. The basic composition of the system
The intelligent warehouse management system based on RFID is composed of the following 15 subsystems:

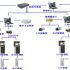
5. Schematic diagram of system hardware structure
The entire system is composed of 15 subsystems, each subsystem is required to have good coordination and linkage, can achieve automatic identification of large quantities of files in and out of the library, linkage alarm of illegal outbound system, intelligent file inventory and other functions.
Schematic diagram of the hardware structure of each area of the system
1. File query and use hall and warehouse

1. File query and use lobby work area

5. Intelligent warehouse management system architecture module
The system architecture module is mainly divided into five parts: warehouse three-dimensional map, file management, file borrowing, warehouse management and system management. The system architecture module is shown in the figure below.

[ad_2]