Application of RFID in exhibition tickets
[ad_1]
I. Introduction
With the rapid development of the domestic economy and the extensive needs of information, business communication, and entertainment, various forms of public communication activities such as exhibitions, conferences, and sports events have become more frequent, and they have even developed into a new industry. The participants of these public events generally range from a few hundred to tens of thousands, which brings great challenges to the organizers and venue management staff and their event management. There are two main types of tickets issued for various exhibitions or events: visitor (audience) tickets and staff certificates. The staff certificates include exhibitors, venue staff, organizing committee staff, temporary entry permits, and so on. At present, most exhibitions use manual ticket checking. For some major (important) exhibition activities, the traditional ticket issuance and management methods mainly have the following problems:
(1) Fake tickets: For exhibitions, conferences and sports events with high participation value, the possibility of fake tickets is very high. Traditional tickets rarely use anti-counterfeiting functions; even if some anti-counterfeiting functions (such as barcodes, lasers, etc.) are used, the technical means are easily mastered and used by counterfeiters, and it is difficult to prevent counterfeit tickets. This not only brings economic losses to the organizer, but also causes potential problems to site management, the order and safety of exhibitions/events (this is particularly obvious in sports events);
(2) Some exhibition tickets allow the holder to enter and exit the venue multiple times, which causes many people to lend the tickets and sell them to others for use. This brings huge economic losses to the organizer;
(3) Scalper tickets: For exhibitions or events where tickets are in short supply, scalper tickets are also an inevitable problem. The “scalper party” bought large amounts of hoarded tickets for huge profits and turned over at high prices, which not only hindered the normal participation of spectators who really need them, but the distortion of ticket information also interferes with or even misleads the organizer’s management and market activities; in addition, the reputation of the exhibition is also affected by this. damage;
(4) The efficiency of manual ticket checking is low, it is difficult to cope with the peak period of personnel entering the venue, and it inevitably provides an opportunity for fake tickets;
(5) Information management, mining and utilization of exhibition visitors. A large number of visitors will generate a huge amount of relevant data during the exhibition and activities, and these data will be needed by the organizer, especially the exhibitors. At present, almost most of the organizers are only at the stage of providing exhibition (conference) venues for exhibitors, they have not worked hard on “services”, and have not realized that “data” and “information” have a great impact on themselves and their customers (exhibitors). Quotient) may bring great value.
Yuanwanggu Company uses advanced RFID technology combined with database technology, positioning technology, communication and information technology, etc., to effectively solve the problems of exhibitions, conference venues, sports competitions, concert ticketing and information management. The ticket management system based on RFID technology not only solves the problem of traditional tickets, but also achieves revolutionary breakthroughs in improving customer satisfaction, improving customer experience, and providing information collection and available value-added services for relevant departments.
2. RFID ticket system achieves its goals
The RFID ticket system uses advanced RFID technology combined with communication, database and information management technology to provide exhibition organizers and managers with a new type of exhibition information system based on real-time data collection of electronic tags. The goals achieved by the system are:
(1) Establish a complete electronic label ticketing computer management system to realize the business management of the entire process of computer ticketing/ticketing, ticket checking/checking, ticket management, data collection and settlement, data summary statistics, information analysis, query, and reporting;
(2) Bring all the business work of the exhibition into the unified management of the computer, improve work efficiency, and plug the loopholes in finance and ticket issuance;
(3) Solve the issue of ticket anti-counterfeiting and avoid possible huge economic losses;
(4) Data collection is more accurate and timely, providing customers (including exhibitors and visitors) with rich and in-place information value-added services (passenger flow, personnel composition, identity, interests, activities, etc.), for organizers and exhibitors Provide information support for market decision-making;
(5) Further improve the service level of the exhibition and increase customer satisfaction through in-depth mining of customer information at the exhibition.
(6) Enhance the image and brand of exhibition activities.
