Linsen Tiancheng RFID Data Center Asset Management System
[ad_1]
1. Introduction to the system
The assets of the data center are not the same as ordinary IT assets, and the data involved is very sensitive. Even a small error may lead to serious consequences. With the development of the economy, the IT equipment in the data center of the banking and telecommunications industry has also doubled, but the equipment management of the data center still adopts the method of regular inspection on paper documents. The labor intensity of the management personnel has increased significantly, but the real-time is still not possible. Surveillance can only wait for problems to “fight the fire” everywhere. In recent years, data center managers have also tried to use barcode management systems, but due to the limitations of the barcode itself (easy to be defaced, can be copied, precise alignment, etc.), a lot of manual operations are still required to complete the management of the equipment , Did not realize real-time monitoring in the true sense, and did not liberate the managers fundamentally.
In response to the above problems, Shenzhen Linsen Tiancheng Technology Co., Ltd., with its advanced technology and rich implementation experience, has developed an asset monitoring system that meets the characteristics of the data center. Using RFID automatic identification technology and network and software platforms, it provides faster, more careful and more accurate daily management for the monitoring of important business assets such as cabinets, and realizes the functions of real-time monitoring, automatic recording and asset inventory, which further reduces the occurrence of security risks Possible.
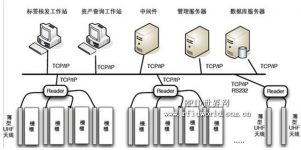
2. System composition

(1) Reader and antenna: RFID reader (reader) wirelessly communicates with RFID electronic tag through antenna, which can read or write tag identification code and memory data.
(2) Electronic tags: The communication industry assets have a wide variety of different specifications, and most of them are metal surfaces. Metal interference has always been a difficulty in the application of RFID technology. In order to solve the problems of metal interference and easy attachment to assets of various specifications, special Developed attached tags and tag tags suitable for assets of different sizes and specifications. Through the special design and packaging of the tag’s built-in antenna, the tag has good anti-metal interference performance.
(3) Card issuer: write data for the electronic tag, such as asset name, model, barcode number, etc., and can set a password, lock the data area, and prevent the data in the electronic tag from being rewritten.
(4) Handheld: Used for asset inventory, it can quickly read the electronic tag information on the device, and send the read tag information to the background server for processing through the built-in GPRS wireless communication module.
(5) Asset management system
Three, work flow
Asset management includes operations such as the addition, allocation, idleness, scrapping, maintenance, and inventory of assets. It includes the entire process of equipment from leaving the factory, putting into use, and scrapping. The equipment is equipped with electronic tags when leaving the factory, and the asset information is written in the tags. Every time an asset management operation is performed, the reader will read the electronic tags on the assets and send the information to the server for processing, thereby realizing asset tracking management .
(1) Asset addition operation: fill in the relevant information (site name, asset barcode, model, name) of the equipment to be managed in the card issuance program, and save the record in the database. Attach electronic tags with asset information (or hang on assets) as required.
(2) Asset transfer operation: prepare the assets to be transferred, open the door that controls the travel switch, and the reader is in the state of reading tags at this time. Take out the asset with the electronic label, walk out from the door, observe the sound and light prompt on the reader and the LED display to show the number of assets, and confirm that the electronic label on the device is read. After closing the door, the assets have been transferred from the computer room at this time. Bring the asset to the destination that needs to be allocated, open the door, bring the asset into the computer room, and confirm that the electronic tag on the asset is correctly read. Close the door and complete the asset allocation operation.
(3) Asset maintenance operation: prepare the equipment that has failed, and open the door that controls the travel switch, so that the reader is in the state of reading tags. Take out the faulty device, observe the digital tube display on the reader, and confirm that the label is read correctly. Close the door of the machine room, and the faulty equipment will be removed from the machine room. Take the equipment to the warehouse maintenance area, press the reader control button (the indicator light on the button is on), confirm that the label information on all devices is correctly read, press the reader control button again (the indicator light on the button) Off), the device is now under maintenance.
(4) Asset scrapping operation: prepare the scrapped equipment, open the door that controls the travel switch, so that the reader is in the state of reading tags. Take out the end-of-life equipment and confirm that the label is read correctly. Close the door of the computer room, and the scrapped equipment will be removed from the computer room. Take the equipment to the scrap area of the warehouse, press the control button of the reader in the scrap area, and confirm that the label information on the equipment has been read correctly. Press the reader control button again to complete the equipment scrapping operation.
(5) Asset inventory operation: press the “I/O” switch of the handheld to turn on. At the top of the interface, click to open the connectivity window, and click to connect to GPRS. Start the inventory process.
Four, system advantages
The data center management solution uses RFID electronic tags, wireless radio frequency networks, handheld readers, environmental monitoring software, automatic alarm systems, and access control systems to perform real-time and real-time monitoring of the location, movement, and real-time status of equipment in the data center. Regular monitoring and statistical analysis, and triggering follow-up actions based on the relevant status of the equipment, greatly facilitate the data center managers to understand the location status and working status of the concerned equipment anytime and anywhere, and can find problems early and eliminate hidden accidents. The RFID data center management solution also satisfies the all-round monitoring and supervision of important equipment in the data center, significantly improving the efficiency and accuracy of management, and greatly reducing the labor intensity of managers.
This solution is suitable for companies or institutions with centralized data, high sensitivity, and strong security such as banks, securities companies, and insurance industries.
[ad_2]