RFID fixed asset management solution
[ad_1]
1. Overview of RFID fixed asset management system
At present, the fixed asset management of many enterprises and institutions is basically sticking stickers and identifying device numbers through one-dimensional bar codes or two-dimensional codes. This traditional management method has the following serious shortcomings:
1. It is inconvenient for statistics, the speed of inventory is slow, and the personnel investment is large. Both one-dimensional barcodes and two-dimensional barcodes need to be scanned one by one manually, which is time-consuming and labor-intensive, and the efficiency is very low.
2. The equipment is moved away from the fixed place and cannot be discovered in time and is difficult to manage.
3. The stolen device can be difficult to find
Traditional asset management methods are becoming more and more inconvenient, and there are a lot of repetitive tasks, and it is difficult to take inventory. Not only does it cause greater pressure on the employees responsible for these things, but it is also difficult to know well! At the same time, due to changes in personnel, Difficult to track responsibility!
Fixed asset management is a management system based on UHF RFID technology launched for asset management. Inventory of the company’s fixed assets, optimize the configuration of the department, print labels, affix uniformly numbered labels, and hand them over to a designated person to strictly follow the process.
2. Asset Management System
2.1 RFID management
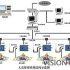
RFID electronic label management can be divided into: active electronic label and passive electronic label management. The asset management system adopts the most effective non-contact automatic identification technology recognized by modern times-RFID (radio frequency identification) technology for the storage of assets, assets, etc. Comprehensive and effective management of the application and inventory life cycle, detailed records through the management of the entire process of asset purchase, acquisition, maintenance, and scrapping, to achieve efficient and reliable fixed asset management. The system composition mainly includes central data server, handheld PDA, mobile APP, RFID tag, barcode, two-dimensional code and other asset management systems.

2.1.1 Active electronic label management
Active electronic tag management is adopted for valuable assets, and the reading method is active; the active tag is the most effective non-contact automatic identification technology recognized by the current asset management system-RFID (radio frequency identification) technology, and the active electronic tag has a longer The reading distance and the large memory capacity that can be accommodated can be used to store some additional information sent by the reader. Active electronic tags can record in detail through the entire process of asset purchase, requisition, maintenance, and scrapping, realizing efficient and reliable fixed asset management.
2.1.2 Passive electronic tags
For some electronic products, such as computers, cameras, printers and other assets, passive tag management is adopted, and the reading method is passive. Passive tags are now recognized as the most effective non-contact automatic identification technology in the asset management system—RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology. The warehousing, application, and inventory life cycles of assets, assets, etc. are fully and effectively managed, and detailed records are managed through the entire process of asset purchase, acquisition, maintenance, and retirement, so as to achieve efficient and reliable fixed asset management.
2.2 System flow
The RFID asset management system uses computers, all-in-ones, mobile hard drives, printers, fax machines, desks and chairs and other asset information to enter the system and allocate RFID tags, register the asset department and the applicant, and write the data to the corresponding tags Inside. Quick asset management and inventory work can be achieved through handheld reader or mobile phone APP scanning, which greatly saves manpower and material resources, improves asset management efficiency, and provides fast asset query and search tools for relevant management departments. The figure below is a schematic diagram of asset inventory and monitoring.

2.3 Function planning
Function planning includes: asset registration, asset management, asset inventory, asset monitoring, statistical query, system management and other functions. As shown below:

2.4 System function
2.4.1 Electronic label management
On the basis of the centralized display terminal program, the electronic label management module is added, and no additional client program is added, which can reduce user operations.
2.4.2 Asset Information Management
Information management of assets (new addition, modification, scrapping, etc.) can be performed, and asset information, user information, etc. can be inquired.
2.4.3 Asset Claim Management
All asset claims need to make corresponding business applications in the system. After the approval is approved, the system automatically writes the claimant, claim time, return time, etc. through the reader.
2.4.4 Asset archives (asset life cycle)
After the assets enter the system, an asset file is formed. You can query purchase information, user information, claim and return records, maintenance records, violation records, scrap records, etc.
2.4.5 Asset inventory
Handheld PDA inventory
The financial department conducts mobile inspection and inventory operations on all assets through the handheld PDA. The handheld PDA can identify assets and display relevant information, statistics, etc. As shown below:

