Kailu Microelectronics XPM-RFID Library Management System
[ad_1]
1. Concept and characteristics of RFID and XPM-RFID
RFID is the abbreviation of Radio Frequency Identification, that is, radio frequency identification.
RFID technology is a non-contact automatic identification technology, which uses radio frequency signals to automatically identify target objects and obtain relevant data. It can recognize objects within a range of several centimeters to tens of meters, and can be read in batches, and can identify items, equipment, vehicles, and people in various motion states, making it a dazzling star in the field of automatic identification. , Is another new technological revolution brought after the Internet.
XPM, namely Super Permanent Memory (Super Permanent Memory). It is a new type of non-volatile memory (NVM, Non-Volatile Memory) technology. It uses 100% deep sub-micron standard CMOS process, which is the same as manufacturing logic circuits (CPU, DSP, etc.) without adding floating gate process.
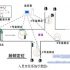
Schematic block diagram of XPM-RFID chip
Antenna terminal
XPM-RFID uses the XPM patented technology and applies it to the RFID chip, replacing the traditional EEPROM with XPM memory as the ID code storage device, so that the advantages of XPM memory are concentrated. It can be widely used in document anti-counterfeiting, ticket management, access control, electronic payment, manufacturing, single product identification, logistics and supply chain management and other fields. It has the characteristics of low cost, high process compatibility, high confidentiality, and physical indelibility. .
Note: From “A Novel Embedded OTP NVM Using Standard Foundry CMOS Logic Technology>>,
Jack Zezhong Peng, ect. NVSMW 2006, Monetary, CA, USA
2. The working principle of XPM-RFID
(1) Composition of XPM-RFID system
The most basic XPM-RFID system is basically composed of three parts: electronic tags, readers and antennas (Antenna).
The electronic label is the core of the radio frequency identification system, also known as the radio frequency label. Its English name is TAG, and it is also called LABEL. The electronic tag is the real data carrier of the radio frequency identification system. Under normal circumstances, radio frequency tags are composed of coupling elements and chips. Each tag has a unique electronic code, which is attached to an object to identify the target object; when illuminated by radio frequency signals, it can reflect back to the radio frequency that carries alphanumeric information. Signal for the reader to process and recognize. According to the different power supply methods of the radio frequency tag, it can be divided into active (Active Tag) and passive (Passive Tag). The active tag is equipped with a battery, and the passive tag has no battery.
A reader is an electronic device that reads or reads/writes electronic tags. Sometimes it is also called a reading device, an interrogator, a communicator or a reading device, which is used to generate and transmit radio frequency signals and The device that receives the radio frequency signal reflected by the electronic tag, and obtains the tag data information after processing, and sometimes can also write the tag information, can be designed as a handheld or fixed type. The radio frequency signal is transmitted between the tag and the reader, and the antenna of the reader can be built-in or external.
(2) The working principle of XPM-RFID
The reader is a device that generates, transmits, and receives signals. The radio frequency signal generated by it is amplified by the power amplifier and transmitted through the antenna. At the same time, it receives the signal reflected by the tag, and is separated by the radio frequency receiver. Then it is detected, demodulated, amplified by the preamplifier, and sent to readout. The computer processes. The electronic tag reflects the memory data and modulates the microwave carrier signal. When the object carrying the tag passes through the communicator, the tag receives the microwave emitted by the antenna and modulates the microwave signal. The communicator receives the information modulated by the tag and restores the “object information” in the tag, thereby achieving the identification of the object. Purpose.
The reader sends out a certain frequency radio frequency signal through the antenna. When the tag enters the magnetic field, it generates an induced current to obtain energy. It sends out its own code and other information, which is read and decoded by the reader and sent to the host computer for relevant processing. The reader sends a set of electromagnetic waves with a fixed frequency to the tag. There is an LC series resonant circuit in the card whose frequency is the same as the frequency emitted by the reader. Under the excitation of the electromagnetic wave, the LC resonant circuit resonates, so that the capacitor has To calculate the charge, a unidirectional electronic pump is connected to the other end of the capacitor, which sends the charge in the capacitor to another capacitor for storage. When the accumulated charge reaches 2V, this capacitor can be used as a power supply for other circuits. Provide the working voltage, transmit the data in the card or receive the data of the reader.
