Asset management solution based on RFID and WSN
[ad_1]
1. System Overview
1.1. System background
Assets are important economic resources of the country and enterprises.
For enterprises, on the one hand, assets are the cornerstone of creating income for the enterprise, and on the other hand, assets are also large producers of costs and expenses. How to effectively control costs and expenses while making assets generate more benefits is a deep concern for every enterprise. . As far as administrative institutions are concerned, assets are the material basis for the construction of political power at all levels and the normal operation of state machinery, as well as an important guarantee for social management and career development. The assets occupied by administrative institutions are mainly formed by state financial investment and are typical representatives of state-owned assets. The pros and cons of their asset operation and management will directly affect the operation and stability of administrative institutions.
Fixed asset management is an important part of the management of enterprises and public institutions. Fixed assets have the characteristics of high value, long service life, scattered use locations, and difficult management.
1.2. Current situation analysis
Fixed assets are often used in scattered locations and in various categories. In line with existing management systems, the nature and workload of the work such as manual production or printing of labels with ordinary printers, filling in or printing, pasting, and asset status tracking, inventory taking, etc. have not been achieved. It is easy to improve, and there are many human factors that lead to unclear asset status and asset loss. It mainly has the following problems:
Inaccurate asset depreciation data;
Inaccurate book value statistics, such as loss of assets, etc.;
Heavy inventory work, time-consuming and labor-intensive-information is not reflected in a timely manner, which affects the operational efficiency of the enterprise and leads to repeated asset purchases;
Unable to judge the operating status of the asset;
Unable to judge whether the asset can operate normally;
It is impossible to judge the environmental status of the asset, and it is impossible to estimate the impact of external factors on the asset, etc.;
It is not possible to accurately obtain the location of the asset.
1.3. User needs and analysis
1.3.1. User requirements
Combined with the current status and drawbacks of the existing asset management system, users will put forward the following requirements:
The data collection of asset management data is real-time, and the records of each state of the asset are kept consistent in time;
Real-time data collection of asset operating status and asset environment;
Realization of asset location positioning;
Unmanned operation of data collection to ensure reliability and stability, accurate data, and wireless data transmission;
Asset data report is converted from manual sorting and summarization to computer completion;
Improve the efficiency of data management, register various asset detailed accounts in time, and achieve the consistency of the account, the account and the account and the card;
The system is flexible and has extended functions;
The system is practical and easy to operate, and is aimed at users with different levels of professional quality.
1.3.2. Demand analysis
According to user needs, the following three categories can be proposed:
1) Analysis of technical requirements
Data requires the realization of long-distance automatic collection and wireless data transmission, etc. This system recommends the use of RFID and WSN integration technology to achieve.
2) Analysis of management needs
Automated asset management is realized through RFID and WSN, which is divided into three parts: collection layer, transmission layer and execution layer:
Acquisition layer
The collection layer is divided into RFID collection and WSN data collection. RFID is used to collect asset information, operator information, equipment information, asset flow information, etc., and WSN is used to collect asset environmental information, asset operating status information, etc.
Transport layer
Realize the wireless transmission of the collection layer information through WSN.
Executive presentation layer
Process the information transmitted by the transmission layer, record and control the working mode of the front-end acquisition layer, and analyze and report all the information of the system at the same time.
3) The system achieves its goals
