Design Scheme of Library Security Authentication Protocol Based on RFID
[ad_1]
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) is a non-contact automatic identification technology that automatically recognizes target objects and obtains relevant data through radio frequency signals. RFID can be widely used in many fields such as industrial automation, commercial automation, transportation control management, library management system, etc. It is listed as one of the ten important technologies of the century.
The application of RFID technology in the library field is booming: Molnar pointed out in 2004 that more than 130 libraries in North America use RFID systems. In China, Chengyi College of Jimei University in Xiamen took the lead in becoming the first domestic library to use the RFID collection management system in February 2006; then the Shenzhen New Library also chose the RFID system as a technical means for library service system improvement. , Wuhan Library became the third library to develop and use RFID intelligent collection management system across the board.
Security issues such as confidentiality and authentication are current research hotspots of RFID technology, and different application fields have different requirements for RFID security. In order to ensure the security of the RFID system in the library application environment, it is necessary to systematically study the security requirements and propose security solutions.
This article will focus on the application of RFID technology in library document management to discuss the issue of its authentication protocol. This article first analyzes the composition structure of the RFID system and the current status of the research on the security agreement authentication protocol. Based on the construction of the library RFID system security model, an authentication protocol to ensure the secure communication of the library RFID system is designed: PA-Lock protocol, and finally , Analyzed the security performance of the PA-LOCK protocol and compared it with other protocols.
2 RFID system composition and current status of security protocols
This part briefly introduces the basic structure of the RFID system, the communication model and the current research status of the security protocol.
2.1 RFID system composition
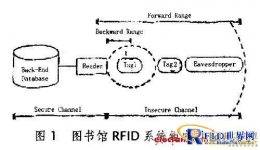
The RFID system generally consists of three major parts: RFID tag (tag), RFID reader (reader) and back-end database (database, back-end server), as shown in Figure 1.

1) RFID tag: It is composed of a chip and a coupling element (antenna). The chip is used for calculation and the antenna is used for wireless communication. The calculation and storage capacity of the chip is very limited. Each label has a unique electronic code.
2) RFID reader: It consists of a radio frequency interface and a control unit, and its computing power and storage capacity are relatively large. The RFID reader uses the radio frequency interface to obtain the data in the tag and transfer it to the back-end database. The channel between the RFID reader and the tag is an insecure channel.
3) RFID back-end database: receives data from the RFID reader and stores tag information or associated information. There is a secure channel between the RFID reader and the back-end database.
2.2 Research status of RFID security authentication protocol
The characteristics of wireless transmission, signal broadcasting, and weak computing power of RFID technology put forward special requirements for the design of RFID system security mechanism. Designing a safe, efficient, and low-cost RFID protocol has always been a challenging subject. .
Using cryptographic methods to design RFID security authentication protocols is a major research method. So far, many RFID security authentication protocols have been proposed. These protocols can be roughly divided into two categories: one is to design from the general security aspects of the protocol, such as Hash-Lock protocol, Hash chain protocol, hash-based ID change protocol, etc. These authentication protocols mainly solve the problem in the label identification process. Security issues, such as confidentiality, information leakage, and untraceability, etc.: The other category is to design RFID security authentication protocols from the particularity of the application field. Through detailed analysis of the characteristics of the application process, targeted design of RFID security issues to meet the needs of the application field, such as the universal and composable security RFID communication protocol in the supply chain environment, the protocol is through the supply chain management field In-depth research is conducted on the security mechanism of RFID technology in order to design an application-specific RFID security authentication protocol.
Like other specific RFID application fields, the characteristics of the library document resource management field also put forward special requirements for RFID security protocols. Its characteristics are mainly manifested in the following aspects:
ADDING-BOTTOM: 0px; MARGIN: 20px 0px 0px; WORD-SPACING: 0px; FONT: 14px/25px Times New Roman, arial; TEXT-TRANSFORM: none; COLOR: rgb(0,0,0); TEXT-INDENT: 0px; PADDING-TOP: 0px; WHITE-SPACE: normal; LETTER-SPACING: normal; BACKGROUND-COLOR: rgb(255,255,255); orphans: 2; widows: 2; -webkit-text-size-adjust: auto; -webkit-text -stroke-width: 0px”> 1) The book has two states during the whole circulation period: in the collection state and the loan state. The book management has different restriction rules for books in different states, such as the collection state in the library Books are not allowed to be taken out of the library, while books in loan status can be freely entered and exited from the library.
2) The state of books changes periodically. Each book starts from the state of collection in the library, and then returns to the state of collection in the library after being loaned out.
3) Book management requires real-time tracking, status positioning and statistical analysis of books. Analyze the usage and utilization of books. At present, there are no in-depth research results on RFID security mechanism in library document resource management. The focus of this article is to analyze and design a security authentication protocol for RFID tag authentication and identification for various main processes in library document resource management, to ensure that only authorized users can identify specific tags, and attackers cannot track these tags.
3 Library RFID security requirements modeling
An important prerequisite for designing RFID security authentication protocol is the need to define the security model of the RFID system. The security model is closely related to the actual application scenarios of the system. Therefore, before designing the library RFID system security authentication protocol, we must first analyze in detail the application model of the library RFID system, the main security threats, and the security requirements of the system.
3.1 Library RFID system model
Under normal circumstances, a library RFID system consists of three parts: tags, readers and back-end databases. Since there is a secure channel between the reader and the background database, we consider these two parts as a whole when designing the security protocol. Therefore, we mainly care about the reader and the tag. For tags, we assume that there are both legal and malicious tags. There are four main types of readers: tag converters, shelving devices, self-checking machines and security inspection doors. The tag converter is mainly used to realize the rapid conversion from bar code to RFID, and is responsible for writing related information. The shelf-arranging device scans the RFID tags of the books and performs positioning and counting in combination with the tier tags, which requires less information. The self-service borrowing machine scans the RFID and processes the book borrowing and returning, and it also needs to connect to the back-end database. The security detection door recognizes the book and determines whether the book is in the borrowing state.
The RFID tags used in the library are mainly passive tags with a working frequency of 13.56MHZ. This kind of tag has a small storage capacity and can only store a small amount of book information such as book titles and shelf numbers; at the same time, the computing power of the tag is also very weak. It can only compare two numbers, perform hash hashing, generate random numbers, and retrieve itself. Simple functions such as information are easily implemented on the Class 1 Generation 2 standard label.
3.2 Major security threats
Combining the characteristics of the library RFID system application model, the following important assumptions can be made:
Hypothesis: The communication between the reader and the tag that occurs inside the library is secure and can be transmitted in plain text; the communication outside the library has security threats and requires confidentiality and authentication measures.
On the basis of this security assumption, the security threats faced by the library RFID system mainly include the following:
1) As a normal reader, the attacker has the ability to scan tags.
2) The attacker has the ability to clone tags, that is, to rewrite the content of tags.
[ad_2]