(3) XPM-RFID working frequency band
For RFID systems, the most important frequencies are 0~135kHz, and ISM frequencies 6.78MHz, 13.56MHz, 27.125MHz, 40.68MHz, 433.92MHz, 869.0MHz, 915.0MHz (not used in Europe), 2.45GMHz, 5.8 GHz and 24.125GHz. The working frequency of a typical radio frequency tag (radio frequency identification system) is shown in the figure.
3. Comparison of the advantages of XPM-RFID and traditional technology RFID and barcode
The daily services of the library usually involve the management of the flow of people and logistics, which requires a large number of readers and books to be identified, access control, and statistics. Today, with the popularization of automated systems, libraries basically use barcode technology as a Identify methods to achieve these functions. However, although barcodes have the advantages of low price and convenient production, they also have some inherent shortcomings that are difficult to overcome. For example, because they are easy to wear, they must be affixed in the book, causing inconvenience to use, etc., and they are not completely suitable for libraries. On the one hand, RFID is fully equipped with bar code functions, and on the other hand, it has many new functions that cannot be realized by bar codes. The development and utilization of these new functions will bring revolutionary changes to the traditional service work of the library.
The use of RFID technology to automate library operations must require RFID tags to have extremely high requirements on the data storage period, cost tolerance, and data security. According to the current most common EEPROM-based technology RFID tags have shortcomings such as short data storage time, low security, high cost, and easy data loss.
Therefore, among various RFID technologies, XPM technology is the most suitable for RFID library management system. This not only effectively solves the data storage period and security, but also relatively reduces the operation and implementation costs of the RFID library management system, and also provides sufficient conditions for the wide application of RFID in the library industry.
It can be seen from the above-mentioned characteristics of RFID that the RFID system using XPM technology has more advantages than other RFID technologies and bar codes (see Table 1 and Table 2).
|
Features |
Bar code |
XPM-RFID |
|
Reading convenience |
Need to be visible and clear when reading |
Can be very thin and concealed in the package and still be able to read the data |
|
Number of reads |
Only one at a time when reading |
Can read and write multiple at the same timeRFIDLabel |
|
Literacy |
Information cannot be updated |
Electronic tags can be read and written repeatedly |
|
Data capacity |
Data storage capacity |
Large storage capacity |
|
Long-distance reading and writing |
Need auxiliary means such as light |
Read and write without light |
|
High-speed reading and writing |
There are restrictions on reading while on the move |
Can perform high-speed mobile reading and writing |
|
Data accuracy |
Need to rely on manual reading and writing, so the possibility of human negligence |
Data transmission is stable and reliable by built-in chip |
|
Label robustness |
When stained or damaged, it will not be able to read or write, that is, no durability |
Can read and write in harsh, harsh and dirty environments |
surface1 XPM-RFIDCompared with barcode function
Note: From “Henan Library Journal”, Yang Xiangming,2006year12January, Zhengzhou, Henan, China
|
Unique IDPerformance requirements
|
Mask Rom
|
EPROM
|
EEPROM
|
XPM
|
|
Per cardUIDGuaranteed not the same
|
–
|
OK
|
OK
|
OK
|
|
No modification
|
OK
|
OK
|
–
|
OK
|
|
Data confidentiality (anti-detection)
|
Low
|
middle
|
middle
|
high
|
|
Data retention
|
high
|
middle
|
middle
|
high
|
|
Embedded ability (standardCMOScompatible)
|
–
|
–
|
Low
|
high
|
|
price
|
Low in large quantities
|
middle
|
high
|
Low
|
surface2 XPM-RFIDAnd otherRFIDTechnology comparison
First, scan quickly. Only one barcode can be scanned at a time. The RFID reader can read several XPM-RFID tags at the same time, and can write and access data. The writing time is less than that of printing barcodes.
Second, the volume is miniaturized and the shape is diversified. XPM-RFID is not limited by size and shape in reading, and does not need to match the fixed size and printing quality of the paper for reading accuracy. In addition, XPM-RFID tags can be miniaturized and developed in various forms to be applied to different products.