This system uses RFID and WSN fusion technology to intelligently manage assets. Enterprises and institutions can understand asset flow, asset working status, asset environment status, etc. in real time without human monitoring and manual participation, which greatly improves corporate efficiency. Improve the level of government management and so on. According to statistics, the asset management system combining RFID and WSN has the following direct advantages:
1) Reduce the cost of repeated purchases by 20%;
2) Reduce audit costs by 75%;
3) Increase the warranty application by 50%;
4) Reduce 40% of spare parts inventory
5) Reduce equipment “missing” by 45%
5) Increase asset utilization rate by 30%
5) Extend the operating life of the equipment by 10%
6) Reduce equipment downtime rate by 50%
2. Technical introduction
2.1. RFID technology
RFID radio frequency identification is a non-contact automatic identification technology, which automatically recognizes the target object and obtains relevant data through radio frequency signals. The identification work does not require manual intervention and can work in various harsh environments. RFID technology can identify high-speed moving objects and can identify multiple tags at the same time, and the operation is quick and convenient. The RFID system is mainly composed of three parts: a reader, an antenna and a tag. It has the following characteristics:
1) Non-contact identification;
2) Object identification: The tag has a unique ID number to realize the unique identification of the object;
3) Long recognition distance: using different RFID frequency band technologies, it can achieve different distance requirements from 0 to 1000m, which is suitable for different occasions;
4) Anti-conflict: a large number of tags can be identified at one time;
5) Strong anti-interference ability: RFID wireless identification can be used in harsh environments and can work normally.
2.2. WSN Technology
WSN, or wireless sensor network, uses a large number of micro-sensors deployed in a specific area to monitor, perceive, and collect various information about the sensing objects that are of interest to observers in the node deployment area ( Such as physical phenomena such as light intensity, temperature, humidity, noise, and harmful gas concentration), and send some information to the background system wirelessly after processing.
WSN has the following characteristics:
1) Data collection: Collect asset operation or environmental status information through sensors;
2) Self-organizing network: The nodes have the function of automatic networking, and the nodes can communicate with each other and coordinate work;
3) Short network establishment time, network self-organization, network self-recovery and other functions;
4) Low cost, the use of wireless network can reduce wiring and labor costs;
5) Long communication distance;
6) Low power consumption, the node can be directly powered by button batteries.
2.3. RFID and WSN integration
RFID realizes the identification of objects and the collection and transmission of object information, WSN realizes data collection and transmission, and the fusion of RFID and WSN can cleverly realize the identification of objects and the collection and transmission of object information.
3. System introduction
3.1. System Principle
Information Collection
First, fix or embed the RFID tag or terminal collection node on the asset. The unique ID number of the tag or the data written by the user can be used as the identification code of the asset. The data is used to record the asset name, purchase time, department, work characteristics, etc. information. When the reader/writer installed in each channel recognizes the tag, all information of the asset can be obtained.
data transmission
RFID tags, terminal collection nodes, terminal transmission nodes, and readers form a wireless network. The system can transmit asset ID numbers, status information, and environmental information through the wireless network to the back-end data center for processing and analysis.
Asset positioning
The system can use the relay transmission node and the reader in the channel management as the positioning beacon, and combine the RFID and the RSSI function of the terminal collection node to realize the regional positioning function of the asset. In addition, the location information of fixed assets can be registered in the back-end database, and the specific location of the asset can be known by reading the asset tag information, thereby realizing the asset positioning function.
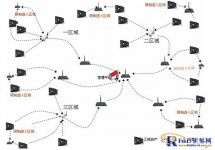
3.2. System Topology Diagram

