RFID electronic archives (file) information management construction plan
[ad_1]
1.1 Project background
With the large-scale application of computers and networks, the generation and management of a large number of electronic files has become an urgent problem for all units to solve. Knowledge resource management is an important part of the information management of enterprises and institutions in the future, and it is also the basis of unit information management. Future development trends and development directions. Archives are the core part of a unit’s knowledge resources and the most basic part of knowledge resource management.
Therefore, in order to realize the management of the unit’s knowledge resources, we must first manage the electronic archives. Only by taking the archives management as the core and foundation can we gradually expand and extend the scope of management, and finally realize the management of knowledge resources.
Archives management is necessary for future knowledge resource management in terms of talent reserve, information classification and organization, management system and methods, retrieval and utilization methods, and information collection mode.
1.2 Project demand analysis
1. According to the management needs of various industries, a public, independent and applied file management information platform is constructed for electronic file monitoring and management to support the physical and virtual file information management involved in various businesses, so as to achieve “physical information management”. The information management of archives and the archive management of electronic information”.
2. The “archive sources” involved in electronic archives include: electronic physical files (photos, scans, images and other multimedia data files), archival electronic information (formatted data files), and structured databases (uninstalled from the application) , And can load reusable database files) and so on.
3. Historical records with preservation value and electronic information as a legal basis (forms and certificates) must be able to have the attributes of archives: “directly formed clear, definite, and solidified information with a complete record function; it is directly formed “The historical record of the document”, and must have the original recordability of the document and the historical reproducibility.
4. The electronic information that will be managed as archives must be processed through an archiving process before it can be called an electronic archive. Otherwise, it can only be called a file. This process is mainly to encapsulate each piece of electronic information into a volume unit. The basic unit of archives, and each volume has a standard metadata (electronic cover).
5. The management of electronic archives is not only to manage the electronic information of archives, but also to realize the informatization management of physical archives and the associated management of electronic information and physical archives.
1.3 Advantages of RFID technology application
Because RFID uses the principle of radio frequency identification, it can work in a variety of harsh working environments, can penetrate certain obstacles and have good penetrability; it can also identify files in motion, and can be identified in batches; RFID tags can also repeatedly erase and write data information, and the tags can be reused. The information in the RFID tag is quickly uploaded to the enterprise information system for comprehensive management, which can avoid errors that may occur in manual operations.
The use of RFID technology can carry out fixed information query and mobile information query on file archives, and can also read all the file information through platform management.

1.4 RFID electronic file management planning
1.4.1 Features of Electronic Archives
1. Non-human readable information;
2. High density of information storage;
3. The separability between information and carrier;
4. The inheritance of multiple information media;
5. System dependence.
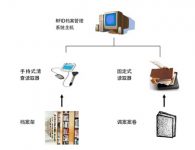
1.4.2 Management system hardware architecture planning
This system adopts the B/S mode, which can support operation within the LAN or the Internet; it can run on a stand-alone computer or support distributed operation of the server; the user uses the browser mode to use the system, which can make daily maintenance simple and version It is convenient to update and save investment cost.

1.4.3 Archives management management information platform planning
The goal of the archival management information platform is to realize the informatization management of paper archives and the archival management of electronic information.
The informatization management of paper archives is: with the support of electronic imaging technology, the paper archives are transformed into electronic information for management.
The archival management of electronic information is: after the electronic information of the application system is vouchered, an electronic archive is formed, and the electronic information is separated from the application system to form a format that is irrelevant to the application, non-repudiation, and can be directly read. Documents.
Build a public support environment for electronic archives management, and provide a unified platform for collection, management, query, loading and display of all types of archives, mainly to achieve the following functions:
1.4.3.1 Unified electronic archive entry.
Supported by technologies such as imaging technology, barcode technology, format electronic data files, etc., it can realize standardized packaging processing of different media and different types of files, and convert them into unified entry files, forming the smallest granularity “pieces” of electronic files to unify It is stored in a format that ensures the non-repudiation and traceability of electronic files.
1.4.3.2 Unified management of collected electronic data “pieces”.
In accordance with the relevant regulations on file management, a process-based approach is adopted to implement unified and standardized file management for electronic data. It mainly includes registration, archiving, sorting, transfer, receiving, custody, relocation, appraisal and destruction, inquiry and borrowing, backup and restoration, etc., covering the entire life cycle of the file management. And can realize the operation of recording and querying the circulation traces of each link of the process.