Third, anti-pollution ability and durability. The carrier of traditional bar codes is paper, so it is easy to be contaminated, but XPM-RFID has strong resistance to water, oil, chemicals and other substances. In addition, because the barcode is attached to the plastic bag or the outer packaging carton, it is particularly vulnerable to damage; the XPM-RFID tag stores the data in the chip, so it can be protected from contamination. It has a long service life and can work in harsh environments.
Fourth, it can be reused. Nowadays, the barcode cannot be changed after it is printed, and the XPM-RFID tag can repeatedly add, modify, and delete the data stored in the RFID tag to facilitate the update of information.
Fifth, penetrating and barrier-free reading. When covered, XPM-RFID can penetrate non-metal or non-transparent materials such as paper, wood, and plastic, and can perform penetrating communication. The bar code scanner must be at a close distance and there is no object blocking the situation before it can read the information.
Sixth, the memory capacity of data is large. The capacity of one-dimensional barcode is 50Bytes, the maximum capacity of two-dimensional barcode can store 2 to 3000 characters, and the maximum capacity of XPM-RFID is 256M Bytes. With the development of memory carriers, the data capacity also has a trend of continuous expansion. In the future, the amount of data that items need to carry will become larger and larger, and the demand for the expansion of the capacity of the label will also increase accordingly.
Seventh, high security. Since XPM-RFID carries electronic information, its data content can be protected by a password and its physical characteristics can be changed, so that its content will not be forged or altered.
Fourth, the application of XPM-RFID in the library
In recent years, KILOWAY has devoted itself to the application of XPM-RFID technology with independent intellectual property rights in the library field, and has launched a library management system based on XPM-RFID technology. XPM-RFID technology is mainly used in libraries such as self-borrowing stations, self-service book return boxes, counter workstations, collection sorting systems, machine inspection service stations, electronic security doors, bookshelf management systems, etc.
(1) Overview of XPM-RFID Library Management System
The use of XPM-RFID technology is not simply a replacement for barcodes. It is guided by the creation of a brand-new service concept and business model, which promotes the improvement of reader service quality and document management level from the content and form, so that the connotation of modern libraries lies in digital books. On the basis of the pavilion, the meaning of intelligence is given. The XPM-RFID-based intelligent library management system can manage the location, distribution, circulation and flow of books and objects in the library, and can enhance the classification, coding, positioning and data collection of books, thereby greatly improving the efficiency of the library. Give library staff more time to assist readers.
(2) System composition
XPM-RFID tag can provide convenient data management, and has anti-theft protection function; the antenna mainly provides security work at the entrance and exit, it can accurately identify the book title of each book that triggers the alarm, and truly ensure that there is no false alarm; The counter workstation is for the administrator to read the RFID code of the book when going through the procedures of borrowing and returning the book. It is convenient for the librarian to carry the handheld code reader at any time to capture the information of the smart label on the book, quickly search for the book, and put it on the bookshelf. Book management and categorization; the self-service borrowing and returning machine allows readers to go through the borrowing procedures by themselves. It consists of a library card reader, RFID reader, touch screen and a receipt printer; automatic sorting system, Use the reader to identify tags to achieve the purpose of automatic sorting; the application software uses SIP2 interface to connect with LAS and other components through the Ethernet interface to connect the intelligent library management system with the library’s circulation automation system. Bring convenience to readers and librarians.
(3) Advantages of using XPM-RFID system
1. Speed up the circulation operation
The application of the XPM-RFID system in the library shortens the time required for circulation services. Relying on the support of RFID radio frequency identification technology, the borrowing process becomes very simple. When the user selects several collection materials and comes to the reader to borrow books, they no longer need to scan them one by one like a barcode system, but only need to perform batch processing operations, and the lending status will be clearly displayed on the screen at once. superior. The same is true for the book return process. In addition, most of the current RFID systems can also integrate and store barcodes, magnetic strips, bibliographic information, and circulation records to provide system identification and utilization. In this way, the use of RFID electronic tags can not only query bibliographic information and borrowing information, but also track the precise location of specific collection materials in the library, thereby speeding up the circulation operation.