Figure 2: System structure diagram
3.3. System Function Module

Figure 3: System function diagram
3.4. System function introduction
Asset management includes operations such as the addition, allocation, idleness, scrapping, maintenance and inventory of assets. It includes the entire process of equipment from purchase, putting into use and scrapping. RFID tags or terminal collection nodes are installed when the equipment is purchased, and the information of the assets is written inside. Each time the asset management operation is performed, the reader or the data center will read the tags on the assets and send the information to the server for processing , So as to realize the tracking management of assets. For confidential materials, operators can be designated, and unauthorized operators and actions will trigger an alarm.

Figure 4: Asset flow diagram
All RFID tags, terminal collection nodes, readers, and data centers form a wireless network, and asset information is wirelessly sent to the back-end system through the nodes and readers for processing and analysis

Figure 5: Wireless information transmission
3.4.1. Asset information initialization
For all new assets, the information needs to be initialized, that is, the RFID tag or terminal collection node writes the asset information and saves it in the background data.
3.4.2. New asset operations
After the asset information is initialized, the asset is brought into the warehouse or studio, and it is recognized and recorded in the background by the reader-writer installed in the warehouse, indicating that the device is a newly-added device. If you want to collect the operating status of assets, you need to install corresponding sensors to collect relevant information.
3.4.3. Operator
When assets are moved, allocated, repaired or scrapped, specific personnel are required to execute them. For characteristic personnel, an RFID tag needs to be distributed. The distributed RFID tags have different permissions. The reader needs to recognize the tag held by the executive while identifying the asset tag. When only the asset tag is identified but the executive tag is not recognized, the system will alarm; when the identified execution tag does not meet the scope of authority, the system will automatically alarm.
3.4.4. Asset allocation operations
The assets to be allocated will be recognized by the reader installed next to the channel when they pass through the access control or in and out of the channel. The reader records the current tag information and information and sends it to the back-end center. The back-end center judges whether it is warehousing, outgoing, or transfer based on the data.
3.4.5. Asset maintenance operations
When the reader installed in the maintenance area recognizes the tag, the reader will send the information to the back-end center through the wireless network for recording and processing. When the reader/writer installed in the maintenance area recognizes the tag, the reader/writer will send the information to the back-end center via the wireless network to record the completion of the asset maintenance operation.
3.4.6. Asset retirement operations
First, the scrap equipment is recognized by the reader when it is taken out of the studio, the reader records and sends it to the back-end center, and then the device is recognized by the reader when the device is brought into the scrapped area, and the reader sends the information to the back-end center To record and process, that is, treat the asset as scrap.
3.4.7. Asset inventory operation
The operator can take the handheld device to read the asset data and upload it to the background server to start the inventory program.

Figure 6: Asset inventory
3.4.8. Asset flow control
Install a reader at each entrance and exit, and the system can determine the flow of assets based on the information status of the reader’s identification tag; at the same time, some fixed assets may need to restrict the flow, by installing RFID readers at the door of the office that needs to be controlled. To control the flow of assets, unauthorized asset flow behavior will trigger an alarm.
3.4.9. Control of confidential materials
Certain confidential materials, such as notebooks, precision instruments, files, USB flash drives, etc., cannot leave the office without permission. We can set up operators for these materials and issue operation cards to the operators. Unauthorized operators and unauthorized entry and exit of classified assets will trigger an alarm. The legal entry and exit behavior will be automatically recorded and entered into the system for future reference.
3.4.10. Asset operation status control
Install sensors on the assets that need to be monitored. The sensors will send the collected information to the RFID tag or terminal collection node and then send it to the back-end center. The back-end center judges whether the asset is in good condition based on the collected information, etc., and prompts or Alarm, management personnel will deal with it as soon as possible. For example, in the building, every fire hydrant and gas valve needs to be managed. Sensors can be installed on the fire hydrant and gas valve. When the fire hydrant is opened abnormally or the gas valve leaks, the background will be processed according to the data sent by the wireless sensor network. Judgment and analysis can be processed immediately.
3.4.11. Assets operating environment monitoring
Install relevant terminal collection nodes with environmental monitoring sensors in the environment where the assets are running. The background can judge and analyze the current environment status based on the information sent by the wireless sensor network. If the environment affects the assets, it will be processed immediately.For example, museum assets have strict requirements on temperature, humidity, and air pollutants, and collection nodes with corresponding sensors can be installed on the museum assets and in every corner to facilitate the implementation.
Collect environmental conditions from time to time, avoid unnecessary losses, and ensure that the exhibits are damaged due to environmental influences.

Figure 7: Assets and asset environmental monitoring
3.4.12. Asset positioning
The system can use the relay transmission node and the reader in the channel management as the positioning beacon, and combine the RFID and the RSSI function of the terminal collection node to realize the regional positioning function of the asset.
There are two ways to locate an asset: 1) Write its location information in the asset tag, and you can know the specific location of the asset by reading the asset tag information; 2) WSN itself forms a wireless network, and the network can relay and transmit nodes , The reader is used as a positioning beacon in the terminal collection node and channel management, and the RSSI function of the RFID and terminal collection node is combined to realize the regional positioning function of the asset.