Three, system introduction
For large-scale conferences, exhibitions, concerts, etc., due to the large number of participants and the huge amount of data, the data should be stored in the central database server, and when necessary (including unified ticketing, statistics, etc.), send a request to call In addition, for some users who temporarily purchase tickets, their personal information needs to be collected at each ticketing point and then uploaded to the central database. Therefore, each ticketing point client needs to have certain data processing capabilities. In addition, some viewers need to provide an online transaction platform due to the inconvenience caused by queuing at peak time for ticket purchases and long distances.
Therefore, the system should be developed in combination with the C/S and B/S modes, highlighting the advantages of the two methods can quickly and better achieve system requirements.
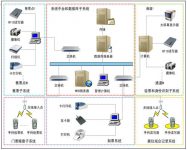
1. Schematic diagram of the overall system architecture topology

picture1 Schematic diagram of the overall system architecture topology
2. Function Module

picture2 Function block diagram
(1) Basic functions of ticket manufacturing and sales subsystem
Ticket issuance: The ticket seller chooses the type, unit price and validity period of the tickets to be sold, and completes the delivery on the spot. The label issuing/printing terminal can print and sell all the tickets that have been delivered;
Display the current ticket sales status;
Submit ticket information to the server.
(2) Basic functions of ticket checking monitoring subsystem
The information of the electronic tag ticket is read through the fixed reader when entering and exiting the venue, and the security certification is performed through the list of legal personnel and the security certification module. If the certification is passed, the information is read out correctly, the confirmation information is returned, and it is legally passed; otherwise, it will be prompted Call the police.
No matter how rigorous the entrance ticket inspection procedure is, a small number of omissions may be caused. The ticket inspection in the venue is a random spot check, and the purpose is to further discover illegal personnel entering the venue during routine security inspections. Inspectors can use a hand-held ticket checking machine to directly read the ticket information on the audience from a long distance without disturbing the audience. If you have any doubts, you can ask the audience to cooperate in further inspections.
Double checkpoints for ticket checking through RFID, to minimize the appearance of fake tickets.
Download the list of legal spectators, and enter the authenticity information of the personnel and tickets.
(3) Basic functions of booth audience recording subsystem
For interested customers, with the consent of the other party, the exhibitor can use the handheld to identify the RFID tickets of the audience, and after the exhibition, the information can be retrieved from the database for analysis and printing (if conditions permit Can connect to the central database through the wireless transmission function on the handheld for real-time data update and view);
It is helpful to collect data such as booths that customers are interested in and the length of stay.
(4) Basic functions of statistical analysis subsystem
On-site statistics of ticket sales for different sessions and various time periods;
Conditional query statistics based on ticket sales time, ticket location, ticket type, admission situation, etc.;
Income statistics and query for each session, daily and monthly;
Print statistical reports of various data;
The following statistics and analysis can be further carried out:
Statistics of the number of units and people participating in the exhibition (including exhibitors, purchasers, other units and ordinary visitors), which can be counted by various methods such as region, industry, scale, and nature;
Statistical analysis of the basic information of the audience: gender, age, position, nature of the unit, etc.;
The purpose of exhibitors and visitors: sourcing, finding partners, understanding the market, learning, etc.;
The degree of attention paid to various industries/exhibitors and products in the exhibition, and the visit frequency and length of stay of visitors to different venues and booths.
(5) Basic functions of system maintenance subsystem
Complete the ticket system operation user registration, authorization, operation log, system parameter setting, data reception and transmission and other functions.
(6) Basic functions of online registration subsystem
Exhibitors and visitors of the exhibition can submit the corresponding personal information online in advance to avoid the inconvenience caused by the queue congestion when temporarily filling in the information to purchase tickets, and at the same time, it also reduces the pressure of the system’s overload operation to a certain extent.
Fourth, the system workflow
The system work flow chart is shown as in Fig. 3.

picture3 System workflow
Detailed description of the process:
(1) Registration
Similar to the current exhibition process, visitors should fill in the information collection card to register before entering the venue, so as to print tickets and follow-up information collection and statistics. You can use the online registration subsystem to register in advance before the exhibition to avoid congestion.
