Intelligent warehouse management system
[ad_1]
With the development of Internet of Things technology, it provides a reliable means for modern manufacturing enterprises to implement refined management. With product as the main line and bar code technology as the means, starting from the plan, automatic identification, recording and monitoring of product materials, production processes, semi-finished products, and finished products are implemented, fully transparent management is implemented, and errors are prevented, discovered and corrected in time during production. The product can also be traced afterwards, and the authenticity, whereabouts, storage, process records, producer, quality inspector and production date of the product can be clearly inquired, and the reasons for the production of defective products can be analyzed. MTS (Manufacture Traceability System) production traceability The system came into being.

Overview
This production traceability system uses barcode technology to assign product electronic labels, barcode identification of materials, automatic recording of process operations and other information technology methods to perform error prevention, monitoring, real-time analysis and tracking, etc., to achieve error prevention in product production , Lean production and management have greatly improved production efficiency and product quality, and greatly improved customer satisfaction.
System background
As the manufacturing environment changes, product cycles are becoming shorter and shorter, a variety of production methods are available, and the requirements for inventory restrictions are getting higher and higher. Therefore, it is necessary to establish and implement a supply chain management system, with the help of computerization and information technology to connect suppliers, Manufacturers and customers are closely united to share inventory risks. Warehousing management can be briefly summarized as 8 key management modes: tracking-receiving-checking-storing-picking-issuing-stocking-returning.
The optimal control part of inventory is to determine the business model of the warehouse, that is, to determine the management objectives and management mode of the warehouse (according to the requirements of the previous design). If it is an execution link in the supply chain, it is a cost center. With service quality and operating costs as the control objectives, we pursue reasonable inventory or even zero inventory. Therefore, an accurate understanding of warehouse item information is very important to the system, so we propose to solve accurate warehouse management.
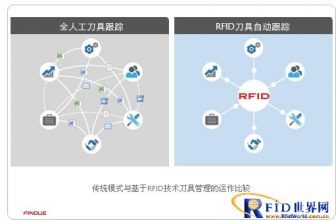
Warehousing management and precise positioning play a very important role in the entire management process of an enterprise. If timely and accurate purchase, inventory control and delivery are not guaranteed, it will bring huge losses to the enterprise, which is not only manifested in the management of the enterprise. The increase in costs will also make it difficult to guarantee the quality of customer service, and ultimately affect the market competitiveness of the company. Therefore, we proposed a new RFID-based warehouse system solution to solve the problem of precise warehouse management. Let’s analyze the economic benefits brought to the enterprise by adopting radio frequency identification technology.
System advantages
√ Convenient and fast reading: Data reading does not require a light source, and can even be carried out through the outer packaging. The effective identification distance is longer. When the active tag with its own battery is used, the effective identification distance can reach more than 30 meters;
√ Fast recognition speed: as soon as the tag enters the magnetic field, the reader can read the information in it instantly, and can process multiple tags at the same time to achieve batch recognition;
√ Penetration and unobstructed reading: Bar code scanners must be close and without obstructions before they can read bar codes. RFID can penetrate non-metallic and non-transparent materials such as paper, wood, and plastics for penetrating communication. It does not require a light source and has a longer reading distance. But it cannot be identified through conductive objects such as metals.
√ Large data capacity: the capacity of a two-dimensional barcode is 50Bytes, the maximum capacity of a two-dimensional barcode can store 2 to 3000 characters, and the maximum capacity of RFID is a few MegaBytes. With the development of memory carriers, the data capacity also has a trend of continuous expansion. In the future, the amount of information that items need to carry will become larger and larger, and the demand for tags that can expand the capacity will increase accordingly.
√ Long service life and wide range of applications: its radio communication method allows it to be used in dust, oil and other highly polluted environments and radioactive environments, and its closed packaging makes its lifespan much longer than printed bar codes; the carrier of traditional bar codes is paper , So it is susceptible to contamination, but RFID has strong resistance to substances such as water, oil and chemicals. In addition, because the barcode is attached to the plastic bag or the outer packaging carton, it is particularly vulnerable to damage; the RFID label stores the data in the chip, so it can be protected from contamination, and the RFID has strong anti-pollution ability and durability.
√ The label data can be changed dynamically: the programmer can write data into the electronic label, thus giving the RFID label interactive portable data file function, and the writing time is shorter than printing a bar code;
√ Better security: RFID electronic tags can not only be embedded or attached to products of different shapes and types, but also can set password protection for the reading and writing of tag data, thus having higher security;: because RFID carries For electronic information, the data content can be protected by a password, so that the content is not easy to be forged and altered, and the security is higher.
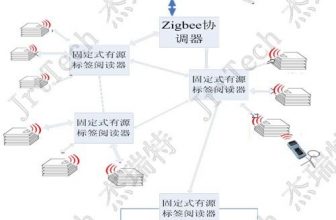
√ Dynamic real-time communication: The tag communicates with the reader at a frequency of 50-100 times per second, so as long as the object attached to the RFID tag appears within the effective recognition range of the reader, its position can be dynamically tracked and monitored .
√ Small size and diversified shapes: RFID does not need to match the fixed size and printing quality of the paper for reading accuracy, and is more suitable for the development of miniaturization and diversified forms to facilitate embedding or attaching to products of different shapes and types .
system introduction
The precision warehouse process generally includes several processes: receiving, putting on shelves, picking, replenishing, shipping, and inventory. The following describes the specific implementation process of the RFID warehouse management system:
data preparation
-All delivered goods need to be imported into WMS in advance by EDI, Excel or manual entry
– All customer orders need to be imported into WMS in advance by EDI, Excel or manual entry
In order to support the use of modern logistics equipment such as RFID or electronic tags, conveying and sorting lines in the logistics center, barcode planning and design are required in the following links.
— Barcoding of all operation units in the warehouse, including pallets and turnover boxes. Paste the fixed serial number label directly on the job container.
— Barcoding of storage locations in warehouses.Encode the cargo location and paste the barcode label in the order of library-rank-position-layer
— Barcode of job documents and job instructions.
— Print the barcode of the document number and product code on the warehousing list, and assist the receiving staff to use RFID for receiving operations
— By printing picking labels, guide pickers to obtain picking tasks and facilitate the identification of goods on the conveyor line
Labels for different uses
Receipt
-Use RFID in the receiving area for code discs (if needed) and receiving operations. All goods stacked in the receiving area must have a unique pallet number, and the pallet number is pasted on the pallet in the form of a barcode label
– If the SO has not been delivered, the system instructs to send the goods to the temporary storage area for tally
-The system assigns a corresponding shipping area for the order according to the vehicle information and volume information of each order
– The system automatically matches the received goods with SO, and generates a distribution task for each pallet of goods in the receiving area.
-The tally staff scans the label of each pallet in the receiving area, and moves the goods to the temporary storage area or the waiting area of the corresponding order according to the instructions. If you need to distribute the goods to multiple orders, you need to confirm each shipping area and quantity separately. Use a new pallet when distributing goods and confirm the new pallet number.
-When it is necessary to distribute goods from the temporary storage area,RFIDInstruct the tally staff to pick goods from the temporary storage area and then divide the goods.
Review
-After the order is distributed, the system prompts the reviewer to review the product and quantity for delivery
– Scan each pallet in the to-be-delivered area in turn, confirm the vehicle number for delivery
[ad_2]