Power safety equipment management UHF RFID application solution
[ad_1]
I. Introduction
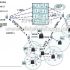
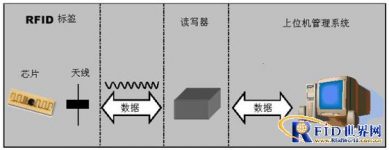
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID), commonly known as electronic tags, is widely used in the fields of tools, assets, personnel, and supply chain management. Radio frequency identification is a non-contact automatic identification technology. It automatically identifies target objects and obtains relevant data through radio frequency signals. The identification work does not require manual intervention and can work in various harsh environments.UHFRFIDThe technology can recognize high-speed moving objects from a long distance, and can recognize multiple tags at the same time, which is quick and convenient to operate. The most basic RFID system consists of three parts: Tag: consists of coupling elements and chips, each tag has a unique electronic code, attached to the object to identify the target; reader (Reader): read (sometimes also The device that can write tag information can be designed as a handheld or fixed type; Antenna: Transmit radio frequency signals between the tag and the reader. The basic RFID system composition is shown in Figure 1.

Figure 1. Composition diagram of RFID system
Comparing radio frequency identification technology with barcode technology, radio frequency identification has many advantages, such as long identification distance, no need for visual visibility of tags during identification, ability to be used in harsh environments, content can be updated, and multiple tags can be read in batches , Can identify high-speed moving objects, large amount of information, not easy to imitate, etc.
Radio frequency identification technology is considered to be one of the most promising information technologies in the 21st century. In terms of current technological development, the RFID field is at the forefront of the development of the Internet of Things and is also one of the basic technologies for the realization of the Internet of Things.
2. Project background
At present, UHF RFID technology is developing rapidly, with a wide range of applications and a high degree of automation. With the internationalization and popularization storm sweeping the world, the industrial growth it brings is immeasurable. In the target market, its application is quite extensive, such as in tool management, asset management, traffic monitoring management, personnel access management, confidential media management, cargo tracking management, and so on. Its essence is to add RFID tags to make people, tools, IT assets, vehicles, secret media or goods, etc., the targets that can be identified by the system by means of artificial identification. Information is managed to achieve the purpose of effective, efficient and scientific management.
“Electric safety tools and equipment” refers to various special tools and appliances to prevent electric shock, burns, falls, falls and other accidents, and to ensure the personal safety of staff; safety production is the eternal theme of electric power enterprises, and the quality of safety tools and appliances , It will directly affect the personal and equipment safety of power companies in the production process. The traditional management mode of power safety tools and equipment is difficult to meet the needs of new forms of power safety management in terms of quality and efficiency. Therefore, it is inevitable to find a simple and efficient management method. The current safety tool management mainly adopts a combination of manual management and/or barcode management. The manual management method is inefficient and has a high error rate. The barcode technology management method itself has certain limitations, such as fragility and strict environmental restrictions. The current safety tools and appliances have the following common problems: a. The awareness of regular safety tools and appliances is relatively high. Indifferent, b. Appearance inspection once a month is a mere formality. c. There are problems in the selection and purchase of safety tools and instruments. d. The use of safety tools and appliances is not standardized and lacks maintenance and maintenance. e. Safety workers in some units The configuration of appliances and equipment is unreasonable; and RFID technology can effectively regulate management. RFID electronic tags are affixed to the surface or inside of fixed assets, and safety tools and appliances related information are recorded in the tags and associated with the database. At the same time, the fixed readers installed in the main channel and at different locations in the area will automatically read and record the information in the tags. The staff can also use the handheld readers to make regular or irregular inventory of safety tools and instruments. . The application of RFID technology in fixed asset management can achieve the following effects: Based on the management of the life cycle of safety tools and equipment, and the principle of maximizing the use of resources, it can help enterprises and institutions improve the management quality and efficiency of safety tools and equipment, and reduce the incidence of safety accidents.
The management of electrical safety tools and equipment is one of the areas where the application of RFID technology is growing rapidly. This RFID application solution mainly uses the characteristics of UHF RFID non-contact wireless automatic identification technology to install different electronics for tools and tools of different materials. Label, and write the usage information of each object into the electronic label. When checking assets, the electronic tag information is read through mobile read-write devices, and combined with the central asset management system, the information on the purchase, acceptance, testing, use, storage, and scrapping of power safety tools is automatically and Real-time identification, to achieve efficient and accurate use of safety tools and equipment management, thereby improving the efficiency and safety of the use of safety tools and equipment, reducing safety accidents, and reducing costs.
According to the specific needs of the power industry for the management of tools and equipment, this solution uses RFID technology to realize the integrated management of open safety tools and personnel (optional). It is mainly used for safety tools and tools (such as safety helmets, insulating gloves for climbing boards) and Management of its users (that is, those who touch, use, and keep the tools and instruments). The goal and management, process and behavior are organically combined to form a complete management chain. In addition, it can also realize the full life cycle management of all labeled power safety tools.
Three, solution introduction
3.1, management object
The objects of the early-stage management of the electric safety equipment management system are electric safety equipment, and the tools and equipment that have an impact on safe production should belong to the safety equipment, which can generally be divided into 4 categories:
1. Protective safety tools and equipment, such as: safety helmets, sign boards, temporary shelters, safety fences, etc.;
2. Electrical insulation safety tools, such as: electroscopes, insulation rods, insulation gloves, insulation boots (shoes), insulation pads, grounding wires, etc.;
3. Climbing safety tools, such as climbing boards, foot buckles, safety belts, ladders, etc.;
4. Lifting equipment, such as: all kinds of hoists, poles, pulleys, twisting mills, wire clamps, wire ropes, double hooks, shackles, wire rope connectors, etc. , The later management objects are extended to all assets of the entire R&D center.
In the later stage, the personnel management function can be expanded, and the unified management of safety tools and users can better reduce safety accidents and improve investment efficiency.
3.2. Functions, features and implementation benefits
The schematic diagram of power safety equipment management is shown in Figure 2.

