Shantou University Library successfully applied UHF RFID technology
[ad_1]
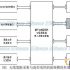
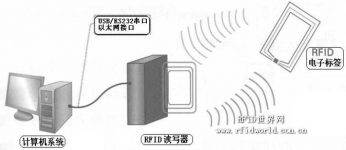
The working principle of RFID automatic identification system
The automatic identification and data acquisition system using RFID technology consists of at least the following three parts:
(1) Reader: A device used to read (or write) tag information;
(2) Radio frequency tag (Tag): used to identify the target and provide user data area to store, read and write target data.
(3) Computer application support system: process and use data according to the needs of users

Application status of RFID technology in libraries
The situation of RFID application cases in the world investigated by IDTechEx
1. The application status of RFID technology in libraries
In the late 1990s, the National Library of Singapore began to experiment with the application of RFID in libraries;
In August 2003, the 69th IFLA Conference established a special RFID library application forum to introduce and promote RFID application experience;
In 2004, the Library Authority of Singapore began to comprehensively upgrade the RFID system implemented in the late 1990s and promote the RFID application system nationwide;
From 2004 to 2006, many foreign libraries began to deploy and implement RFID application systems. Libraries in Singapore, Switzerland, the Netherlands, Denmark, Sweden and other countries have basically popularized the application of RFID in libraries;
In March 2006 and June 2006, the Chengyi College Library of Jimei University and the Shenzhen Library implemented RFID application systems in the libraries.
1. The application status of RFID technology in libraries
According to the retrieved information, the RFID technology implemented in libraries before 2005 was based on HF, and UHF RFID has only been applied to libraries and book supply chains after 2006;
At the beginning of 2005, the library automation system supplier Civica developed a library RFID application system based on UHF RFID technology, and it began to be used in some libraries in Australia and Singapore in 2006;
In May 2006, the famous Dutch bookstore BGN began to carry out EPC UHF G2 RFID application test in one of its branches, and it is expected to be fully promoted in other bookstores in 2007.
Why does our library conduct UHF RFID application test
Our library signed an agreement with Ningbo Yuanwanggu Company to carry out UHF RFID technology library application test in September 2006, based on the following reasons:
1. Although the existing HF RFID library solutions are relatively mature, they have high prices, poor tag installation concealment (anti-theft), and some problems in inventory inventory. Some problems are unlikely to be broken in short-term; while UHF The advantages of RFID technology and the rapid development trend will provide the possibility to solve these problems.
2. After the EPC G2 standard was formulated in the second half of 2004, ultra-high frequency (UHF) tags began to be produced on a large scale, and they have developed rapidly in the product supply chain management, retail, and pharmaceutical industries. “Because of their advantages in remote identification and low cost, It is expected to become the mainstream in the next five years.” (The Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China and other 15 ministries and commissions, June 9, 2006: China Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) Technology Policy White Paper)
3. In 2006, the Dutch BGN bookstore chain adopted EPC UHF G2 RFID technology for its book supply chain and sales management considering the development prospects of UHF and its price factors; another Dutch bookstore that began to use HF RFID for its book supply in 2005 NBD|Biblion has also begun to explore the feasibility of applying EPC UHF G2 to books.
4. CIVICA’s library management system SPYDUS integrated the UHF RFID module in 2005 and implemented it in some libraries in Australia and Singapore in 2006
5. In 2006, Zebra Company suggested on the application of RFID in logistics: “If you are preparing to implement RFID pilot projects, you should directly adopt the UHF G2 standard.” , January 11, 2006)
6. Extensive discussions and in-depth exchanges with domestic and foreign libraries, library RFID system suppliers and technical experts have enhanced our understanding and confidence in the technical and economic feasibility of UHF RFID application in libraries.
7. Long-term communication and cooperation with Ningbo Yuanwanggu Company. Founded in 1999, Yuanwanggu Information Technology Co., Ltd. is a well-known high-tech enterprise engaged in the research and development of radio frequency identification technology. It was listed on the Shenzhen Stock Exchange in August 2007. Its subsidiary Ningbo Yuanwanggu Company specializes in UHF RFID libraries. For the research and development of application systems, our library had many contacts with the company from 2005 to 2006. In 2006, after Ningbo Yuanwanggu Company completed the basic equipment and tags for UHFRFID application in libraries, it looked for libraries that were willing to cooperate with the company for experiments. Based on the above reasons, our library signed a cooperation agreement with the company in September 2006 for the application of UHF RFID in the library.
A brief description of UHF and HF
The issue of RFID standards is one of the issues that everyone is most concerned about. The promulgation of international standards for HF and UHF air interface communication technologies is as follows:
In 1999, ISO/IEC formulated the ISO/IEC 15693 standard, which regulated the implementation of high-frequency radio frequency identification technology;
On August 15, 2004, ISO issued the ISO/IEC 18000-6A/6B 2004 International Standard (Information Technology—Radio Frequency Identification Based on Single Product Management—Part VI: Air Communication Interface Parameters with Frequency 860—960MHz) ;
On December 16, 2004, EPCglobal formally approved and announced the EPC UHF Class 1Generation 2 RFID standard.
On June 15, 2006, EPC C1G2 was approved by ISO/IEC and officially became an international standard—
ISO/IEC18000-6C. Tags that comply with this standard are referred to as G2 tags for short (EPC C1G2 standard is an air interface communication technology standard between electronic tags and readers that are launched by EPCglobal based on the concept of EPC and the Internet of Things to give each item a unique identification code)

