RFID beef quality and safety traceability system
[ad_1]
I. Overview
The system includes aquaculture enterprise information management system, RFID hardware system, consumer anti-counterfeiting traceability query system (Web, WAP, two-dimensional code) handheld information processing system and other systems.
2. Explanation of terms and abbreviations
Breeding bull: A healthy bull used to collect semen for calf reproduction.
Cow: A healthy cow used to conceive a calf.
Calf: A cow from birth to 6 months of age.
Observe the cattle in the adaptation period: 6-month-old cattle recovered from the breeder and undergoing a 1-month quarantine period after entering the company.
3. Breeders information management system
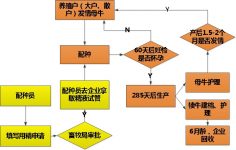
1. Breeding process

figure 1
2. Demand analysis
Farmers mainly complete the breeding of a generation of cattle.
2.1, apply with precision
2.1.1, application form management
Before breeding cows in heat within their jurisdiction, the breeder should fill in the application for the use of sperm, including the date of application, the amount of sperm used, and the breeder.
After completing the application with precision, the system will automatically submit it to the relevant department of the Animal Husbandry Bureau.
Frozen semen can be collected after approval by the relevant departments.
2.1.2, application form query
Query the refined application form according to certain conditions.
2.2. Breeding management
During breeding, the breeder records information such as the date of estrus, the use of sperm, the date of mating, the veterinarian, and the cow’s visual number (UID).
It can complete the query function of related breeding information according to the conditions.
2.3. Calf Management
A file is created when a calf is born, including weight, body size (waist circumference, body oblique length, body height, tube circumference, shoji length, etc.), gender, date of birth, parental line, strain (algebra), health and other information. This information is passed Handheld input, where the parental information system automatically retrieves and generates it through the cow’s visual number (UID).
The breeder initializes the ear tag through the handheld device.
Ear tagging of calves is performed by breeding, and the initialized ear tags are inserted into the ears of the cows through ear tag pliers.
2.4. Epidemic prevention management
2.4.1. Vaccine information query
Vaccine information comes from the system.
2.4.2. Epidemic prevention records
Record the epidemic prevention records of the epidemic prevention management personnel (veterinarians), record the visual identification number (UID), cattle type, cattle breed, vaccine name, vaccine manufacturer information, vaccine specifications, vaccine approval number, and vaccine validity period of the epidemic prevention cattle Etc., the time of vaccination, the injection personnel, whether there is a stress reaction, etc.
2.4.3, statistical analysis
Perform statistical analysis on epidemic prevention information.
2.4.4. Early warning management
Provide early warning reminders for cattle that need epidemic prevention (for example, 6 months apart), analyze according to the type of cattle and epidemic prevention type, and the system automatically summarizes which cattle (in which stage of cattle) the breeder is responsible for and what vaccines are needed at what time Anti-epidemic treatment.
Remind the calf (2 months old) to prevent the epidemic.
2.5 Management of pregnant cows
2.5.1 Early warning management
When the mating day reaches 60 days, the breeder is reminded to check the cow (rectal examination) to determine whether it is pregnant.
2.5.2, inspection management
The system records information such as inspection time, breeder, and visual number.
2.6. Quarantine management
When the 6-month-old calves raised by farmers are collected by the enterprise, they need to check and issue quarantine certificate information, including quarantine certificate number, quarantine personnel, quarantine unit, quarantine time, etc.
And can complete the inquiry of quarantine cattle quarantine information according to certain conditions, and display relevant details.
2.7, inspection management
Enter daily inspections, including information such as inspection content, inspector, and visual number (UID), which are automatically summarized and uploaded through the system.
4. Consumer anti-counterfeiting traceability query
1. Website query
1.1. Flow chart

figure 2
1.2, demand analysis
The query website has an independent domain name.
According to the barcode information entered by the user, the beef traceability information is fed back, including breeding information, quarantine information, epidemic prevention information, and slaughter information.
2. QR code query
2.1 QR code generation system
The system can customize the number of QR codes and the size of the QR codes according to the tetrad tags. The QR codes include cattle breeding information, epidemic prevention information, quality inspection information, and slaughter information.
2.2 QR code query system
Consumers can trace beef cattle breeding information, epidemic prevention information, quality inspection information, and slaughter information by scanning the QR code on the packaging bag.
[ad_2]



