Tobacco enterprise RFID supply chain management system technology application program
[ad_1]
Chapter 1 System Introduction
1.1 Overview
The state of China’s tobacco industry that is highly dependent on the domestic market has not changed for a long time. With the accelerated pace of WTO accession, tariff reductions, and the cancellation of the special (foreign) cigarette retail license system, foreign cigarettes have more opportunities in the domestic market. Competitive advantage, the domestic tobacco industry is facing unprecedented competitive pressure.
At present, because the management of domestic enterprises is still relatively extensive, the cost of each link is still high, and the cost of the supply chain link is 2 to 3 times higher than that in developed countries. Whether the tobacco industry can closely connect every company, every partner and even every customer in the supply chain, so as to reduce costs more and capture the market faster, is a hot issue of current information construction. The application of the tobacco enterprise supply chain management system has become another new business hot spot and bright spot in the Chinese tobacco industry, strengthening the core competitiveness of the enterprise, competing against the international tobacco giants, winning a place in the competition, and providing new competitive methods and methods.

At this stage, the problems that have led to the high cost of the supply chain of domestic tobacco companies mainly include the following aspects:
●Many manual intervention, low efficiency and high error rate
●In order to ensure the continuity and accuracy of the information chain, the investment cost is too high
●Unable to realize real-time monitoring and tracking of goods
The application of bar code partially solves the above problems. However, due to the shortcomings of bar code such as low reading and writing efficiency, unchangeable information, and small amount of information, it appears to be inadequate in the application of bulk logistics management.
The market launched the RFID-based radio frequency automatic identification technology, according to the actual situation and demand in the supply chain management, integrated the company’s existing applications and bar code technology, and developed the “RFID Supply Chain Management System”.
This system completely solves the problems in supply chain management, breaks the technical bottleneck restricting the development of the enterprise, improves the degree of intelligent production, warehouse management efficiency, distribution accuracy and throughput, and realizes the tracking and visual management of the whole process. , To help companies reduce operating costs and enhance their core competitiveness.
Supply Chain (Supply Chain) refers to the network formed by manufacturers, suppliers, retailers, etc. through mutual provision of raw materials, parts, products, and services.
Supply Chain Management (Supply Chain Management) is to design, plan and control the information flow, logistics and capital flow in each link of the supply chain, so as to enhance the competitiveness and improve the efficiency and benefits of each member in the supply chain. Supply chain management runs through the entire process of purchasing, processing, warehousing, distribution, and retail.
1.2 Introduction to key technologies
1.2.1 RFID technology
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) is a technology that uses radio frequency signals for automatic target identification and two-way data communication.
RFID technology is mature and has a good application foundation. Compared with traditional identification methods, RFID has strong advantages.
●Long-distance reading and writing (1-10 meters)
●Multi-target, recognition in motion (up to 1000/sec)
●Large storage capacity, rewritable (100,000 times)
●Long service life (10 years)
These characteristics makeRFIDThe technology can complete information reading and writing and processing without direct contact, optical visualization, and manual intervention, and the operation is convenient and fast. It can be widely used in production, logistics, transportation, medical treatment, anti-counterfeiting, tracking, equipment management and other fields that need to collect and process data, and it is considered as a future substitute for barcode labels.
A typical RFID system generally consists of RFID tags, readers, and computer systems.
●Tag (Tag): Composed of coupling components and chips, each tag has a unique electronic code, attached to the object to identify the target object;
●Reader: a device that reads and writes tag information, which can be designed as a handheld or fixed type;
●Middleware (Savant): Connect RFID equipment and application system software.
Chapter 2 System Structure
2.1 Overall architecture
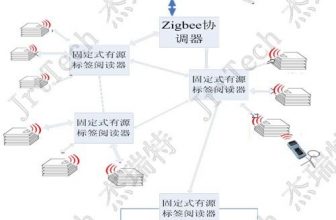
This system perfectly integrates existing technology and hardware and software systems through trays embedded with RFID electronic tags, read-write equipment and auxiliary equipment arranged at various key nodes, and related software systems, and achieves accuracy, efficiency, and visibility. Intelligent enterprise supply chain management with control and large throughput.
2.1.1 System block diagram

