Xinrui Equipment Inspection System—(Universal Version)
[ad_1]
Chapter One System Overview
Equipment inspection systems are often used in power generation, cement, chemical, steel, substations, power transmission and transformation industries, to prevent equipment failures through periodic inspections of equipment at fixed points and timing. For equipment-intensive enterprises, there are many equipment components, any problem with any component may affect the normal operation of the equipment, and abnormal shutdowns will bring huge losses to the operation of the enterprise. Therefore, through continuous and uninterrupted manual inspections, timely handling of abnormalities in equipment to avoid equipment failures or defects is a common management method for enterprises.
Xinrui company began research and development of inspection system as early as 2003. In the previous generations of product development, it has experienced meter reading inspection, line inspection, random inspection and other product development, from the initial single-chip inspection device to barcode-based inspection Identified the collector of the wince system to the latest android system handheld computer. Through years of digging and refining the inspection business needs of various industries and integrating the excellent performance of the products of various manufacturers, a new generation of general-purpose android device inspection system is now launched, making full use of the touch screen operation of android smart machines, high-definition photography, WIFI communication, etc. Function, combined with Rfid recognition technology, there are few key operations in the whole inspection process, simple on-site operation, automatic confirmation by swiping card, if abnormality is found, it will record or take pictures, allowing inspectors to focus on the equipment status and abnormal inspections middle. The back-end software is designed according to the generalized software design. The inspection points, routes, plans, etc. can be flexibly set. The system interface is simple and generous, the operation is simple, the reports are practical, the green software, no installation process is required, and the user can get started after simple training. The management software is developed based on a mature platform and has strong scalability. It can also be customized according to user needs on the basis of meeting inspection management.
In addition to power generation companies, the equipment inspection system can also be widely used in substations, transmission lines, petrochemical, railway, steel and other asset-intensive industries.
Chapter 2 System Composition
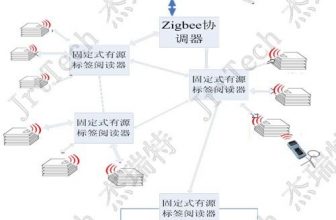
The system consists of background management software (B/S green software), industrial android handset (also called handheld), and radio frequency information card.
The background management software completes the basic information of the inspection point, the inspection route, the inspection plan, etc., completes the inspection record query, the statistics of the in-place rate and the missed inspection, and other basic information modules of the system.
The radio frequency information card is used to identify different inspection points on site.
The handheld computer adopts the industrial-grade model of Android system, which is sturdy and durable. In addition to the basic functions of the mobile phone, it also has functions such as bar code, RFID recognition, WIFI communication, and taking pictures.
Chapter 3 System Features
1) The new generation of inspection system is simple in design and simplifies the complexity of on-site handheld computer operations
2) Use mainstream industrial Android machine as data acquisition machine, compatible with RFID tag and barcode recognition, support high-definition camera, WIFI, 3G signal, etc.;
3) Backstage B/S green version software, no installation process, easy to maintain and upgrade;
4) The project implementation process is simple, the user completes the system initialization work by importing basic data through several excel templates;
5) The system is cost-effective, and the actual user experience is good. The report can be used for team assessment and competition
Chapter 4 Pocket PC Functions
Handheld functions include:
Data download: download the basic information of the system to the handheld computer;
Data upload: upload the inspection records in the handheld computer to the system;
Inspection: Perform on-site inspections on the equipment of the selected route. The inspection process does not require frequent button confirmation. There is no order restriction on the inspection points. The total number of inspections and the number of inspections are prompted during the inspection process to prevent missed inspections. During the inspection process, you can choose the route at will, and all equipment inspections are complete.
Inspection point setting: complete the initialization of the on-site tag card with a handheld computer, and establish the association between the tag card and the device.
Network setting: Set the server communication address to realize the communication between the handheld computer and the background for uploading and downloading data.
According to user needs, handheld computers can choose RFID or barcode recognition methods. RFID or bar code is only used as the only identification of on-site inspection points.
Chapter 5 Background Software Functions
The inspection background software completes the basic information settings such as inspection points, inspection routes, inspection plans, and department personnel. Before the inspection, the basic information that has been set needs to be downloaded to the front-end handheld computer, and then the inspection starts. After the inspection, the data from the handheld computer is uploaded to the back-end database of the system, and the system automatically forms various statistical analysis reports.
Through the above report analysis, effective supervision and management of on-site inspection can be carried out, and it can also provide a basis for competition and assessment of teams or personnel.
5.1. Functional structure diagram
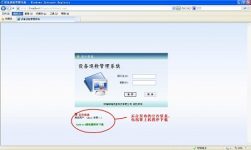
5.2. Login interface