1.4.3.3 The system shall provide management of the archive process.
Use productized process management tools to achieve process maintainability. Users can customize workflow links and paths. When meeting process changes, operators can add or modify processes through the platform by themselves, and can assign different business roles to each link according to business needs. At the same time, it meets the different needs of various business file management processes.
1.4.3.4 Support new service loading.
The initial stage is to build a unified electronic archives management platform, and load more standardized archives management services (such as official documents) on it, so that all operators can manage different types of archives on the same platform. The platform should support the business loading of new types of files, so that business personnel can add and modify other business electronic files (such as personnel files, financial files, etc.) only by using the tools provided by the platform.
1.4.3.5 Realize the reliability and safety management of electronic archives.
On the one hand, the application support environment can guarantee the non-repudiation of electronic files and the value of their certificates through advanced technologies such as digital certificates and electronic seals. On the other hand, there must be a security mechanism to ensure the security of information in the process of packaging, transmission, sorting, filing, storage and utilization of electronic files. It is necessary to realize the classification and marking of the security level of electronic archives, and conduct access control according to different levels and permissions.
1.4.3.6 Realize flexible and convenient management of permissions.
The system can use CA and data encryption technology to achieve user identity control over data access. The authority system can adapt to different organizational settings of the tax system and different management modes. It can realize the hierarchical management, shared use, group sharing, separate configuration and temporary distribution of permissions.
1.5 Electronic filing system management planning
1.5.1 Overall functional design planning

The overall design plan of the electronic document information automation management system is as the above system logic architecture. According to the division of labor of document management, it is divided into six parts: information collection, daily management, information service, system security, system settings, and software interface.
Among them, the three parts of information collection, daily management and information service include the main business content of user document information management, which realizes the network and electronicization of the collection and arrangement of document information, daily management and utilization of services.
Information collection is mainly responsible for the sorting of document information, cataloging and automatic linking of electronic files, and completing the collection, entry and digitization of document information.
The daily management part mainly completes the identification, destruction, transfer, compilation, research, and collection of electronic documents. At the same time, it can assist entity management, form document catalogs, perform borrowing, utilization, and statistics management tasks.
Information services mainly provide users with fast document information services in a simple and convenient way.
System security fully guarantees the security of the file system and data, so that the security management of electronic document information can control each specific function operation and each specific file.
The system setting part provides users with custom tools to build a document management structure that meets their own document information management needs, allowing users to tailor their own document management structure, whether it is in the immediate or long-term consideration, it will be better than any other The system is more able to adapt to the ever-changing and growing functional requirements of users themselves.
1.5.2 System Management Planning

1.5.3 Function description
1.5.3.1 File Management
File archiving in file management refers to the process in which the clerical department or the business department organizes and files the documents with preservation value after the file materials are processed, and periodically transfers them to the unit’s archives organization or archive personnel for centralized management.
The management module includes: document description, document classification and sorting, document identification, auxiliary volume grouping, confidentiality period setting, decryption, setting directory, generating archive number, document filing, association relationship setting, sorting by dictionary, adapting to institutional changes and other functions.
1.5.3.2 File management
This module covers the business process of each link in the work of archives management personnel, including description, composition, adjustment, retrieval, transfer, reception, and catalog production.
Archive description: For historical archive data, the archive manager can perform the traditional sorting method (enter the file information first and then the file information in the file) or the simplified sorting method (single-level file) description, as well as the addition and linking of the original text.
File adjustment: In the process of filing, the file manager needs to correct the wrong filing results, including: splitting, closing, unwinding, inserting, filling blanks, adjusting the order in the file, adjusting the order of the file, and adjusting the file order. Number adjustment and so on.
Excel output: To be able to output the data selected by the user to Excel, the user can make necessary adjustments to the data and format.Note: This function is also applied to the file management function module
1.5.3.3 Handover and reception
The lower-level archives departments or other units transfer the files, related data entities, original texts and retrieval catalogs they manage to be transferred to the upper-level archives departments. After the archives department has received the correct experience, it will issue the handover documents to the transfer unit.
(1) Handover
The lower-level archives department or other units shall transfer and record the files to be transferred, related data entities and original texts and retrieval catalogs under their management to the upper-level archives department.