Mobile APP inventory
Other departments can only perform mobile inventory operations on the assets of their own department through the mobile phone APP. The mobile phone APP can identify bar codes and QR codes affixed to ordinary assets (such as tables, chairs, benches), and can display related information, statistical quantities, etc. .
2.4.6 Asset Ledger Management
Assets can be divided into office assets, computers, electronic products, and other asset management, and can also be classified according to user-defined standards;
Each asset has all-life logs related to purchase, use, inspection, maintenance, Internet access, transfer, take-out, firmware changes, and scrap;
Equipped to specify multiple types and multiple condition combinations of search queries, export EXCEL reports, classified statistics (reports and graphics in two ways).
2.5 Function description
2.5.1 System background management
System background management is the foundation of the secret-related asset management system. It is mainly responsible for the establishment of initial data, system configuration, creation of users, adding unit departments, position (role) management, resource registration, and authority distribution. System background management includes organization management, system resource management, system integration authority management, log management, and system configuration management.
2.5.2 Asset Management
The addition of assets, the initialization of tags, the modification and query of asset information, etc. UHF tags are used for warehouse entry and exit records, patrol inventory, illegal alarms, etc., used for (desktop computers, portable computers, mobile hard drives, digital cameras, digital video cameras, office seats and other types of fixed assets).
2.5.3 Asset inventory
By installing the inventory program on the handheld or through the mobile phone APP, the automatic identification of the handheld PDA or mobile phone APP can be realized, which can be recognized in batches, and the number of various tags is calculated. Poor quantity, and detailed information).
The user conducts mobile inspection and inventory operations through the handheld PDA or mobile phone APP. The handheld PDA or mobile phone APP can identify assets and display relevant information, statistics, etc.
2.5.4 Asset file records
The asset file can view the entire life cycle of the asset from asset purchase to scrap, such as the person applying for purchase, approving person, purchase time, approval time, all violation records (violator, violation time, and reason for violation, processing result, etc.), all Outgoing records (exit time, person carrying, reason for outgoing, return time, etc.), scrap application, approval status, scrap verification result, etc.
2.5.5 Query of Asset Information
Query the basic information, current status, access records, violation alarm records, and asset file information of assets.
Violation records can view all violation records of a certain asset, the person who violated the law, the time of the violation, the reason for the violation, the processing result, etc.
Access records can view the access records of a certain asset, the time of each entry and exit, the person to bring, the reason for going out, the return time, the approver, approval opinions, etc.
Asset archives can view the entire life cycle of assets. Such as the person applying for purchase, the person who approves, the time of purchase, the time of approval, the record of violations (the person who violated the regulations, the time of the violation, the reason for the violation, the processing result, etc.), the entry and exit records (the time of each entry and exit, the person carrying, the reason for going out, etc.), Retirement application, and approval status, etc.
2.5.6 Ledger Management
Assets can be divided into office assets, computers, electronic products, and other asset management, and can also be classified according to user-defined standards. (As shown below)

Asset management classification icon
Each asset has a life log related to purchase, use, inspection, maintenance, Internet access, handover, take-out, firmware change, and scrap.
Equipped to specify multiple types and multiple condition combinations of search queries, export EXCEL reports, classified statistics (reports and graphics in two ways).
3. RFID product function
3.1 Electronic label requirements
The main key points of RFID label style and requirements are as follows:
High requirements for the environment: mainly considering outdoor use, so it can withstand relatively harsh environments, specifically: long-term high temperature resistance up to 70 ℃; ② resistance to friction; rain and snow, moisture-proof; ③ sunscreen does not fade; ④ acid-proof Alkali corrosion; ⑤ prevent transformer oil pollution; ⑥ anti-metal interference. ⑦The electronic label is cured to ensure good sealing and no gaps can appear;
Requirements for reading performance: Mainly considering outdoor inspection, passive electronic tags need to be able to read >5m;
Requirements for writing data to RFID tags: UHF UHF tag data needs to be written with 64 bytes of content;
Safety requirements for data written by RFID tags: users cannot intuitively understand the basic product information for the information written by UHF tags;
3.2 Electronic label solution
For the labeling requirements, the following solutions are proposed:
Using PCB/FR4 material as the label carrier, PCB/FR4 has higher mechanical and dielectric properties, better heat resistance and moisture resistance, and can be used outdoors for a long time. At the same time, Longfan Information is designed with a three-dimensional antenna, so that RFID electronic tags can have good read and write performance on metal surfaces.
According to the size requirements and read-write performance proposed by users, outdoor inspection (through a handheld RFID terminal) reading more than 5m does not meet this requirement. Two more suitable models are the specific sizes of 95*25*3.7mm and 28*28*3.7mm, and the handheld RFID terminal can read the distance over 3m.
For RFID tag writing data and security requirements, the RFID tag chip provided by Langfan Information adopts the imported chip Alien Higgs 3, which has 512bits Userdata area (user storage area) and 32bits Access Password (read and write access password area), It can fully meet the requirements of writing 64 bytes (that is, 512 bits) of data and encrypting the written data.
Note: Encrypt the label through Access Password, you can set an 8-digit (hexadecimal) password when writing the label. When reading and writing later, you need to check the password. If the password does not match, the EPCID cannot be performed. Writing, reading and writing of UserData.
3.3 Electronic label performance
In this project, special UHF RFID tags are selected, produced by the company itself, with reliable quality and stable performance. They have been applied in many domestic industries and have been unanimously recognized by customers.


[ad_2]