(2) Ticket collection
The information entry personnel enter the basic information of the completed information collection card into the database and make corresponding tickets. The tickets contain the basic information of the visitor (such as name, unit, etc.).
(3) Entrance
Visitors wear the ticket directly through the entrance channel, and the RFID reading device effectively recognizes and automatically releases the ticket. If the ticket is invalid, expired, or exceeds the limit, an alarm will be prompted.
(4) Booth
For interested customers, with the consent of the other party, exhibitors can use handheld devices to identify the customer’s RFID e-tickets. After the exhibition, they can retrieve their personal information, booths viewed, and stay time in the database after the exhibition. Perform analysis and print.
(5) Export
When leaving the exhibition hall, you must pass through the exit channel. RFID reading equipment can effectively identify and automatically release. If the ticket is invalid, it will prompt an alarm. It is also convenient to record the time of the customer’s stay in the exhibition hall and count the number of people in the exhibition hall.
(6) Ticket recycling
In consideration of environmental protection, visitors can throw RFID tickets into the recycling bin after leaving the exhibition hall.
Five, system characteristics
1. Advantages
The system has a full range of real-time monitoring and management functions;
Eliminate the economic loss caused by forged tickets;
It can effectively prevent the entry of people without a ticket and strengthen the safety protection measures of the venue;
It can accurately count the visitor flow, operating income and ticket inquiry, eliminate internal financial loopholes, and have significant economic and social benefits for improving the modern management of the venues;
Provide information classification and available value-added services by classifying the different identities of exhibitors and visitors;
Through long-term data accumulation and analysis, it is possible to accumulate market dynamic data of related industries;
For the organizer, it has made revolutionary breakthroughs in improving customer satisfaction and improving customer experience.
2. Potential deficiencies
(1) Low efficiency
We know that the implementation of this system has a better effect on eliminating counterfeit tickets and reducing security risks. However, due to the current technical conditions are not very mature and people’s awareness of RFID, for example, fixed readers in and out of the venue misread or miss multiple tags, and at the same time, manual or camera verification of the identity of personnel entering and exiting are all to a certain extent. This reduces the operating efficiency of the system.
But with the maturity of technology and people’s understanding of RFID, efficiency will be further improved.
(2) Personal privacy issues
Since the introduction of RFID into the field of identification, personal privacy has been a topic of debate, and the system also faces this security concern. The user’s personal data information is stored in the system database. If it is leaked, it will bring unexpected consequences.
We believe that the following privacy policy should be followed on a voluntary basis by both parties:
Before the participants pass their personal information to the organizer, both parties shall sign a confidentiality agreement. The participants authorize the organizer to use the information for legal purposes during the exhibition; the organizer shall also guarantee that the information shall not be leaked to the organizer for any reason. The three parties, at the same time, promise to delete the information immediately after the exhibition ends;
There must be an explicit notice and privacy statement near the reader and the tag that use RFID tags;
Should have reasonable access rights to modify or correct personal information;
There should be a corresponding mechanism to resolve disputes between participants and the RFID data collector (this is the exhibition organizer). In addition, if relevant complaints and disputes are not resolved, there should be an independent mechanism to submit disputes and complaints to relevant parties for resolution.
Six, concluding remarks
In summary, the exhibition ticket system based on RFID technology is a high-tech application system that combines the latest international automatic identification technology-radio frequency identification technology (RFID), modern computer technology, database technology, wireless communication technology, and automatic control technology. It integrates all exhibition affairs into computers for management, which greatly improves work efficiency, minimizes the occurrence of counterfeit tickets, substitutions, etc., reduces the loss of ticket revenue, and at the same time, it can form management decisions and improve the organizers. Revolutionary breakthroughs have been made in customer satisfaction and customer experience improvement, which has improved the image of the exhibition and has significant economic and social benefits.
It is believed that in the near future, the RFID venue ticket application system will be widely promoted and applied.
[ad_2]



