The military, public security and other security industries use RFID electronic tags to achieve informatization management solutions
[ad_1]
Chapter One Project Feasibility
Looking at any country in the world, there is no doubt that the development of the military does not rely on information technology as a support point, but integrates its own development and growth. Regardless of the branch of the military, the development and utilization of information resources as the core information construction work has been included in the agenda of army building. The new military revolution centered on information technology is causing a profound change in the military field. The essence of this change is the transformation from the mechanized military form of the industrial society to the informationized military form of the information society. Along with this huge historical change, military informatization has gradually become an important means of accelerating the realization of military modernization, and it has also become an important research content of military modernization.
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology is an automated identification technology that has matured from the 1980s. It has its own immeasurable advantages over traditional barcodes and other identification technologies. It stores a large amount of information, The content can be dynamically changed, the target can be read farther away, and multiple targets can be identified at the same time. Its automatic, real-time recognition capability is especially suitable for the military’s militarized management requirements for the entry and exit of personnel, vehicles, ordnance, and materials.
According to the military of various countries, at present, the most representative use of RFID technology is the US military. The U.S. Department of Defense’s application of RFID technology stems from the needs of modern warfare: During the 1991 Gulf War, the U.S. shipped about 40,000 containers to the Middle East, but due to unclear identification, more than 20,000 of them had to be reopened and registered. , Package and put into the transportation system again. After the war, more than 8,000 opened containers remained unused. Later, the US military estimated that if RFID technology was used to track the whereabouts of logistical materials and obtain a list of the contents of the container, it would save the Department of Defense about US$2 billion in expenditure. After the Gulf War, the U.S. military provided rapid and accurate logistical support to combat troops in order to solve serious practical problems in the process of claiming, transporting, and distributing materials. Highly transparent. The application of RFID technology makes it possible for the U.S. military to realize the transparency of logistical materials, and provides a convenient and flexible solution for automatically obtaining visualized information about materials in storage, in transit, and in use.
RFID technology has been widely used by the US military in the field of military logistics support, such as a specific item search system, a visualized management system for materials on the way, an electronic medical record card for individual soldiers, and the management of ordnance materials in and out of warehouses, which have greatly reformed the traditional logistics tracking methods. By adopting RFID technology, the average logistics supply time of the US military has been greatly shortened.
The information management of ordnance and other armament materials is precisely the weak link of our army’s overall information construction. Most warehouse management mainly relies on manual operations, which cannot adapt to the requirements of fast and accurate guarantees for future wars. Therefore, make full use of RFID technology to realize ordnance The automated management of armaments and supplies is a key element of our military in the field of logistics informatization, and it is also the basis for realizing the visualization of the entire process of material support in the future, establishing a “precision” battlefield material support system, and realizing scientific and rapid material support decision-making.
Case: The 2003 Iraq War saved billions of dollars for the US military
In the 2003 Iraq War, the U.S.-British coalition used RFID technology to build a visualized logistic network that made the U.S. military’s logistic supply capabilities unprecedentedly powerful. The U.S. military can easily grasp all real-time information about logistic supplies; the British military also uses this network. , So that up to 90% of the logistics materials can be efficiently transported to the front line. This is a far cry from the situation during the Gulf War in 1990.
During the Gulf War, the US military used radio frequency identification tags installed at assembly points in Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Turkey, the United Arab Emirates, Qatar and Yemen to obtain real-time logistic material availability. During operations, the U.S. military’s logistics supply line also uses mobile radio frequency identification readers to ensure that supplies to the front line arrive on time, and use automatic identification technology to shorten the time in the process of handing over materials and inventory, and to improve the benefits of logistics supply. fully use.