Figure 8: Schematic diagram of asset positioning
3.4.13. System integration with other subsystems
In the asset management system, there are other subsystem modules: such as video surveillance system, relevant personnel authority system and so on. Data connection and matching can be carried out between various systems through a back-end database, etc., so as to form a complete system.
3.5. System Features
Compared with traditional asset management systems, asset management systems based on WSN and RFID have the following unique advantages:
Asset life cycle management
Realize the intelligent dynamic real-time tracking and centralized monitoring and management of the asset life cycle (new addition, allocation, idle, scrap, maintenance, etc.) process. The entire management process is highly intelligent and requires less manual intervention.
Synchronous management of people, place, time and things in asset management
Realize the recording of tasks, locations, objects, time and other information involved in the daily operation process of assets, and introduce the SMS reminder and alarm function. The system realizes effective supervision of daily work, reduces the pressure of daily asset management, and saves every year The cost of investing a lot of manpower and material resources for asset inventory and allocation has avoided the loss of assets due to various factors and improved the efficiency of enterprise management.
Paperless asset management
The system can use the public network IP access address, and users can access the system through IE browser anytime and anywhere.
Put an end to the loss of assets
Prevent unauthorized asset flow and realize asset preservation and appreciation.
Automatic monitoring of asset operation status
Real-time monitoring of the operating status of assets to ensure the effective work of assets and avoid losses caused by assets not working.
Automatic monitoring of asset operating environment
Real-time monitoring of the asset’s current environment to avoid the loss of assets caused by environmental abnormalities and environmental changes.
4. Technical realization route
4.1. RFID technology implementation route
When assets are placed in scattered locations, require long distances, and are not very cost-sensitive, 433MHz and 2.45GHz RFID can be used, which have the following advantages:
Long recognition distance, under normal temperature and open environment, 2.45GHz can reach more than 200m, 433MHz can reach 1000m;
Strong anti-collision capability, 2.45GHz and 433MHz readers can recognize more than 500 tags at the same time;
Penetration ability: Compared with 2.45GHz, 433MHz has stronger penetration ability, which is suitable for dense buildings or asset management between floors.
4.2. WSN technology implementation route
Our 433MHz and 2.45GHz RFID products can also form a WSN wireless sensor network. Our WSN wireless sensor network has the following characteristics:
1) Self-developed protocol, with strong scalability, can be targeted for different users and different applications;
2) Lower cost: Compared with Zigbee, which is commonly used in the industry, its overall cost is lower;
3) Low power consumption: Both terminal acquisition nodes and relay transmission nodes can be powered by batteries, with a standby current of 0.8uA and a working current of 35mA. If calculated by sending data once per minute, a 1100mAh button battery can be used for 5 years;
4) Intelligent network management: All devices have self-organizing network function, can automatically select the optimal network path, have network self-recovery function, and the network establishment time is short (the time can be set by the user).
5) Compatible with RFID equipment: When the RFID reader adopts 433MHz or 2.45GHz, the reader and tag used can be used as WSN data center, terminal collection node and relay transmission node.
5. Other application areas
Intelligent street lamp management;
Intelligent monitoring of library environment and library asset management
Mine environment monitoring, mine assets and miner positioning management
Intelligent management of smart streets
Intelligent gas pipeline management system
Intelligent collection of information from granaries, base stations, etc.
Building automation, security, wireless monitoring of equipment room equipment, etc.;
Intelligent management of mobile devices;
Oil well and water regime forecasting, biological signal acquisition, hydrometeorological monitoring, etc.
Agricultural greenhouse management and environmental monitoring in the greenhouse, etc.
6. Hardware equipment selection


[ad_2]