Process:
1. The transfer unit or department fills in the “File Handover Documents”, and exports the file directory and file directory data of the transferred files to the superior archives department;
2. After receiving the transfer documents reviewed and signed by the higher-level archives department, the transfer status will be summarized in the “File Transfer Register”, and the “preservation status” of the entity’s transferred archive index will be assigned a transfer mark.
(2) Receive
The superior archives department receives archives, relevant data entities and electronic documents and retrieval catalogs handed over by other units.
Process:
The higher-level archives department enters or receives the data of the file directory and file directory to be received by means of importing, online transmission, etc.;
The superior archives department examines and signs the transferred documents after the inventory is correct. The transferred documents are included in the complete file of the transferred archives and a copy is returned to the transfer department at the same time, and the relevant receipts are summarized in the “Archives Receipt Register”.
1.5.3.4 File storage
1.5.3.4.1 Warehouse management
Provide the description and maintenance of information such as warehouse area, related equipment, and shelf storage, and conduct information query and statistical processing.
1.5.3.4.2 Storage location management
The storage location information of files can be set in batches, and the storage location index can be established. And can print “Fonds Storage Index”, “Warehouse Storage Location Index”.
Process:
Through the retrieval process, select the relevant files, fill in the corresponding storage location information, and replace the relevant “storage location” information of this batch of files.
1.5.3.4.3 File storage status management
Regularly inspect the files in the warehouse, and record the inspection results in the file inspection status register; when the files are restored, fill in the restoration status register to record the restoration work, which is convenient for future work statistics; the file entries can be automatically updated during registration “Storage Status” information.
1.5.3.4.4 Temperature and humidity management of archive warehouse
Daily registration form data entry or conversion, statistical analysis. Record information through data tables, and provide functions such as description, retrieval, statistics, and printing. The user manually fills in the corresponding descriptive items. For some descriptive items, the value of the previous record is required to be inherited.
1.5.3.4.5 Inbound and outbound management
In the warehouse management, you can manually enter the archive information, and record the warehouse in and out information of the archives.
In the warehouse management, after receiving the file entities, disinfecting and putting them on the shelves, or transferring the files out of the warehouse, the “File In and Out Register Book” must be registered according to the in and out actions of each warehouse.
1.5.3.5 File utilization
1.5.3.5.1 Use registration
When borrowing a physical file, you must manually register the file utilization form. If there is no original text under the retrieved item and the carrier of the file is “paper”, you can register the file utilization application information on the page, and then go to the archives room to proceed. Borrow. When borrowing, the file manager can directly call up the user’s application information for direct transfer; the options for the use method and use purpose should be freely defined. After registration, if it is a physical file, the system will prompt the user to go to the file room to borrow the file. For files that you do not have the right to view, you need to apply for use. After approval, if it is a physical file (without original text), you can go to the archives to borrow it. If it is an electronic file, you can use it directly through inquiries.
1.5.3.5.2 Utilization Management
It manages the borrowing and utilization of archives, can perform operations such as recall, return, and renewal, and can retrieve the historical information used.
Utilization process:
1. Fill in the corresponding borrowing file information by searching or manual input, and then input the user information, fill in the use method, use purpose, and return date. After the information is filled in, you can register, and print the registration form, borrowing form, and recall Orders, supervision orders, etc.;
2. After the user has finished using it, he can return the file entity to the administrator in a single or in batches;
3. Use the administrator to enter and return the file information and register the use effect;
4. If the borrower needs to renew, then the administrator will retrieve all the borrowed files of the borrower, select the file to be renewed, and then directly transfer to the utilization registration. If the registration is successful, the corresponding file information will be automatically returned and borrowed.
1.5.3.5.3 Recall process
1. The system automatically retrieves the list of persons who need to be recalled;
2. Select the person to be recalled;
3. Print the reminder to the selected person.
1.5.3.5.4 Utilization statistics
It can be divided into different ways of use, such as checking electronic, checking entity, lending, copying, faxing, etc. Perform statistics on the number of people, volumes, pieces, number of sheets, etc., and can count the archive entities that have not been returned at a certain point in time.
Inquiries can be made by user, time of use, method of use, lending operator, etc. When the relevant file information is retrieved and the original text is browsed, the use registration is automatically performed (no need to return).
You can count the number of times a document has been accessed. You can count the number of times that files are accessed through applications.