Figure 2. Schematic diagram of the management of electrical safety tools and instruments
The management of power safety tools and equipment includes the management links of the purchase, acceptance, testing, use, storage, and disposal of tools and appliances. It includes the entire process of tools and appliances from purchase, putting into use and discarding. Before the tools are put into use, add electronic tags. The information of the tools is written in the tags. Every time the tools are managed, the reader will read the electronic tags on the tools and send the information to the server of the tool management system. Processing, so as to realize the whole life cycle tracking management and safety alarm of tools and instruments.
Features:
The relevant management department shall register (initialize) the safety tools and instruments, and carry out the whole life cycle tracking management of the labelled safety tools and instruments;
The relevant management department shall register (initialize) the operators, and conduct reasonable and effective management of personnel entry and exit; (optional)
Automatically record when personnel and tools pass through key import and export, determine the safety of tools and appliances, and alarm the damaged or scrapped tools and appliances. If the system manages the personnel, the tools and appliances will be Personnel conduct identification and comparison to prevent the loss of tools and equipment, and untrained personnel bring out safety tools and equipment, etc.;
The warehouse of safety tools and equipment can be checked regularly or irregularly, and the tools and appliances that do not meet the safety standards can be found in time, such as damage, failure to repair according to regulations, etc., and inventory shortages can also be found in time; safety can be achieved Quick search of tools and instruments;
Features:
It can realize the rapid identification of long-distance multi-targets of electric safety tools and instruments, with high reliability and safety;
Establish files for various electric safety tools and instruments, strengthen the supervision of electric safety tools and appliances through RFID technology, rationally allocate resources, reduce resource waste, and prevent safety accidents;
Establish an intelligent power safety equipment management platform based on RFID technology to greatly improve the company’s real-time dynamic management of internal power safety equipment;
It can effectively and accurately identify, collect, record and track the data of electrical safety tools and appliances equipped with electronic tags to ensure the rational use of assets;
The real-time data of the collected electronic tags are transmitted to the back-end power safety equipment management system in a timely manner, and the allocation and use of the power safety equipment can be clear at a glance;
It can realize the transparent item-level management of the entire life cycle of power safety tools from purchase to scrap;
The tools and their users will be identified and compared to prevent the loss of tools and tools, and untrained users will bring out safety tools and tools; (optional)
It can easily expand other RFID management objects in the existing power safety equipment management system, and fully protect the existing investment of the enterprise.
Implementation benefits:
Complete life cycle management functions of power safety tools and appliances, improve management efficiency and information management level;
Supervising the entry and exit of electrical safety tools and equipment, effectively preventing unqualified electrical safety tools and equipment from being put into use, and reducing safety accidents;
Automatic management, humanization, avoid conflicts, and have a unique alarm function;
Real-time management, fast operation, detailed records, and complete management links.
4. Solution system architecture and main equipment performance
4.1, system architecture
The system architecture of the RFID application solution is shown in Figure 3, including the object layer, the collection layer and the application layer; the object layer is mainly labeled controlled power safety tools and their users (optional); the collection layer mainly includes fixed RFID data collection System and handheld RFID data acquisition system. The fixed RFID data acquisition system is installed at the entrance and exit of the warehouse. The identified data is communicated with the application layer through the local area network. The handheld RFID data acquisition system can be used to inspect and count electric safety tools or personnel. It communicates with the application layer through WIFI, GPRS or USB; the application layer realizes various management functions through data communication with the collection layer.