EPC UHF Class 1 Generation 2 electronic tags, generally called G2 tags, have the following characteristics:
(1) Open standards: This means that the acquisition of labels is multi-channel, which will promote the rapid reduction of prices.
(2) Storage and password: Gen2 tag has 96-bit EPC code in the chip, and a unique password, larger storage capacity and better security performance can effectively prevent the chip from being illegally read.
(3) Size: The chip will be reduced to 1/2 to 1/3 of the current version.
(4) Multi-vendor compatibility: devices from different vendors will have good compatibility.
(5) High reliability: The tag has a high reading rate.
(6) Better label reading performance: Avoid repeated reading during batch label scanning.
(7) “Inactivation” function (Kills): The tag can be permanently destroyed by itself after receiving the inactivation instruction of the reader.
(8) Security: The tag has a better security encryption function to ensure that the data will not be diffused during the process of reading the information by the reader.
(9) Real-time: Allow tags to enter the reading area after a delay and still be read, which is not achieved by Gen 1.
(10) Global frequency allocation: Wider spectrum and radio frequency allocation improves UHF frequency modulation performance to reduce interference with other radio equipment.
(11) Reading rate: The reading and writing rate of Gen 2 tags is 10 times that of existing tags, which enables high-speed automatic operation through the application of RFID Gen 2 tags
Shantou University Library UHF RFID Application Test
The test mainly consists of two parts:
The first part is the test of self-service lending and anti-theft detection. This part of the test is mainly realized through the actual operation of the reader’s self-service lending and returning;
The second part is a comprehensive experiment of the functions of the association between the electronic tags of books and library cards and related information of books and readers, book inventory and mis-shelf sorting, which are mainly carried out through the daily work of library managers. The application test results show that the UHF RFID system is correct in the library business process, and can well realize the functions of book self-checking and returning, book anti-theft alarm, electronic tag conversion, book inventory and wrong shelf sorting, etc. The distance control and reading and writing performance reach the same performance as the HFRFID system, and some aspects even exceed the HF RFID system.
The UHF RFID application test conducted by Shantou University from September 2006 to June 2007 mainly tested the application of ISO18000-6B electronic tags and related equipment in the library. The test results are as described above.
Since September 2007, our library has adopted UHF G2RFID technology to formally carry out new book circulation and collection management applications. As far as the current state is concerned, the operation is in good condition, and the G2 tag has better performance than the 18000-6B tag used in the test. And performance.
Shantou University Library (new book loan area) officially launched UHF RFID application project

At present, the main functions realized by our library using UHF RFID technology are:
1. The association and identification of electronic tags with books and reader-related information;
2. Book self-service borrowing and returning;
3. Book anti-theft detection;
4. Book inventory, including the next shelf and the whole shelf, etc.;
5. Book search;
[ad_2]