RFID-based manufacturing execution system solution
[ad_1]
1. Problems faced by the manufacturing industry
·The real-time production information of the workshop does not have a unified data view, and the system is difficult to integrate
·There is a gap between enterprise resource system and workshop production
·Multiple and complex systems lead to inconsistent real-time information and lack of standardization
·There is a gap between the process control system and the manufacturing execution system
Can not detect and prevent problems that may occur in the production process of the workshop
In response to these problems, although the idea of lean production is advanced, how to implement its concept into actual work? First, it is necessary to find a way to implement the concept, secondly, establish methods and measures that can operate in the workplace, and finally implement it in production activities. It is only through such a process that it can be implemented.
Let’s analyze the bottleneck of the problems faced by the manufacturing industry: Lean production involves the collection, transmission and processing of information. At this stage, the development of enterprise informatization in the three parts is not consistent, and the bottleneck problem largely comes from information collection.
Lean production requirements for information collection:
·Real-time: Collect and upload production line information in time
·Accuracy: to ensure the accuracy of the collected information
·Information collection scope: collect all kinds of information needed to implement lean production
Second, the application of RFID (electronic tags, radio frequency identification) in the manufacturing industry
·Start to gradually open up the logistics chain of the enterprise, and realize the whole process tracking of manufacturing and logistics transportation;
· Gradually transition from the stage of technical verification to the implementation of enterprise-level RFID applications;
·Internationally well-known large companies such as Ford, Toyota, BMW, etc. have used RFID systems on their automobile production lines to track work-in-progress and monitor production status.
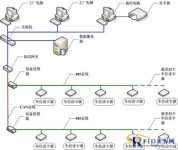
Figure 1: Network structure diagram of RFID (electronic tag, radio frequency identification) applied to manufacturing

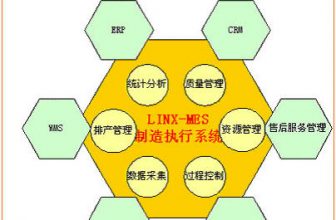
3. Manufacturing execution system based on RFID (electronic tag, radio frequency identification)
Utilize the above-mentioned RFID (electronic label, radio frequency identification) characteristics, introduce RFID technology into MES, promote the manufacturing process management and control, and adapt to the modern production process management changes. RFID is an effective way to improve the management of the production site of discrete manufacturing enterprises. Realizing the management and control of the production process based on RFID is the current technological development trend. Through the introduction of RFID in the manufacturing process, the following goals can be achieved:
1. Manufacturing Information Management
Combining RFID with existing manufacturing information systems such as MES, ERP, CRM, and IDM can establish a stronger information chain and deliver accurate data at accurate time and time, thereby enhancing productivity, improving asset utilization, and Higher-level quality control and various online measurements. Usually after obtaining data from RFID, middleware is needed to process the data and feed it to the manufacturing information system.
2. Manufacturing execution, quality control and standard compliance
To support lean manufacturing and 6 Sigma quality control, RFID can provide a continuously updated real-time data stream.Complementing the manufacturing execution system, the information provided by RFID can be used to ensure the correct use of labor, machines, tools, and components, thereby achieving paperlessness
Production and reduce downtime. Furthermore, when materials, parts and assemblies pass through the production line, the production process can be controlled, modified and even reorganized in real time to ensure reliability and high quality.
Manufacturing needs to comply with national standards and regulations, and RFID can provide additional information streams to enable the manufacturing execution system to closely comply with and pass standard certification, including compliance with 21 CFR 11 of the U.S. Drug and Food Administration (FDA).
3. Tracking and tracing
The growing demand for compliance with FDA quality regulations has prompted consumer packaging products, food and beverage companies to require accurate tracking and tracing of product information throughout their entire supply chain. In these aspects, RFID can complement the existing manufacturing execution system. For most components, the manufacturing execution system can already collect product identifiers, time stamps, physical attributes, order numbers, and batch sizes for each process. Information, which can be converted into RFID codes and transmitted to the supply chain to help manufacturers track and trace product history information.
4. Factory Asset Management
The RFID on the asset (equipment) provides information such as its location, availability status, performance characteristics, and storage capacity. The production process, maintenance, labor adjustment, etc. based on this information can help increase asset value, optimize asset performance, and maximize asset utilization. Due to reduced downtime and more effective maintenance (planned and unplanned), it can positively affect very important manufacturing performance parameters, such as the overall equipment effectiveness (Overall Equipment Effectiveness).
5. Visualization of storage volume
As contract manufacturing (Contract Manufacturing) becomes more and more important, the synchronization of the supply chain and the clear visibility of the manufacturing process becomes the key. RFID is suitable for application systems of various scales (partially or extended to the entire factory). RFID can visualize the input, WIP, packaging, transportation and storage until finally sent to the next destination in the supply chain, all of which are related to information management.
Nowadays, barcodes are commonly used in manufacturing. However, for many barcode systems, manual modification and update are often required during the production process, which is time-consuming and labor-intensive. A direct function of RFID is to liberate labor, eliminate this manual operation, and provide real-time data accurately, quickly, and reliably, which is particularly important for large-volume, high-speed manufacturing companies.
Figure 2: Visualized electronic billboard
Note: The picture in this case is a view of RFID implemented by a clothing company

System Features:
RFID (electronic tag, radio frequency identification) workshop manufacturing and execution system or work-in-progress tracking and management system has the following characteristics:
Production plans and processes are directly transferred to procedures and equipment (while ERP and MRPII can only be transferred to varieties and workshops), they directly guide equipment processing, prevent cross-process processing, and reduce process errors;
Real-time data collection, plan assessment can be carried out in time, and production progress can be monitored in real time;
The functional departments of each workshop can share production data, understand the production progress of related processes, and facilitate production coordination. Accurately confirm the delivery time and realize batch management;
Process feedback correction: correct process errors in time and shorten the process correction cycle;
Processing data is effective, reducing manual input and paper transfer;
Facilitate quality traceability;
Smart Kanban: complete quality information collection and quality analysis;
Extended logistics management: RFID batch number-barcode-product;
[ad_2]