Figure 1: Radio frequency identification equipment (fixed and handheld readers) used by the US-British coalition forces
Figure 2 U.S. military containers are equipped with radio frequency identification readers in ports, airports, railways, and logistics centers to collect dynamic data on logistics supplies
Figure 3 In the process of transporting supplies from the material assembly point to the front line, the US military installed mobile radio frequency identification reading devices along the line. Click here to enter
Figure 4 RFID tags installed on the helicopter
Figure 5 Helicopter transportation
The U.S. Department of Defense continues to use radio frequency identification technology, which has been extremely effective in military logistics, and has helped the U.S. military complete the following tasks:
※ Increase productivity through automation and limit manual intervention to avoid human error;
※ Achieve complete visualization of the supply chain;
※ Eliminate excess inventory (application for excess supplies);
※ Obtain fast logistics management and real-time supply chain dynamic data;
※ Speed up the transportation of logistics materials from the factory to the foxhole and improve the control of transportation;
※ Reduce redundant data entry and improve the accuracy of data;
Chapter 2 Overview of RFID System
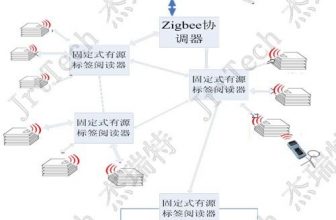
The long-distance radio frequency automatic identification system uses radio frequency signals to realize contactless information transmission through spatial coupling and realizes the automatic identification of items in different states (moving, stationary) through the transmitted information, thereby realizing the automated management of targets.
The system can perform network management according to different management requirements, and realize the network application of long-distance radio frequency identification.
use. The system’s reading equipment adopts ultra-high frequency shortwave frequency (transmitting and receiving frequency 902-928MHz) to realize reliable full-duplex wireless data communication.
The basic principle of RFID management product data
Chapter 3 System Process
According to the information scanned and identified by the system, if irregular operations are found, such as incorrectly fetching firearms and equipment belonging to other companies, the system will give an alarm.
Chapter 4, System Product Composition
The system product consists of a software system and a hardware system. The software system mainly refers to application software. If a handheld data acquisition device is used, the software system also includes an embedded software part, which is mainly used to complete information collection, processing and transmission. The hardware system is composed of electronic tags, antennas, readers and PCs, and is used to complete information collection, identification and running application software.
in:
Electronic tag: Attached to the identified object to identify the object.
Antenna: used to transmit and receive radio signals;
Reader: Used to collect tag information.
PC: Run application software.
5.1 Electronic label
As shown in the figure:
The main considerations for electronic label selection are:
◎ The actual application mode and environment of the customer;
◎ The reading and writing distance of the label;
◎ Transmission rate;
◎ Reading and writing speed;
◎ Working frequency;
◎ Memory and packaging form.
According to user needs and referring to the above factors, in order to achieve accurate reading and prevent cross-reading, we choose passive single-frequency electronic tags.
◎ The working frequency of the label is UHF frequency band, 915M;
◎ The tag memory adopts EPC CLASS 1 Gen2 standard;
For the complex situation of monitored items, special materials are used for packaging, which is suitable for the surface of metal items.
5.2 Reader
As shown in the figure:
The reader/writer plays a pivotal role in the RFID system. The frequency of the reader/writer determines the working frequency band of the RFID system, and the power of the reader directly affects the distance of the RFID system. Generally speaking, a high-frequency tag has a greater reading distance, but it requires a greater electromagnetic wave energy output by the reader. A high frequency tag can be read within a distance of 3 to 8 meters.
The selection principle of the reader is as follows:
◎ High reading rate, high stability;
◎ The radio frequency module and control software part of the reader have a high degree of consistency;
◎ Comply with multiple protocols and can read multiple types of tags;
◎ The reader software can be smoothly upgraded according to the development of multiple standards such as EPC;
◎ With rich interfaces;
◎ It can read multiple tags at the same time in the reading and writing area, with anti-collision function;
◎ Check the error information in the process of reading and writing;
◎ Support TCP/IP protocol, easy to configure and manage through network.
◎ The current of the matching antenna coil is large enough;
◎ Antenna power matching;
◎ The antenna has sufficient bandwidth to ensure the transmission of carrier signal.
Handheld Reader
You can also choose a handheld read-write device, as shown in the figure below:
Read and write protocol: UHF Gen 2.
Card reading distance: 0-2.0 meters
[ad_2]