Understand the principles and applications of radio frequency circuits in one article
[ad_1]
What is a radio frequency circuit
Radio frequency is abbreviated as RF, radio frequency is radio frequency current, which is the abbreviation of a high-frequency alternating current changing electromagnetic wave. The alternating current that changes less than 1000 times per second is called low-frequency current, and the alternating current that changes more than 1000 times is called high-frequency current, and radio frequency is such a high-frequency current.
A radio frequency circuit refers to a circuit whose electromagnetic wavelength and the size of the circuit or device are in the same order of magnitude. At this time, due to the relationship between the size of the device and the size of the wire, the circuit needs to be dealt with by the related theory of distributed parameters. This type of circuit can be considered as a radio frequency circuit without strict requirements on its frequency, such as long-distance transmission AC power lines (50 or 50 or 50). 60Hz) Sometimes the related theory of RF is also used to deal with.
RF circuit block diagram
Principles of RF Circuits
The principle of the radio frequency circuit is introduced in detail with the radio frequency circuit of an ordinary mobile phone:
1. The structure and working principle of the receiving circuit:
When receiving, the antenna converts the electromagnetic wave sent from the base station into a weak AC current signal, filtered, amplified by high frequency, and sent to the intermediate frequency for demodulation to obtain the received baseband information (RXI-P, RXI-N, RXQ-P, RXQ- N); Send it to the logic audio circuit for further processing.
circuit analysis:
(1) Circuit structure
The receiving circuit is composed of antenna, antenna switch, filter, high amplifier tube (low noise amplifier), intermediate frequency integrated block (receiving demodulator) and other circuits. Early mobile phones had primary and secondary mixing circuits, whose purpose was to demodulate after lowering the receiving frequency (as shown in the figure below).
Receiving circuit block diagram
2. The structure and working principle of the transmitting circuit
When transmitting, modulate the transmit baseband information processed by the logic circuit into a transmit intermediate frequency, and use TX-VCO to change the transmit intermediate frequency signal frequency to a frequency signal of 890M-915M (GSM). After being amplified by the power amplifier, the antenna is converted into electromagnetic waves and radiated out.
circuit analysis:
(1) Circuit structure.
The transmitting circuit is composed of internal transmitting modulator, transmitting phase detector, transmitting voltage controlled oscillator (TX-VCO), power amplifier (power amplifier), power controller (power control), transmitting transformer and other circuits. (As shown below)
3. The structure and working principle of the local oscillator circuit: (local oscillator circuit, phase-locked loop circuit, frequency synthesis circuit)
This circuit generates four local oscillator frequency signals (GSM-RX; GSM-TX; DCS-RX; DCS-TX) without any information; they are sent into the IF, and the received signal is demodulated when receiving; when transmitting, the signal is transmitted Baseband information is modulated and transmitted for phase discrimination.
circuit analysis:
(1) Circuit structure: The mobile phone local oscillator circuit has four circuit structures:
a) Composed of frequency synthesis integrated block, receiving voltage-controlled oscillator (RX-VCO), 13M reference clock, preset frequency reference data (SYN-DAT; SYN-CLK; SYN-RST; SIN-EN), composed (early mobile phones Multi-purpose; as shown below).
b) Integrate the frequency synthesis integrated block into the IF, combined with an external RX-VCO (multi-purpose for mid-term phones and Nokia phones; (as shown below)
c) Integrate the frequency synthesis integrated block and the receiving voltage-controlled oscillator (RX-VCO) into one, called the local oscillator integrated block or the local oscillator IC (multi-purpose for mid-term machines and Samsung machines; as shown below).
d) Integrate the frequency synthesis integrated block and the receiving voltage-controlled oscillator (RX-VCO) into the intermediate frequency (new models and other brand-name machines are multi-purpose; the following figure).
It is worth noting that no matter what structure mode is adopted, the only difference is the generated frequency; its working principle, the direction and function of the generated frequency signal are the same.
Application of radio frequency circuit
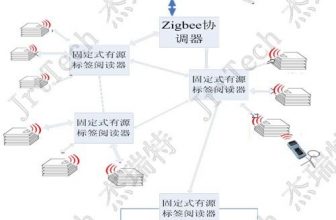
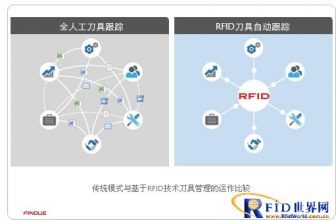
RF (Radio Frequency) technology is widely used in many fields, such as: TV, broadcasting, mobile phones, radar, automatic identification systems, etc. The special term RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) refers to the use of radio frequency identification signals to identify targets. RFID applications include:
1. ETC (Electronic Toll Collection)
2. Recognition and tracking of railway rolling stock
3. Container identification
4. Identification, certification and tracking of valuables
5. Target management of commercial retail, medical care, logistics services, etc.
6. Management of entrance and exit prohibition
7. Animal identification and tracking
8. The vehicle is automatically locked (anti-theft)
[ad_2]