Enterprise mold management plan based on RFID technology
[ad_1]
1. Mould management project background and problems:
With the rapid development of industry, China’s position as a world manufacturing base has been consolidated. Various mold industries have been increasing in my country in recent years. However, there are currently many problems in the mold industry market. Mold determines product quality and affects production schedule. Therefore, mold management is bound to attract more and more attention from enterprises, and it will become the focus and key link for improvement of corporate management.
How to use high-tech means to strengthen the safety and quality management of the mold industry market, supplier management, and reduce operating costs, so that the company’s various data can be collected and tracked effectively from time to time, and provide visual real-time data for management. It is the mold industry Issues that urgently need to be addressed.
Nearly a thousand electronics, hardware, plastics and mold companies across the country found that only about 5% of companies use systems to manage mold development, use, and maintenance, while other companies mostly use Excel tables or Access databases to do simple things. Procedures are used for management. These management methods basically use file sharing to share the collected data with users, often with the following shortcomings:
◆ Data integrity and logic are not strong
◆ Insufficient data security and inconvenient control
◆ Insufficient timeliness and flexibility of data statistical analysis
◆ Lack of automatic reminder function, etc.
2. Problems in mold management:
1. Production management personnel
1.1 The production and material control department (PMC) cannot know the quality of the mold in advance during production scheduling. It is often found that the mold is defective after the upper mold is produced. The production rate of defective products is high, and the scheduling is often disrupted;
1.2 There is no record of the cumulative total number of presses (number of shots) of the mold or the record is not in place, so that the life of the mold cannot be predicted;
1.3. Unfinished records of mold parameters, such as pressure, forming time, temperature, etc.;
2. Mold management personnel
1.1 The mold file data search is time-consuming, and the mold location is difficult to find, and it often takes a long time to find;
1.2 If the mold is lost or stolen is not reflected in time, it is often that the file records exist, but the mold has not been found when the actual search is carried out, and the record cannot be searched;
1.3 It is very difficult to count mold assets. It is often necessary to count to know the asset classification and asset status of the mold;
1.4 The combined mold (mold base + mold core) is very messy, and there is no good way to manage this type of mold. Often the system is configured well, but it is difficult to find a match. ;
3. Managers of the mold department
3.1 If multiple workpieces are processed separately, it is not easy to know the mold opening progress of the overall mold.
3.2 At the end of the month, it is difficult to know the distribution of working hours of each machining center, or the processing time occupied by each set of molds.
3.3 It is very difficult to analyze the man-hours and costs of mold opening, mold repair, and mold modification for each set of molds.
3.4 The progress of mold manufacturing can only be roughly controlled, and it is difficult to control the impact of the progress of each workpiece process on the overall progress of the mold in advance.
Three, the goals achieved by this program:
This solution suggests that companies adopt a mold management system based on RFID technology as a data source and use computer networked system operations to quickly check the data, effectively control the operation process, monitor the progress, understand the maintenance use and maintenance status, so as to effectively Manage equipment and evaluate costs to improve work efficiency, strengthen control, and achieve the goal of standardized operations.
Fourth, the benefits of using this solution:
A. Make mold storage more organized, extract more quickly and effectively, and save 60% of the time for mold finding.
B. Make a detailed record of the mold’s use history, such as the very important total number of stampings, so you can quickly determine when a new set of molds should be manufactured. The advantage is to directly improve the quality of the products produced and the phenomenon of misuse of bad molds Reduce by 56%.
C. It can provide the storage status of the mold in the mold warehouse, such as available, out of service for repair, obsolete, etc., and improve the accuracy of this state by 68%.
D. Record the maintenance data of each mold in detail.
E. Record in detail the precautions when using the mold, such as the conditions of the mold and the machine used with it.
F. Asset management: It is easy to calculate whether the mold belongs to the company’s assets or the customer’s assets, saving time for inventory or data checking, and accurately tracking who owns the mold.
G. Can quickly and accurately know the matching molds needed to produce a product.
H. It can quickly and conveniently calculate the actual material of each mold, the cost of each process and the cost of outsourced processing, etc., and summarize the statistics.