2. Reduce the workload of the cashier’s desk staff
The user interface of the XPM-RFID system is very simple and friendly, and it can be easily completed by simply following the on-screen prompts. The user’s self-service borrowing and returning operation greatly reduces the work intensity of the cashier’s staff, frees them from repetitive work, and can be enriched in other aspects of the service work of the library.
3. Added the function of anti-theft monitoring
Since the RFID electronic tags contain the information of bar codes and magnetic strips, most library RFID systems have anti-theft monitoring functions, which can replace the Electro-Mechanical (EM) and radio frequency anti-theft systems that have been used in libraries for many years. Monitoring system (Radio Frequency, RF for short).
4. Improve the efficiency of collection management
The unique advantage of XPM-RFID system in the management of the bookstore collection is unmatched by the barcode system. When the library manager is doing book inventory or arranging the shelf operation, using the characteristics of RFID remote reading and batch processing, there is no need to take the books out of the shelf one by one, as long as the handheld reader is swept across the shelf, it can be fully automatic Read the information of a large number of tags in an instant, and know the situation of chaos and loss. The XPM-RFID system greatly reduces the time for tracking and searching collection materials, improves the accuracy of query and inventory, and saves the consumption of human resources.
5. Electronic tags have a longer life span than barcodes
Due to the non-contact reading method, coupled with the characteristics of waterproof, anti-magnetic, and high temperature resistance, the life of RFID electronic tags is much longer than that of bar codes. Each electronic tag can be read more than 100,000 times at least. In this way, once the electronic label is affixed, it can be used for a long time.
6. Data retention
Due to the physically non-erasable method, compared to the use of high-voltage electrical boxes to store data, RFID data using EEPROM technology can be stored for up to 10 years, while the data retention of XPM-RFID can reach more than 100 years.
7. Cost advantage
XPM-RFID chip is the only RFID chip in the world that can be manufactured with the most advanced standard CMOS logic process (currently 0.18μm and 0.13μm). It adopts 100% deep sub-micron standard CMOS process without adding floating gate process. Therefore, at the same level of technology, XPM memory is 30% cheaper than traditional EEPROM or Flash memory. And because XPM memory can be produced using the most advanced CMOS process (0.13um), and the die size is 1/4 of that of 0.25um CMOS process, the final cost of the product can be further reduced. Therefore, XPM-RFID has more cost advantages than other RFID technologies. When mass RFID is applied, the label cost can be reduced to less than 5 cents.
Five, the development trend of XPM-RFID system
Due to the current development status of my country’s libraries and the realization of XPM-RFID, the promotion and application of XPM-RFID in the field of Chinese libraries are restricted by various factors, even if a few powerful libraries can achieve this in a short period of time RFID, but for most libraries, it takes a long time to implement RFID. However, RFID can enable the library to achieve truly intelligent management. RFID technology can provide readers with simple and rapid self-service, improve the work efficiency of librarians, save manpower for the library, and provide a safe environment for readers. The unique advantages of XPM-RFID are unmatched by other identification technologies. The XPM-RFID system is the development trend of library management systems. It will eventually replace and eliminate the currently widely used barcode identification technology.
Some libraries in our country have realized the advancement and superiority of RFID, and are working hard to gradually realize RFID. The Shenzhen Library has adopted the RFID system after the system’s preliminary demonstration and field application inspection. This indicates that Shenzhen Map has taken the lead in realizing the transformation from an automated library to an intelligent library, and it also means that the Chinese library community has moved towards RFID technology. step. At the same time, Wuhan Library, National Library, and Chengyi Library of Jimei University have all implemented RFID library management systems. The international community is now working to reduce the price of tags to 50 cents. If it is realized, RFID will be used in libraries on a large scale. We firmly believe that with the continuous improvement of RFID technology, the unification of RFID technology standards, the adjustment of the price of RFID-related equipment, and the update of the development concept of domestic libraries, the library will increase funding investment appropriately. Through the joint efforts of all parties, in the near future In the future, RFID will be increasingly popularized and popularized in the field of Chinese libraries, and the application of RFID technology will promote the construction and development of digital libraries in my country.
[ad_2]