1.5.3.5.5 File Utilization Process
1. This process is aimed at files for which users do not have permission. For those files with permission, users can use the files without going through this process.
2. This process can be customized by users according to actual working conditions.
1.5.3.6 Appraisal and destruction
The system automatically retrieves the expired files, and after passing the storage period appraisal and destruction appraisal, the files to be destroyed will be formed into the “Destroy List”. When appraisal and destruction, relevant information should be recorded; the destroyed archives are automatically given the “entity destroyed” mark, and they are also included in the archive destruction database.
It is necessary to split and merge the case files, and be able to modify the case file number and catalog number information. As a result, the “Appraisal and Sorting Register” is formed, which can perform work statistics based on relevant data.
1.5.3.7 File Statistics
Create, maintain, import and direct statistical reports of relevant archive data.
The relevant reports (basic statistics annual report) stipulated by the Archives can be customized in advance; print out; can output the report to an Excel file; can import the data reported by the lower-level row; can export the report in the system as a file; can export Import the report file into the system.
1.5.3.8 File compilation and research
Carry out the compilation and research work of memorabilia, organizational history, basic digital compilation, important document compilation, and personnel appointment and dismissal compilation. Relevant files can be found through retrieval, the corresponding original text can be opened, and editing operations such as copying and pasting of the original text can be carried out for editing and research.
1.5.3.9 View
The headquarters or archives and various branches can consult each other’s data and share and utilize information resources. Provides a variety of advanced retrieval methods such as simple query, combined query, and classified retrieval, and quickly accesses information through the Internet, and can directly browse the original text through the browser within the scope of authority, and perform operations such as printing and downloading the original text.
When there is only a physical file in the file and no electronic original text, the user can directly apply for registration, and the registration information can be directly sent to the archives department. When the user goes to borrow it, the application registration information can be directly called.
1.5.3.10 System Maintenance
1.5.3.10.1 Information category management
According to the characteristics of the files, the various catalog data of the system are divided into logical categories. The lower logical categories include several layers of specific physical tables. The user can set the association relationship between these several layers of physical tables through the system, such as case files and File relationship. For each physical table, the user can customize the table name and table description. For each field of the table, the user can customize the field name and field type, and specify whether the field can be empty, unique, value inherited, automatically incremented by one, and Fields can be added, deleted, and modified.
Processing steps:
1. The system initializes the definition of the category. Initialization will generate fixed fields and optional fields. Fixed fields are required. Users can only modify field descriptions, not field names; users can add or modify optional fields;
2. The user can modify the fields as needed. For fixed fields, users can and can only modify the field description, not the field name. For optional fields, users can add, modify and other operations.
1.5.3.10.2 User Management
The content of user management is the management of user objects and user-authority.
Specific control permissions are divided into data permissions (query, modify, and corresponding original text permissions) and permission settings for business function operations.
1.5.3.10.3 File number format definition
The user defines the file number format of each category through the system.
The default setting provided by the system is the archive number composition structure defined in the national archives archiving standard, and the user can define it on this basis.
1.5.3.10.4 Other system settings The system provides the following setting functions
Archive scope setting;
The setting of storage period rules.
1.5.3.10.5 The data import system provides the following functions:
Data import: It can import data in common database formats including ACCESS, DBF, SQLSERVER, ORACLE, etc.; users can customize the correspondence between fields, and the system imports data according to the correspondence set by the user; it can temporarily based on existing fields Generate a new field and import the data of the new field into the corresponding target field; it can save the import environment set by the user (including the correspondence between fields, defined new fields, import conditions, etc.), and the user can import the environment to avoid repeated settings Define the import environment; the field type and length system can automatically do the corresponding conversion and truncation operations; the range of the imported data can be set;
1.5.3.10.6 Log Management
Login log management: records the user name, login time, logout time and other information of the user who logged in to the system.
Original log management: It records the time, user name and other related information made by the user each time the original material is added, modified, or deleted.
System maintenance log management: It records every time the user makes changes to the system configuration, such as creating new categories, adding, and deleting fields.
In addition to the above log function, it also provides a flexible custom log function, through a small amount of development to customize the log record of a certain operation.
1.5.3.10.7 Authority Management
Multi-level authority management, through the headquarters archives or archives super management users can be empowered to the subordinate file unit or department’s second-level super users, so that they have the authority to manage their own units.