2.1.2 System network diagram

2.2 Software system
2.2.1 RFID pallet automatic palletizing management system
The RFID pallet automatic palletizing management system combines RFID technology, industrial automation technology, and barcode technology. The system automatically completes the entire process of bar code data collection, empty pallet filling, problem pallet screening, goods palletizing and loading, and bar code data writing to the pallet electronic label, realizing the follow-up of goods and information, and the real-time synchronization of offline data and background data , Established the foundation for the follow-up process.
2.2.2 RFID inventory adjustment system
The RFID inventory adjustment system realizes the synchronization of the reorganization of goods and the reorganization of information, and maintains the consistency of offline data and online data through wireless real-time updates, making inventory management more efficient, accurate and intuitive.
This system integrates the functions of wireless network, barcode scanning, and RFID reading and writing equipment, which has changed the situation that the information connection is broken during the adjustment and reorganization of the goods in the past.
2.2.3 RFID visualized warehouse and order distribution management system
RFID visualized warehouse storage and order distribution management system, because the RFID electronic tag stores all the items on the pallet, there is no need to confirm the goods one by one, which realizes the real-time update of bulk goods storage and inventory data, which is dozens of times higher. The efficiency and accuracy of warehouse access management.
By linking to the enterprise sales order system, the execution of each order can be monitored in real time and visually during the storage and exit process.
2.2.4 Monopoly Bureau warehousing management system
The monopoly bureau’s warehousing management system is an extension of the supply chain management of the tobacco production system. It provides accurate and efficient means for the warehousing management of the monopoly system. Through the WAN, the arrival information of the goods can be fed back to the production system in real time.
At the same time, this has laid the foundation and found a connection point for the realization of “large closed-loop supply chain management” in the tobacco production, monopoly, and management system in the future.
2.2.5 RFID tray management and monitoring system
Through the integration and analysis of the pallet circulation information and pallet recycling information of the above systems, the use and circulation of pallets are monitored to ensure the timely maintenance, replacement and supplement of pallets in the system.
2.2.6 RFID middleware system
BEA or RFID middleware has the characteristics of distributed processing and large traffic, providing users with rich functions:
●Provide device operation interface compatible with a variety of RFID readers
●Data filtering and transmission
●Manage RFID reading and writing equipment
●Support multi-application system to request RFID data
●Support integration with existing business systems
2.3 Hardware system
2.3.1 RFID electronic tags
This system uses UHF EPC C1G2 ultra-high frequency electronic tags to realize high-speed, stable and long-distance identification and data exchange; provides larger storage space to meet the requirements of multiple varieties and large data volumes; adopts special packaging, waterproof, anti-magnetic, Anti-static, anti-collision, to ensure that the label can be used for a long time in harsh environments.
2.3.2 Electronic tag reading and writing equipment
This system adopts CSL-461 industrial grade reading and writing equipment, which has the advantages of long reading and writing distance, stable reading and writing, fast reading and writing speed, open interface, and strong environmental adaptability. It is suitable for industrial applications.
2.3.3 RFID goods adjustment mobile processing equipment
In order to ensure the continuation of the information chain after the adjustment and reorganization of the goods, it is necessary to re-associate the information of the goods and the pallet and send the data to the background in real time when the inventory is adjusted. Mobile devices with network functions.
RFID goods adjustment mobile processing equipment integrates wireless network, barcode scanning, and RFID reading and writing functions. It has simple operation and advanced technology, which fully meets the needs of applications and can work continuously under complex conditions.
Chapter 3 System Function
Modern enterprise management actually revolves around data information. The application of RFID technology in supply chain management aims to break through the technical bottlenecks of data information collection, data information transmission and data information processing in each link, thereby improving the entire supply chain s efficiency.
3.1 Production management
Through the integration of RFID technology, industrial automation technology, and barcode technology, the bottleneck of information processing in the palletizing process of goods has been broken.
The system provides the following functions for production management:
●Barcode data collection
●Empty tray filling
●Problem tray screening
●The goods are palletized into the tray
●Barcode data is written into the electronic label of the pallet
●Real-time update of background data
3.2 Adjustment and management of goods in the warehouse
In the link of goods adjustment and management, wireless network technology and RFID technology are used to improve the efficiency of adjustment in the warehouse and ensure the continuity of the information chain.
The system provides the following functions for goods adjustment management:
●Tray electronic label reading
●Barcode data collection, data reorganization
●Bar code data is rewritten into the electronic label of the pallet
●Wireless data communication
3.3 Inbound and outbound management and order delivery
Obtain the order distribution plan from the system, allocate channels for each order, and integrate RFIDReaderWith the large-screen display function, the order information and loading information are displayed at the exit of the channel to monitor the execution of the order in real time.
The system provides the following functions for warehousing management and order distribution:
● RFID storage management
●Order inquiry, order distribution
●RFID outbound management
●Large screen monitoring
3.4 Circulation management
Circulation management mainly refers to the management of the process of delivery of goods out of storage to the monopoly bureau and storage.
The system provides the following functions for circulation management:
●RFID warehousing management
●Real-time feedback of arrival information
●Order execution status query
3.5 Pallet Management
Through the integration and analysis of pallet circulation information in each system, the monitoring of pallet usage and circulation is realized, and the timely maintenance, replacement and supplement of pallets in the system are ensured.
3.6 Statistical analysis
Perform statistical analysis on system data and generate related reports.
Chapter 4 System Features
4.1 Reduce costs and improve efficiency
This system completely solves the existing problems in the current supply chain management, reduces human intervention, ensures the continuity and accuracy of the information chain, realizes the whole process tracking and visual management, and reduces the business cost of the enterprise.
By integrating existing application systems and technologies, the existing investment of users is fully utilized and protected, and the comprehensive use efficiency of investment is improved.
4.2 Large throughput and high accuracy
Through the use of RFID technology, the technical bottleneck of information collection, transmission and processing is broken, and the information of the goods is processed from one by one to batch processing, which increases the width of the information channel, so that the throughput of logistics is greater and the accuracy is higher.
4.3 Open interface
The design of this system has taken into consideration the application of existing information systems in the industry, so as to be fully compatible and easy to expand.
Bar code technology has been widely used in the tobacco industry and has achieved good results. This system combines the advantages of bar code technology and RFID technology, and integrates them perfectly to achieve seamless connection and provide solutions to existing problems. The most ideal solution.
4.4 Support for distributed information management
Distributed information management is realized by integrating the network and RFID technology, so that the information of production locations, storage locations, and distribution locations can be interacted efficiently and in real time. Users no longer need to worry about the negative impact of the dispersion of physical locations on information management.
Chapter 5 Implementation Plan
5.1 Production link

5.2 Warehousing and distribution links

[ad_2]