5.3. Basic settings
5.3.1. Inspection point information
Function description: In order to facilitate the management of the inspection equipment, the equipment is classified and set. Then record the basic information of the device such as device name, device number, corresponding ID card number, card number, description, etc. For the first use, basic equipment information can be quickly imported through an excel template.
Operation note:
All table data in the system can be exported to excel table.
The table title supports up and down sorting by default.
Double-click the record line to enter the editing interface.

Organize the data in accordance with the excel template format. The device code is required to be unique. The card ID is the physical card number of the field device label card, and the card number is the printed number on the label to distinguish different cards.
5.3.2. Inspection route
Function description: When the number of equipment is large, the inspection equipment can be divided into different routes according to equipment specialty, attribute or location area. Different routes are composed of several devices, and the same device can be in different routes. The equipment in the route can be inspected in order or out of order.

5.3.3. Inspection plan
Function description: The inspection plan is made by setting the number of inspections for different routes. The number of inspections can be set for departments, shifts, and routes.
Through the selection of multiple departments, multiple shifts, and multiple routes, the batch plan setting can be realized.
5.4. Query and Statistics
5.4.1. Inspection record query
Function description: This module queries the detailed records of each inspection record. The main and detailed modules are displayed. On the left, one inspection record is generated for each route for each inspection, and the module on the right displays the detailed record of each inspection point. On the left template, you can query the previous inspections, the start and end of the inspection time, the total number of inspections planned for each inspection and the actual number of inspections. The detailed module on the right displays the inspection time, whether it is abnormal, on-site photos or abnormal description of each inspection point in the route.

5.4.2. Inquiry of inspection equipment
Function description: This module filters and queries all the inspection records for the inspection equipment, and is used to analyze the inspection status of different equipment. For example, the number of abnormalities in the device over a period of time, the frequency of inspections, etc.
5.4.3. Route arrival statistics
Function description: Query and count the status of the route for different routes. The statistics include: the number of planned routes, the number of inspection equipment in the route, the total number of planned inspections, the actual number of times, and the in-place rate.
5.4.4. Shift arrival rate statistics
Function description: Calculate the inspection in place rate of each team and realize the inspection of different teams and groups in place. The statistics include: the planned total number of inspections for each shift, and the actual total number of inspections.
5.4.5. Missed detection statistics
Function description: Query and count the records of missed inspections in different shifts every day. All those that do not meet the requirements of the inspection plan are considered missed inspections. Statistics show: the number of planned inspections, the actual number of inspections, and the number of missed inspections of missed equipment in each shift every day.
Planned inspections-actual inspections = missed inspections
5.5. System Management
5.5.1. Basic information
Function description: In order to facilitate system function expansion and flexible setting, define and set the basic types in the system. The type defined by the system cannot be deleted or modified.
5.5.2. Department staff
Function description: Complete the setting of department and personnel information in the system. For the first use, the personnel and department information can be imported through the excel template.
5.5.3. Role permissions
Function description: The system has two roles: administrator and ordinary user. Roles are used to facilitate batch allocation and management of permissions for different types of users. By setting different functional permissions to roles, and then assigning personnel to roles, the authority distribution of personnel is finally realized.
5.5.4. Role User
Function description: Assign different personnel to different roles.
5.5.5. Menu Maintenance
Function description: Set the function menu in the system.
[ad_2]