I. Use a chart to display, so that you can see the cost ratio at a glance.
J. Can quickly and conveniently know the latest completion progress of each process of each set of molds.
K. More effectively monitor and manage the work efficiency of each process.
5. The main content of the project construction
1.Safety standards, testing standards, and application standards formulation
2.A mold data management center
3. RFID middleware system development
4.Each mold is applied to the deployment and information collection system of business nodes and handover links
5. Application integration with existing enterprise management systems.
6. Overview of technical solutions
A. Mold data center management: There is no need to make major adjustments to the original business process of the enterprise, and the mold in and out of warehouse management can be unified, and the borrowing and returning of molds is responsible for the special personnel. All in and out are recorded and signed by the “Mold Basic Information Center” .
B. Data sharing: You can find out the product model, asset ownership, precautions when using each set of molds from the “Mold Basic Information Center” at any time, as well as the current storage location and status, and determine the life according to the total number of stampings And this mold regular or fixed maintenance project, open the computer mold information at a glance at any time.
C. Mold use history tracking: Complete and clear records of the mold’s production, maintenance and other historical details from the birth to the scrap process, so as to facilitate the production, mold, and business to understand the actual use of the mold.
D. System process: Simple and practical mold delivery process, to help companies quickly establish and improve a good mold delivery process, to ensure that mold delivery is clear and clear, responsibilities and powers are clear, and to prevent accidental mold loss.
E. Modular operation process: It can be closely integrated with the company’s existing ERP system, and can be divided into modules and launched independently.
Seven, functional modules
1) System composition:
Basic modules (data center, work platform, system management, packaging tools), document management module (electronic warehouse, document management), workflow module (basic application process management, dedicated process management), product structure and configuration module, project management module , Classification and query management (classification module, query module).
2) Innovation
● Realize dynamic project organization and management;
● Dynamic task allocation, automatic conflict monitoring and intelligent resolution management;
● Distributed workflow management system;
● Seamless integration of multiple application tool sets;
● Publish complete data to CAPP/ERP system;
● Realize innovative knowledge management and mining.
Program features: centralized management of mold data, tracking of mold storage locations, quick understanding of mold-produced products, timely query of mold status, prediction of mold life, and user-controlled mold data usage control.
Eight, the identification of the mold
The identity of the mold is identified as a unique serial number of the electronic tag in this system, which represents a group of data information closely related to the mold. The label can be flexibly installed during installation so that it can be removed and reinstalled during production. The data in the label is stored through encryption, so the reinstalled label can be guaranteed to be the label of the system.
Relevant enterprise operators can create files, edit and maintain this information through the system software. All operators and management personnel involved in mold management, use and circulation can inquire part or all of the information through tag reading and writing equipment or management software according to their permissions.
9. Identification and management of related personnel
All relevant personnel in the system are issued with readable and writable electronic tag identification cards as the basis for identification and handover. All relevant personnel must first go to the company to go through the relevant procedures and receive the card. When the mold is handed over, the reading and writing equipment will automatically modify the relevant information in the card, and at the same time, the handover data will be immediately reported to the central management system.
10. Identification and management of operation personnel
Operators involved in system operations can be divided into the following categories:
1.Die receiving and dispatching management staff
2.Mold Requisition Management Staff
3.Mold inspector
4.Mold user
5.Equipment and mold inspection personnel
6.System Information Manager
7.Decision-making or business management personnel
8.System management and maintenance personnel
For 1 to 6 types of personnel, the system will issue a unique user card for each employee, and the system will automatically determine the legality and authority of each employee and control their operations. After each operation is completed, the read-write device will report its identity code and operation information to the central management system of the system. So as to achieve real-time tracking and inspection of all personnel operations. For the 7th to 8th types of users, the system directly checks identities and permissions by means of user names and user passwords.
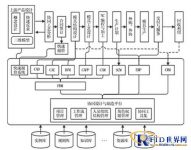
The overall structure of the system

Process analysis
The process specification consists of three steps: 1. Mould ordering, production plan, 2. Collecting data, 3. Data analysis, please refer to Figure-1, ① Mould ordering, production plan: There are detailed records of production plan data in the mold production order. Order number, production mold number, workpiece and process arrangement; ②Collect information: mold production orders are issued to the mold department, and the operators of each group (mold design group→CNC group→kan module→test module, etc.) will construct according to the order. Then enter the manufacturing schedule data into the system in time through the production schedule; ③Data analysis: Cost analysis and the analysis report of the actual manufacturing cost and schedule help managers to realize the demand from rough to fine management.

[ad_2]