Figure 3. System architecture of RFID application solutions
4.2. Main equipment model and performance
The main equipment models and performances used in the plan are as follows.
4.2.1, UHF RFID fixed reader
The SR-2414 fixed reader/writer of the Rui Chi series independently developed by our company is used as the data collector for the entrance and exit of the warehouse of the electric safety equipment management system, as shown in Figure 4.

Figure 4. Fixed reader

4.2.2, UHF automatic identification channel
Using our self-developed RFID automatic identification channel, with a built-in SR-2414 fixed reader, it can achieve a good data collection effect at the entrance and exit, and realize the entrance and exit management of safety tools and equipment, and achieve excellent accuracy And reliability, as shown in Figure 5.

Figure 5. RFID access control antenna

It is also possible to directly fix the antenna and the reader on the side of the safety tool warehouse door without using the automatic identification channel according to the on-site situation.
4.2.3, UHF desktop reader
The SR-3200 desktop reader developed by our company is used as the initialization label (issuing card) and short-distance identification of the power safety equipment management system, as shown in Figure 6.

Figure 6. Desktop reader

4.2.4, UHF RFID handheld reader
The handheld reader is used as the management system of power safety tools and equipment for inventory, search, and audit use, as shown in Figure 7.


4.2.5, anti-metal electronic tags
The use of anti-metal tags can be well adapted to metal safety tools and appliances, as shown in Figure 8. This ultra-high frequency anti-metal electronic tag with mini size and super performance is suitable for the labeling requirements of safety tools and appliances management.

Figure 8. Anti-metal electronic tag

For various safety tools and instruments of different sizes and materials, one label may not be able to cope with all situations. There are labels of various specifications for use, as shown in Figure 9. The specific selection can be made according to the test results and labeling methods.

Figure 9. Other anti-metal electronic tags
4.2.6, paper electronic label
The label can be used in most occasions except for metal and liquid, as shown in Figure 10.

Figure 10. Paper electronic label

4.2.7, personnel electronic tags
This personal tag has a strong adaptability to the human body and can achieve a good recognition rate, as shown in Figure 11.

Figure 11. Personnel electronic label

[ad_2]