Instrumentation Management Program
[ad_1]
1. System background
With the development of society, market competition is becoming increasingly fierce, and improving production efficiency and reducing operating costs are of vital importance to enterprises. In the warehousing management application of instruments and meters, because the information of the items cannot be automatically collected, intelligent management cannot be achieved, and a lot of manpower and material resources are required.
Existing instruments and meters in and out of the warehouse are managed manually. The recording method is cumbersome, inefficient, error-prone and relatively high in cost; although most warehouse goods in and out management use computer management systems, they still record first and then enter the computer. Human factors are large, the accuracy rate is not high, falsified data are prone to occur, human resources are wasted, and management and maintenance costs are high.
useRFIDTechnically carry out warehouse-in/out management of instruments and meters, firstly label each instrument and meter, install UHF readers at the three entrances and exits of the microwave instrument and meter workshop and the entrances and exits of the three test rooms. Automatic data collection is carried out on the data of each operation link such as warehouse, allocation, shifting, inventory counting, etc., to ensure the speed and accuracy of data input in each link of warehouse management, and to ensure that enterprises can grasp the real data of inventory in a timely and accurate manner, and maintain reasonable Control corporate inventory. Through scientific coding, you can also easily manage the item information. Using the system’s location management function, you can also grasp the current location of all inventory materials in a timely manner, which is conducive to improving the efficiency of warehouse management.
2. System structure

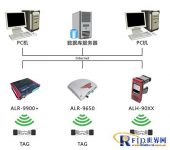
Figure 1 System hardware structure
RFID warehouse instrumentation access management hardware is mainly composed of RFID tags, fixed readers, handheld readers, servers, personal computers, etc., through the network to achieve mutual connection and data exchange.
2.1. System Function Module

Figure 2 System function modules
The RFID warehousing logistics management system consists of card issuance and labeling, outbound management, inbound management, allocation and shifting, inventory counting and additional functions. The outbound management system includes outbound goods claim, outbound goods identification, and outbound record download. The warehousing management system includes location allocation setting, unloading product identification, and warehousing record management.
2.2. Work flow
● 2.2.1. Issuance and labeling
Label the newly purchased instruments and meters and equip them with electronic labels. The unique ID number of the label or the data written by the user can be used as the identification code of the instrument, and the data is used to record the product name, purchase time, warehouse and other information. When the reader installed in each channel recognizes the tag, it can automatically obtain all the information of the instrument.
● 2.2.2. Warehousing
After the instruments and meters are labeled, the loading and unloading tools are put into the warehouse via the channel composed of RFID readers and antennas. The RFID equipment automatically obtains the quantity of the warehouse and records it in the system, and at the same time forms the order data association, and the warehouse is calculated through the computer warehouse management information system. (Or manually specify the storage location for the batch at the beginning), and send the inventory instruction to the warehouse client (or forklift truck system) through the network system, and the forklift personnel will store it in the corresponding storage location according to the requirements. After the warehousing is completed, the system updates the inventory data and marks the location information of each batch of goods.

Figure 3 Flow chart of instrument storage
● 2.2.3. Delivery
The consignor of the logistics department generates an outbound order according to the invoice required by the sales: that is, according to the outbound priority (such as the first out of the warehouse before the production date) to query the warehouse for the storage location and inventory status of the outbound goods, if there are customers The designated batch number will be queried according to the designated batch number, and the outbound cargo pick-up bin and the corresponding pallet belonging to the cargo and the loading vehicle will be generated. The consignee brings the outbound order to the warehouse manager, and the warehouse manager checks the information to arrange for the forklift driver to carry out the corresponding product out of the warehouse. The forklift picks up the goods through the exit gate, and the exit gate RFID reader reads the pallet label on the pallet to obtain the outbound information, and verifies whether the product batch number and location listed in the shipped product and the outbound order are correct. After the delivery is completed, the warehousing terminal prompts the delivery details for the administrator to confirm, and automatically updates the data to the database.

Figure 4 Flow chart of instruments and meters out of library
● 2.2.4. Allocation and library transfer
The goods to be transferred to the warehouse will be recognized by the reader installed next to the passage when they pass through the passageway. The reader/writer records the current tag information and sends it to the back-end center. The back-end center judges whether it is warehousing, outgoing, or transfer based on the sequence of the entry and exit channel identification tags.
You can also use the handheld to move the goods. When the warehouse manager finds that a certain item is misplaced, he can manually place the goods, and at the same time change the label information through the handheld and send it to the server, realizing quick and convenient shifting Features.
● 2.2.5. Inventory check
The staff can use the handheld reader to regularly inventory the goods, read the label information of the goods at close range, and compare it with the back-end management system, and manually check whether the variety, quantity, and production date of the goods in the warehouse are consistent with the back-end system. If they are inconsistent, the system information can be corrected on site. This inventory method can shorten the enterprise inventory time by 85%, greatly improve work efficiency, and at the same time increase the inventory cycle.
● 2.2.6. Additional functions
● Inventory warning
When the inventory of the warehouse is less than the normal inventory, the system will prompt to replenish the inventory to avoid the phenomenon of insufficient inventory.
● The instrument is moved or taken out of the warehouse without permission to give an alarm, etc.
The reader has an ID matching function. When the instruments out of the library are consistent with the instruments in the outbound list (the ID number of the instruments and meters match the ID number out of the library in the system) the instruments and meters are normally out of the library, and the instruments and meters that are brought out When it is brought out without ID matching by the system or moved abnormally, after the reader recognizes the tag, the relay closes the sound and light alarm to alarm to avoid the loss or theft of the goods.
3. System Features
● The system has high reliability, and the error probability is far less than manual operation
● Passive electronic tags, no power supply, durable
● The accuracy of reading information is high, reducing manual errors
● High anti-interference, no special requirements for interference near the warehouse and perimeter environment, strong environmental adaptability
● Improve work efficiency and reduce redundant actions such as manual recording
● Reduce inventory cycle and reduce costs
● Real-time management of warehouse inventory
[ad_2]