User management: Divided into user groups and users, you can specify user groups or user rights, users can inherit the rights of the group they belong to, and can individually grant rights that exceed the group’s rights.
According to the combination of operating functions and file categories, the user can be given the authority of different operating functions for each file category.
1.5.3.11 System expansion function
Users can choose the following extended functions to meet the needs of file management.
1.5.3.11.1 Batch Scanning Subsystem
For batch scanning of paper files, digital processing software provides functions including scanning, optimization, and batch linking.
1.5.3.11.2 RFID identification
It can integrate third-party RFID software in the scanning subsystem to perform RFID recognition on the scanned original text, and store the recognized text information in a database or text file to prepare for convenient use and full-text retrieval; RFID functions can also be integrated into customers End, it is convenient for users to selectively perform RFID recognition when browsing the original text of the image.
1.5.3.11.3 Full text search
It can be integrated with a third-party full-text search engine, which can perform professional full-text search on public files identified by RFID.
1.5.3.11.4 CD release
This system provides a CD publishing tool, which can be used as a backup method for data entries and original texts, and it can run independently, providing a means for file utilization out of the document center platform. The catalog data and original text data stored in the file center management system require convenient offline browsing, fast data migration, and safe CD backup. It includes four functional modules: CD publishing, CD uploading, CD browsing, and CD merging.
1.5.3.11.5 Interface Module
(1) Unified identity authentication interface. The expandable interface left for the unified authorization system within the department can directly read the identity authentication LDAP server for identity authentication.
(2) OA data archive interface. There is an interface with other business systems such as OA, and the interface module can be re-developed according to the actual situation of the user’s system, and the catalog data and original data that need to be archived in other systems such as OA are automatically included in the archive system, and the original files are retained Formats and attachments generated by the process.
(2) Business system data interface. Through the secondary development interface, the file data generated in the existing business system of enterprises and institutions and need to be archived can be directly imported into the file system, and other management operations can be performed through the file management software.
1.6 Advantages of Project Construction
The electronic document management system is a platform-based document management software that fully meets the requirements of the basic design principles of the above-mentioned system. At the same time, it has the following advantages:
1.6.1 Advantages of data centralized operation mode
(1) The headquarters has fully realized the supervision and monitoring of the work of branches.
(2) To facilitate centralized management, maintenance, and backup of data generated by the file management system.
(3) It avoids that the data is scattered among the subordinate units, and the comprehensive retrieval and utilization of the archive data cannot be carried out quickly.
(4) It is convenient to focus on the modification and maintenance of the application logic layer on the server side, and the improvement of the system can be completed without any changes on the client side.
(5) Reduce investment in software and hardware.
(6) Reduce dependence on network bandwidth
1.6.2 Electronic document management platform technology
(1) The document type can be customized freely
(2) The level of document management can be customized freely
(3) The information (database structure) entered in the document can be freely customized
(4) The user’s entry and retrieval interface can be freely customized
(5) The input method can be customized freely
(6) The document classification table can be customized freely
(7) The statistical report of the document can be customized freely
(8) Users can freely customize the operation and use rights of the document
(9) Built-in a large number of functions, providing users with powerful customization methods
(10) The electronic document management system of any enterprise and industry can be established through the above-mentioned customized function platform.
1.6.3 Scalability of application system functions
Multi-layer architecture design, reasonable platform selection, and super customizable functional design can provide good functional scalability without the need to modify the system itself. When the requirements change, the first option is to meet the requirements through simple customization or system configuration; the second option is to meet the requirements by deploying some newly developed modules; and the third option is to modify the system itself.
It can be tightly integrated with third-party software, such as full-text search and RFID identification software, which is greatly convenient to use.
(1) It can form integrated management of documents with OA and other system interfaces: OA system interface and other business system interfaces.
(2) Multi-file browsing: supports the management and browsing of more than 200 graphic image file formats
1.6.4 High degree of standardization
Comply with the national “CAD file archiving specification” and “document management software functional requirements”
1.6.5 High system security
This system supports the use of additional digital certificates to encrypt and decrypt file data externally transmitted, so as to effectively ensure the security of internal digital certificates and file data.
Multi-level security management mechanism, the authority can be aimed at a certain person or a file, file safe use technology, can prevent the illegal use of files on the Internet.
[ad_2]


